Presence Service: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Overview = |
= Overview = |
||
The Presence Service is a background process on the XO that coordinates activity sharing. It uses [[Telepathy]] to find other XOs on the network, and provide information about their owners and the activities that they are participating in. It provides a D-Bus API for activities. Sugar provides a wrapper interface to the D-Bus API. |
The '''Presence Service''' is a background process on the XO that coordinates activity sharing. It uses [[Telepathy]] to find other XOs on the network, and provide information about their owners and the activities that they are participating in. It provides a D-Bus API for activities. Sugar provides a wrapper interface to the D-Bus API. |
||
Sugar's Neighborhood view (or mesh view) acts as the equivalent of an instant messaging (IM) '''buddy list'''. It shows who is on line. We refer to this as '''" |
Sugar's Neighborhood view (or mesh view) acts as the equivalent of an instant messaging (IM) '''buddy list'''. It shows who is on line. We refer to this as '''"presence"'''. Behind the scenes are several layers that provide this information to the mesh view. |
||
'''Presence Service''' is the Sugar component that tracks the presence of these buddies and activities, using [[Telepathy]], a real-time communications framework that can handle multiple protocols. We are using XMPP via a Jabber server, as well as link local XMPP, for presence and collaboration. |
'''Presence Service''' is the Sugar component that tracks the presence of these buddies and activities, using [[Telepathy]], a real-time communications framework that can handle multiple protocols. We are using XMPP via a Jabber server, as well as link local XMPP, for presence and collaboration. |
||
Revision as of 16:46, 27 March 2008
Overview
The Presence Service is a background process on the XO that coordinates activity sharing. It uses Telepathy to find other XOs on the network, and provide information about their owners and the activities that they are participating in. It provides a D-Bus API for activities. Sugar provides a wrapper interface to the D-Bus API.
Sugar's Neighborhood view (or mesh view) acts as the equivalent of an instant messaging (IM) buddy list. It shows who is on line. We refer to this as "presence". Behind the scenes are several layers that provide this information to the mesh view.
Presence Service is the Sugar component that tracks the presence of these buddies and activities, using Telepathy, a real-time communications framework that can handle multiple protocols. We are using XMPP via a Jabber server, as well as link local XMPP, for presence and collaboration.
See Shared Sugar Activities for an overview of collaboration, or Tubes Tutorial for how to add collaboration to an activity.
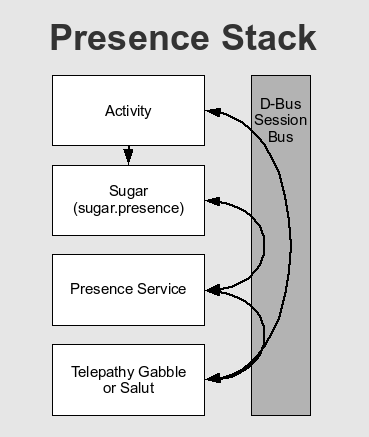
Presence Stack
Python activities (and Sugar) make use of sugar.presence to interact with Presence Service. sugar.presence provides an API for accessing Presence Service over the D-Bus session bus.
Presence Service in turn interacts with telepathy-gabble and telepathy-salut over the session bus, and once everything is set up (or in the case of non-Python activities) the activity can use Telepathy directly (for example, to use Tubes).
Connection Types
Presence Service supports two Telepathy backends (connection managers):
- telepathy-gabble, that provides server-based Jabber/XMPP functionality. It talks to a Jabber server (e.g. olpc.collabora.co.uk) and sets up different chat rooms through which activities talk to each other.
- telepathy-salut, a link-local Connection Manager using reliable multicast over the local network
Plugins
In Presence Service, plugins provide the interface to the telepathy connection managers. server_plugin.py talks to telepathy-gabble, and linklocal_plugin.py talks to telepathy-salut.
Active Connection
Though Presence Service is designed to run both connection managers simultaneously, at this stage only one is in effect at a time, since there is no UI support for showing which activities are shared on which connection.
Presence Service will use Gabble when it has Internet access (a valid IPv4 address) and has connected to a Jabber server, otherwise Salut (but not both at the same time). Here is the sequence of events:
- Both plugins are started when Presence Service starts, unless PRESENCE_SERVICE_DEBUG=disable-gabble or disable-salut are set.
- Salut succeeds faster than Gabble, so link local buddies are shown first.
- PS's server plugin watches Network Manager signals on the D-Bus system bus.
- When NM indicates that we have a valid IPv4 address, we run the _init_connection method of the ServerPlugin instance.
- Gabble is automatically run by the session bus (dbus-daemon) via service activation, the first time the Presence Service uses it, if it isn't already running.
- If the Gabble connection fails, we schedule a timer (starting at 5 seconds with exponential backoff to a maximum of 5 minutes) and retry running _init_connection when the timer runs out.
- (classes TelepathyPlugin and ServerPlugin, methods _init_connection, _reconnect_cb, _could_connect, _handle_connection_status_change.)
- If the server plugin has connected to a jabber server, PS stops the link local plugin (salut). Link local buddies disappear.
- If NM loses the IP address, the server plugin stops itself.
- When the server plugin stops, PS starts the link local plugin.
API
Python code can use the sugar.presence library to talk to Presence Service. Non-python code can use the API that Presence Service provides over the D-Bus session bus.
See Low-level Activity API#Presence for the basic operations, and Presence Service DBus API for a more comprehensive, but out of date, API listing.
Source
git clone git://dev.laptop.org/projects/presence-service