User:Ndoiron/Amazon-Map: Difference between revisions
(Created page with '==1. Maps== Computerized maps improve geography skills, help explain environmental issues, and prepare students for work in the many industries which use maps for planning. I h…') |
No edit summary |
||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Pilot technology program for community mapping and environmental education. |
|||
==1. Maps== |
|||
==Computer Education== |
|||
| ⚫ | Computerized maps improve geography skills, help explain environmental issues, and prepare students for work in the many industries which use maps for planning. |
||
===The OLPC XO-1 Laptop=== |
|||
<table><tr><td> |
|||
One Laptop per Child developed the XO-1 laptop as a step towards universal computer literacy. Nearly 2 million laptops are in use around the world. Each primary school student in Uruguay and Birmingham, Alabama has one of these computers. Peru and the state of La Rioja, Argentina are also approaching a true one laptop per child ratio. |
|||
These laptops are low-power and durable machines, with screens which can be read in direct sunlight, 3 USB ports, and connectors for microphones, headphones, and sensors. The laptops can form a mesh network in the absence of a WiFi access point, allowing students to collaborate on documents and maps (co-editing is similar to Google Docs). |
|||
Science classes could use a mapping activity and the internet to take part in a [[CitizenScience|Citizen Science]] project - real science which uses volunteers' notes for data. |
|||
We can obtain around 10 free laptops through the Contributors Program, in return for contributing technical and educational resources back to the OLPC community. |
|||
I have experience developing online mapping websites which work with Google Maps, Microsoft's Bing Maps and ESRI's ArcGIS. |
|||
</td><td> |
|||
<gallery widths="130px" heights="100px" perrow="2"> |
|||
Image:Green_and_white_machine.jpg |
|||
Image:Hiking01.jpg |
|||
Image:Green-and-white-e-book.jpg |
|||
Image:P1020096-1.JPG |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
</td></tr></table> |
|||
===Content for this project will be compatible with other computers=== |
|||
==2. Websites== |
|||
Several governments in South America are considering a competing Intel Classmate computer for their schools, and schools might already have technology programs. Every component of this project will be open-source and compatible with other computers. |
|||
I can develop websites allowing students and teachers from around Mongolia to go online for new information, story-writing contests, or lesson ideas. I have experience building several websites, including a wiki, a social network, environmental maps, a Facebook app, and a text-messaging service. |
|||
Any written content will be published in HTML / CSS / JavaScript so that they can be loaded onto any computer. I will use HTML5 local storage so that the tools in the [[User:Ndoiron/OfflineMap|Offline Map]] activity can be run in most web browsers. OLPC's interactive and applications (such as the sensor program [[Measure/Kasiisi|Measure]] and music program [[TamTam]]) can be used on all computers, including older donated and recycled machines, using [[Sugar on a Stick]]. |
|||
Ushahidi or CrowdMap platforms |
|||
===Digital mapping=== |
|||
I can also help tell the world about OLPC Mongolia with an English-language blog and participation on wiki.laptop.org ( this wiki website ) |
|||
I developed and maintain the [http://wiki.sugarlabs.org/go/Activities/Map Map activity] and [[User:Ndoiron/OfflineMap|Offline Map activity]] for the XO laptop. The offline maps were a huge success in [[User:Ndoiron/Uganda-Experience|my Uganda project]] and are [http://twitter.com/olpcMAP/status/29638808644 used in Haiti]. The online maps are popular at OLPC's major programs in South America because they use the lower-bandwidth Google Static Maps API. The newest version of this activity connects to online services to add photos, Wikipedia articles, other mapping schools, and points of interest to the map. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==3. Literacy== |
|||
Teaching English is about reading, writing, and storytelling. |
|||
<gallery widths="250px" heights="140px" perrow="3"> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
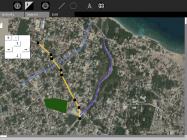
Image:OfflineMapPolyline.png|<center>Drawing a roadmap</center> |
|||
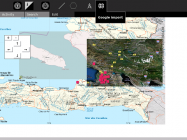
Image:UshahidiMap.png|<center>Import Google Earth KML, GeoRSS, OSM files</center> |
|||
Image:Map-EmbedWiki.jpg|<center>Embed Panoramio photos, Wikipedia articles</center> |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
