DCON: Difference between revisions
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
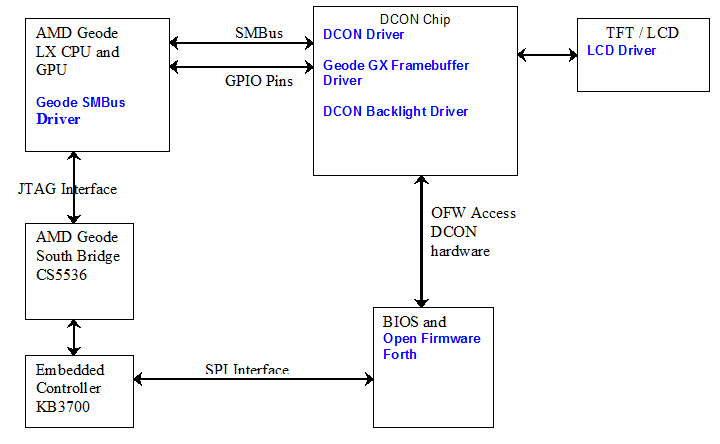
DCON stands for Display CONtroller. As it says on the [[Hardware Specification]] page: The special "DCON" chip, that enables deswizzling and anti-aliasing in color mode, while enabling the display to remain live with the processor suspended. Here is a [http://wiki.laptop.org/go/Image:DCON_Specification%2C_V0.8.odt DCON Specification]. The following is a simple diagram detailing the various connections between the CPU and the DCON: |
DCON stands for Display CONtroller. As it says on the [[Hardware Specification]] page: The special "DCON" chip, that enables deswizzling and anti-aliasing in color mode, while enabling the display to remain live with the processor suspended. Here is a [http://wiki.laptop.org/go/Image:DCON_Specification%2C_V0.8.odt DCON Specification]. The following is a simple diagram detailing the various connections between the CPU and the DCON: |
||
<center>[[Image: |
<center>[[Image:dcon_rev1.2.png]]</center> |
||
== DCON Linux Driver == |
== DCON Linux Driver == |
||
Revision as of 19:00, 29 October 2007
DCON overview
DCON stands for Display CONtroller. As it says on the Hardware Specification page: The special "DCON" chip, that enables deswizzling and anti-aliasing in color mode, while enabling the display to remain live with the processor suspended. Here is a DCON Specification. The following is a simple diagram detailing the various connections between the CPU and the DCON:
DCON Linux Driver
This section describes the Linux kernel drivers for the DCON and associated hardware.
Requirements
The latest and greatest DCON code is in the 'dcon' branch of the geode GIT tree: git://git.infradead.org/users/jcrouse/geode.git.
Make sure that you enable the following devices:
- The Geode GX frambuffer driver (CONFIG_FB_GEODE and CONFIG_FB_GEODE_GX). Make sure you build this into the kernel - its not useful as a module.
- The DCON driver (CONFIG_FB_GEODE_GX_DCON). You can either build this in to the kernel or use it as a module. Its much easier to debug as a module. This option automatically selects the I2C subsystem.
- The Geode ACB (smbus) driver (CONFIG_SCx200_ACB).
- The DCON backlight driver (CONFIG_BACKLIGHT_LCD_SUPPORT and CONFIG_BACKLIGHT_CLASS_DEVICE and CONFIG_BACKLIGHT_DCON). This module allows you to control the backlight through the existing kernel backlight mechanism.
Loading the DCON driver(s)
- Load the I2C driver (if you didn't build it in)
$ modprobe scx200_acb
- Load the DCON driver
$ modprobe gxfb_dcon
- Load the backlight driver
$ modprobe dcon_bl
The driver is now loaded. There should be two new platform drivers in /sys/devices/platform:
dcon i2c-0 power uevent dcon-bl pcspkr serial8250
Using the DCON driver (/sys interface)
The DCON driver functionality is accessable through the /sys interface. This may not always be the case, since it might be a bit of a security issue, but its good for debugging. Here is what the /sys/devices/platform/dcon directory looks like:
bus mode power source uevent modalias output sleep subsystem
/sys/devices/platform/dcon/mode
This is a read only file that shows the current hex value of the DCON mode register (0x01).
/sys/devices/platform/dcon/output
This file lets you change the output mode from color to mono. Write a number to the file to change the mode:
| Output | Value |
|---|---|
| Color | 0 |
| Mono | 1 |
Read the file to see what the current mode is.
/sys/devices/platform/dcon/source
This file lets you change the source of the display from the CPU to the DCON. Write a number to the file to change the source:
| Source | Value |
|---|---|
| DCON | 0 |
| CPU | 1 |
Read the file to see what the current source is.
/sys/devices/platform/dcon/sleep
Allows you to put the DCON into sleep mode. To turn the display off, echo "1" > /sys/devices/platform/dcon/sleep
Using the DCON driver (ioctl)
The DCON functionality can also be accessed with ioctl() calls through the /dev/fb0 device file. The following ioctls are defined:
#define DCONIOC_SOURCE _IOW('d', 0, int)
#define DCONIOC_OUTPUT _IOW('d', 1, int)
#define DCONIOC_SETREG _IOW('d', 2, int)
#define DCONIOC_DUMPREG _IOW('d', 3, int)
#define DCONIOC_GETREG _IOW('d', 4, int)
#define DCONIOC_SETBL _IOW('d', 5, int)
#define DCONIOC_GETBL _IOW('d', 6, int)
DCONIOC_SOURCE
Change the source of the DCON data. The argument should either be 0 (DCON) or 1 (CPU).
DCONIOC_OUTPUT
Change the output type of the display. The argument should either be 0 (color) or 1 (mono).
DCONIOC_SETREG
Sets a register on the DCON. Upper 16 bits of the argument is the register, and the lower 16 bits is the value.
DCONIOC_DUMPREG
Prompts the driver to prink() all of the registers in the DCON.
DCONIOC_GETREG
Get a DCON register value. The argument is the desired register and it will contain the value on return.
DCONIOC_GETBL
Get the current value of the backlight register. The argument will contain the backlight value on return.
DCONIOC_SETBL
Set the current value of the backlight register. The argument should have the new value. Any value from 0 (off) to 15 (full on) is acceptable
Using the backlight driver
/sys/class/backlight/dcon-bl looks like this:
actual_brightness max_brightness subsystem brightness power uevent
Change the brightness by writing a new number to the brightness file. The value can range from 0 (off) to 15 (full on).
This example changes the backlight to about 50%:
$ echo "7" > /sys/class/backlight/dcon-bl/brightness