DCON: Difference between revisions
(shubert diaz puto) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
== Additional Information == |
|||
shubert diaz puto |
|||
* The [[Media:DCON_Specification%2C_V0.8.odt|DCON Specification]]. |
|||
* [[Media:DCON_datasheet_HX8837-A.pdf|DCON Data Sheet]] |
|||
* [[DCON Linux Driver]] |
|||
* XO-1.75 B1 prototype SKU198 does not have DCON RAM, but does have a DCON. |
|||
[[Category:Display]] |
|||
[[Category:Developers]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 22:42, 18 April 2013
Overview
In order to support very low power operation, the XO laptop uses a secondary Display CONtroller, or DCON. This secondary controller is present in the video pipeline between the primary display controller (integrated into the processor or chipset) and the LCD panel. It allows the main processor/display controller to be completely powered off while still retaining an image on the display.
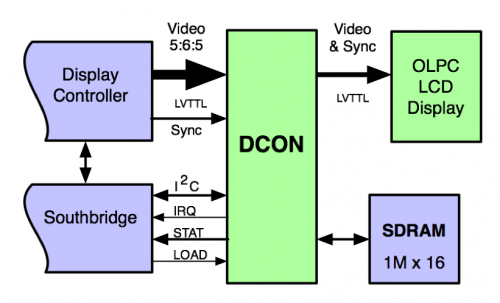
The following is a simple diagram detailing the various connections between the CPU and the DCON:
The processor initializes the DCON using the I2C interface. Typically, the DCON is in pass-through mode, where all video data is simply post-processed as needed for the LCD display and passed to the display. When the processor is about to enter suspend, it asserts the LOAD signal, and the DCON loads the post-processed image into its separate frame buffer and begins outputting that image instead of the video received from the primary frame buffer. Upon resume, the DCON is once again placed in pass-through mode.
The DCON ASIC provides several functions in addition to the secondary display controller functionality. These functions include anti-aliasing of the video and deswizzling in color mode, and luminance calculations in monochrome mode.
Additional Information
- The DCON Specification.
- DCON Data Sheet
- DCON Linux Driver
- XO-1.75 B1 prototype SKU198 does not have DCON RAM, but does have a DCON.