===Literacy and Storytelling=== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | * Programs such as [http://librivox.org LibiVox] audiobooks, [http://en.childrenslibrary.org/ International Digital Children's Library], the [http://schoollibrary.com/OLPC_Collection.htm School Library], and [http://portal.unesco.org/education/admin/ev.php?URL_ID=46812&URL_DO=DO_TOPIC&URL_SECTION=201 UNESCO] can improve students' reading skills in English or another language. |
||
Also, I would continue work on XO BookReport - a project with members from the US, Sudan, and Uganda - to connect the XO laptops to libraries and students' reading history. We should help students keep track of their reading, collect their book reports, and recommend new information to them. They should win game points when they read a difficult book or recommend a book to a friend. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* A [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eiW59UUivc0 New York Times video] shows a family continuing their language and traditions despite immersion in another culture. Raises questions about how to preserve cultural knowledge and language. Recording technology helps linguists capture the grammar and structure, but doesn't fully preserve the stories, traditions, and music of a language and its speakers. |
|||
When I visited Uganda, I had new ideas about how to help. Sometimes I would fall asleep thinking, and wake up in the morning with a new project to work on. When I worked together with teachers, I learned from their questions and their own ideas. |
|||
* Students in Uruguay and Paraguay are frequently using such websites and could connect with classes in these programs in English or Spanish. There are also several students at a school in the Portuguese-speaking island nation of Sao Tome e Principe. |
|||
I hope the same experience is possible in Mongolia. Already, I hear that we should work on an [http://xodock.com/c/blog/ XO Dock] so laptops can be plugged in during class. |
|||
==Ushahidi Map for Activism and Data-Sharing== |
|||
<table><tr><td> |
|||
[http://blog.ushahidi.com/index.php/2011/01/05/ushahidi-video-creating-a-new-narrative/ Ushahidi] is a mapping platform originally invented in Kenya. Reports from many web, e-mail, and text messaging sources can be combined on an online map and used to report on a crisis and community efforts. Official reporters post directly to the map, and administrators can moderate and find reliable sources for information. The Ushahidi system has been part of official responses and reporting efforts by the State Department in Haiti, Al-Jazeera in Gaza, and the Washington Post during DC-area snowstorms. |
|||
[http://crowdmap.com CrowdMap] is a website which hosts Ushahidi maps, so the end-user does not need to run their own server. If you have internet access, this a quick and easy way to start mapping. |
|||
I made several plugins to add realtime environmental sensors and ESRI's advanced mapping services to these mapping platforms. See several example screenshots in [http://blog.ushahidi.com/index.php/2010/11/16/bookmarklets-for-ushahidi-and-crowdmap/ my post on the Ushahidi Blog]. |
|||
</td><td> |
|||
<gallery widths="250px" heights="140px" perrow="2"> |
|||
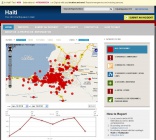
Image:Haiti_Ushahidi.jpg|<center>Haiti.Ushahidi.com</center> |
|||
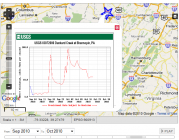
Image:MapWithSensor.png|<center>Mapping USGS Sensors</center> |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
</td></tr></table> |
|||
===Other Web Development=== |
|||
I have experience building different web applications, including social media and text-messaging apps. I have worked on projects with Google Maps, Microsoft's Bing Maps, OpenStreetMap, and ESRI's ArcGIS Server and JavaScript APIs. |
|||
I would use a blog, participate in the education technology community (such as OLPC meetings, this website, and OLPC News), and post for the Ushahidi and Grassroots-Mapping blogs. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
During my visit to Uganda, I would get new ideas about how to help. When I worked with teachers, I learned from their questions and their own ideas. The [[WikiPack]] was based on our discussions: articles connected to books in the reading program, answers to teachers' questions about computers and GPS, and short biographies of Nelson Mandela and William Kamkwamba. |
|||
What are teachers and coordinators' goals for technology and technical skills? How does the project want to share its cultural knowledge and geodata? |
|||
Latest revision as of 04:52, 17 January 2011
Pilot technology program for community mapping and environmental education.
