Creating a collection: Difference between revisions
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
===File Formatting=== |
===File Formatting=== |
||
The first step of this process is to make sure that your collection is |
The first step of this process is to make sure that your collection is saved in a file format that is supported by the library. (Other file formats may be supported on the XO, but not within the library). The following is a list of file formats supported by the library: |
||
; Text : <tt>.txt</tt>, <tt>.doc</tt>, <tt>.abw</tt> - These formats can be read by AbiWord and will launch it from the browser. AbiWord will write <tt>.abw</tt> files. |
; Text : <tt>.txt</tt>, <tt>.doc</tt>, <tt>.abw</tt> - These formats can be read by AbiWord and will launch it from the browser. AbiWord will write <tt>.abw</tt> files. |
||
Revision as of 16:42, 18 December 2007
see also: creating an activity and library grid
If you have been porting your own collections, books or other works to display neatly on the XO, please follow the directions below and list them in the library. To suggest a collection for the core library, nominate it at featured bundles. Some suggested collections, specifically those in languages other than the current targets of English, Spanish, Portuguese, Arabic, French, Thai, and Urdu, are linked on this site but have not yet been incorporated beyond the wiki.
See also Zdenek'snew bundle ideas.
Overview
The OLPC Library is the set of content and materials (outside of the core OS and Activities) that ships with the XO laptops and school servers. In order to add your content to this repository, you must create a self-contained bundle for your content. This page is a proposed spec for such a bundle, providing the information you need to select, format, and package a content bundle.
Note: These instructions explain how to package browsable content for the OLPC library. Materials in a content bundle that need to be run by an Activity other than Browse will have to have a mime-type registered with the Browse activity so they can launch from there. Activities may be part of content packages for the library as well, for instance as sample code to be read. For more information, skip down to the FAQ.
Content bundles unpack into a directory under /home/olpc/Library.
Feedback
As you create your bundle, please note any puzzles or problems you encounter, as well as any thoughts for improvement that you might have.
The process and format is a new one, and feedback helps improve it. One place to do that is on the Talk:Creating a content bundle page.
Selecting Content
The first step to creating your content bundle is to determine what content should be included. In some cases, this is easy: everything! In other cases, there are additional considerations:
- Size
- How big is your collection? If the size of your entire collection is between 5-20MB, you're all set. Otherwise, you'll need to make two bundles-- one bundle of 5-20MB for use on individual laptops, and a second bundle of unlimited (but reasonable) size for inclusion on each school's library server.
- Quality
- Does your collection have a rating system in place? If so, consider including only top-rated material in your content bundle. Otherwise, think about "curating" a selection of high quality material to be included in your bundle (or bundles).
- Relevance
- Is your entire collection relevant to children? If so, terrific! If not, consider including only material that will help children learn, explore, and expand their worlds.
- Language issues
- Does your collection contain material in multiple languages? We hope it does! To the greatest extent possible, please give preference to materials that exist in multiple languages, or that can be easily translated by our localization team.
- Licensing issues
- What kind of copyright exists on the material in your collection? Do you have legal permission to archive and distribute it? Please be sure to review the licensing terms of your collection. For guidance on licensing, see licenses.
Formatting Content
Once you've determined the material you'd like to include in your content bundle (or, again, bundles-- since in many cases, you'll have to make two), you'll need to format it for use on the XO.
- Need to add explanatory info about the browser and how content is viewed on the XO...
File Formatting
The first step of this process is to make sure that your collection is saved in a file format that is supported by the library. (Other file formats may be supported on the XO, but not within the library). The following is a list of file formats supported by the library:
- Text
- .txt, .doc, .abw - These formats can be read by AbiWord and will launch it from the browser. AbiWord will write .abw files.
- .pdf - This can be ready by xbook, which launches automatically from the browser when following a link to a pdf.
- Multimedia document with layout
- .html - Parsed by the browser. Source will soon be viewable.
- .pdf - Read by xbook.
- Formatted text
- .xml, .rss - Read by the browser and by penguinTV (as feeds).
- Images
- .jpeg, .gif, .png - These can be viewed by many applications, including the browser.
- .svg - 99% supported.
- Music
- .csound - This will be playable by TamTam... currently its XO build doesn't provide a way to save or load sound files, however.
- .ogg - See other common audio formats below; can be played by Helix or Gstreamer, not part of the current build.
- .mp3, .wav - These can be played by Helix or Gstreamer, standalone or as a browser plugin, when they are installed.
- .rm, .ra - This can be played by the Helix plugin when installed with a RealAudio codec.
- Currently, audio files selected in the browser will launch a player if it is present.
- Video
- .ogg - Can be played by Helix or Gstreamer, standalone or as a plugin. A Helix activity is now in the build. can now be downloaded in a few steps. To play video, please download this activity along with some videos (see for instance this video).
- .mpeg, .mov, .wmv, .rm - See above.
- Helix
- The Helix Media Activity has more information about media activity
- Python
- The Develop activity will provide one way to view python files; the 'view source key' another.
- Javascript
- This will viewable the same way page source can be viewed through the browser.
- Etoys projects
- .pr files automatically launch etoys from the browser.
If you have a question about a file format that is not listed above, ask it on the talk page.
Visual Formatting
The second step of the formatting process is to make sure that your collection displays correctly on the XO. (The small screen can sometimes lead to unexpected formatting and display issues).
The easiest way to test the visual display of your material is to view it on an XO. If you don't have access to an XO-- or to another person who has one-- you can install and run the Sugar emulator on your computer. Emulating the XO has installation instructions.