Computer Education
The OLPC XO-1 Laptop
|
One Laptop per Child developed the XO-1 laptop as a step towards universal computer literacy. Nearly 2 million laptops are in use around the world. Each primary school student in Uruguay and Birmingham, Alabama has one of these computers. Peru and the state of La Rioja, Argentina are also approaching a true one laptop per child ratio. These laptops are low-power and durable machines, with screens which can be read in direct sunlight, 3 USB ports, and connectors for microphones, headphones, and sensors. The laptops can form a mesh network in the absence of a WiFi access point, allowing students to collaborate on documents and maps (co-editing is similar to Google Docs). We can obtain around 10 free laptops through the Contributors Program, in return for contributing technical and educational resources back to the OLPC community. |
|
Content for this project will be compatible with other computers
Several governments in South America are considering a competing Intel Classmate computer for their schools, and schools might already have technology programs. Every component of this project will be open-source and compatible with other computers.
Any written content will be published in HTML / CSS / JavaScript so that they can be loaded onto any computer. I will use HTML5 local storage so that the tools in the Offline Map activity can be run in most web browsers. OLPC's interactive and applications (such as the sensor program Measure and music program TamTam) can be used on all computers, including older donated and recycled machines, using Sugar on a Stick.
Digital mapping
I developed and maintain the Map activity and Offline Map activity for the XO laptop. The offline maps were a huge success in my Uganda project and are used in Haiti. The online maps are popular at OLPC's major programs in South America because they use the lower-bandwidth Google Static Maps API. The newest version of this activity connects to online services to add photos, Wikipedia articles, other mapping schools, and points of interest to the map.
Computerized maps improve geography skills, help explain environmental issues, and prepare students for work in the many industries which use maps for planning. Science classes could use a mapping activity and the internet to take part in a Citizen Science project.
Literacy and Storytelling
- Programs such as LibiVox audiobooks, International Digital Children's Library, the School Library, and UNESCO can improve students' reading skills in English or another language.
- It is one thing to write an essay, and another to tell a story. Notice how this video tells a story without words. What stories do students have, and how will they tell them?
- A New York Times video shows a family continuing their language and traditions despite immersion in another culture. Raises questions about how to preserve cultural knowledge and language. Recording technology helps linguists capture the grammar and structure, but doesn't fully preserve the stories, traditions, and music of a language and its speakers.
- Students in Uruguay and Paraguay are frequently using such websites and could connect with classes in these programs in English or Spanish. There are also several students at a school in the Portuguese-speaking island nation of Sao Tome e Principe.
Ushahidi Map for Activism and Data-Sharing
|
Ushahidi is a mapping platform originally invented in Kenya. Reports from many web, e-mail, and text messaging sources can be combined on an online map and used to report on a crisis and community efforts. Official reporters post directly to the map, and administrators can moderate and find reliable sources for information. The Ushahidi system has been part of official responses and reporting efforts by the State Department in Haiti, Al-Jazeera in Gaza, and the Washington Post during DC-area snowstorms. CrowdMap is a website which hosts Ushahidi maps, so the end-user does not need to run their own server. If you have internet access, this a quick and easy way to start mapping. I made several plugins to add realtime environmental sensors and ESRI's advanced mapping services to these mapping platforms. See several example screenshots in my post on the Ushahidi Blog. |
|
Other Web Development
I have experience building different web applications, including social media and text-messaging apps. I have worked on projects with Google Maps, Microsoft's Bing Maps, OpenStreetMap, and ESRI's ArcGIS Server and JavaScript APIs.
I would use a blog, participate in the education technology community (such as OLPC meetings, this website, and OLPC News), and post for the Ushahidi and Grassroots-Mapping blogs.
What do you need?
During my visit to Uganda, I would get new ideas about how to help. When I worked with teachers, I learned from their questions and their own ideas. The WikiPack was based on our discussions: articles connected to books in the reading program, answers to teachers' questions about computers and GPS, and short biographies of Nelson Mandela and William Kamkwamba.
What are teachers and coordinators' goals for technology and technical skills? How does the project want to share its cultural knowledge and geodata?