Disk usage
The XO's filesystem invisibly compresses files (poorly) to save space. So you may be using less disk space than you think. Text files are compressed about 50%. Other media are basically unchanged. If you are curious, there are somewhat difficult to apply instructions in JFFS2 to measure likely disk usage.
Packaging Content
Once you've selected and formatted your content, the last thing to do is to package it as a bundle.
Bundle Structure
A content bundle is a directory compressed as a .zip file, renamed to end in .xol. Each content bundle must contain a single top-level directory which has the same name as the bundle, minus the extension. All of the other files in the bundle must be within this directory. The top-level directory must also contain a subdirectory called library that contains certain configuration files.
Here is an example of a content bundle for a collection called "dictionary.xol":
dictionary/
A/
aardvark.html
abacus.html
acacia.html
...
B/
balloon.html
...
C/
...
library/
library.info
library-dictionary.jpg
contents
contents.sig
index.html
- dictionary/
- The top-level directory, which has the same name as the bundle itself.
- library/ (required)
- This directory contains all the metadata associated with the collection. It includes several configuration files which are discussed below in configuration files.
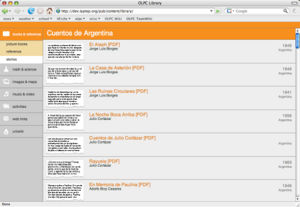
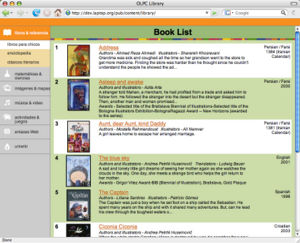
- index.html (required)
- This is the top-level navigation page for the collection. The index.html page is the page that is displayed in the main frame of the reader when a child selects the collection from the library sidebar. If library.xml is present, the index page is automatically generated from that file. Otherwise, a static index.html page must be provided.
- Need to update with info about templates...
- At right are two examples of index.html pages. The first is a standard index page that uses the default library template. The second is an index page adapted from a pre-existing digital collection that uses its own organization scheme and style sheets. For additional examples of index pages, visit the online version of the OLPC Library.
Configuration Files
The "library" directory contains all the metadata associated with the collection. It includes the following files:
- library.info
- The library.info file is a text file that follows a key/value pair format. It contains information about the source, version, language, and subject of the collection (among other things). Sample library.info file is an example. Library.info is the generic version, with information about required and optional entries.
- library-dictionary.jpg (optional)
- This is the icon that represents the collection in the library navigation sidebar. The icon should have the same name as the collection's .xol file, except with library- at the front. The icon can be in any number of supported file formats, including SVG, JPEG, PNG, and GIF. See Choosing image formats for more information.
- Note: This may not need to exist, since icons appear at the category level, not the level of individual collections.
- contents
- contents.sig
The contents and contents.sig are manifest and credential files for the entire bundle contents (excepting the contents and contents.sig files themselves), as described by the Manifest Specification.
Language and Localization
Library localization is still in development. At this point, just indicate the language(s) of your collection in the locale field of the library.info file.
Packaging Instructions
Step by step
- Look at your content, and make sure that no top-level directories are named library/.
- Make a directory for your content, with the name you want to give your bundle. (Let's call it dictionary/ for the sake of example.)
- Copy your content files (with any folder structure you like) into dictionary/.
- Within dictionary/, make a second directory called library/.
- Within library/, create a text file called library.info and give it content as in the sample library.info file.
- If you would like to supply an icon for your content bundle (see configuration files above), copy this icon (.svg, .jpg, .gif, or .png) into the library/ directory and rename it library-dictionary (with the appropriate format suffix).
- Decide whether:
- You want to use standard OLPC formatting (possibly with minor changes to colors and styles) in displaying your content on the XO.
- You want to customize the display children see when using the XO to view your content.
- Based on the above decision:
- If you want to use standard OLPC formatting:
- Create a text file library.xml within library/.
- For every item in your content bundle that you want displayed to students, include items in your library.xml file that mirror those in the example Library.xml file.
- If you want to change the colors and styles of the OLPC formatting, create a text file library.css within library/that gives your preferred css.
- If you want to use your own customized formatting:
- Create a text file index.html in dictionary/.
- In index.html, write html code providing links to all your content items.
- If you want to use standard OLPC formatting:
- Then zip dictionary/, with all its subdirectories into a .zip file with the same name as your bundle (eg dictionary.zip).
- Rename the zip file as a .xol file (e.g. dictionary.xol).
Voila! The .xol file is your content bundle.
Using a setup.py script
needs testing
Make sure all of your files are listed in the bundle manifest (explained in Sugar Activity Tutorial), and create a setup.py file with the following code:
#!/usr/bin/env python
try:
from sugar.activity import contentbundlebuilder
contentbundlebuilder.start("YourBundleName")
except ImportError:
import os
os.chdir('..')
os.system('cat YourBundleName/contents | zip YourBundleName.xol -@')
os.system('mv YourBundleName.xol ./YourBundleName')
os.chdir('YourBundleName')
This way you can run
./setup.py
without sugar installed, and at the end find a zipped up .xol file ready for you to install on an XO or emulator.
FAQ
Can I package an activity as a content bundle?
Yes! Content bundles are designed to coexist with activity bundles. To package your activity as a content bundle, you just need to add the index.html page and the library directory (including relevant configuration files) to your existing activity bundle. Then, rename it as a .xol file and you should be all set.