Browse: Difference between revisions
(/* three problems with browse) |
|||
| Line 330: | Line 330: | ||
I've had three problems with Browse: |
I've had three problems with Browse: |
||
1. When I hit the back button, sometimes Browse spontaneously quits. This error does not happen every time I hit the back button, however. |
1. When I hit the back button, sometimes Browse spontaneously quits. This error does not happen every time I hit the back button, however. |
||
2. I have also had the browser quit when I tried to resize a page. |
2. I have also had the browser quit when I tried to resize a page. |
||
3. Sometimes Browse takes almost 5 minutes to start up (most of the time it is much faster). |
3. Sometimes Browse takes almost 5 minutes to start up (most of the time it is much faster). |
||
Revision as of 00:30, 31 January 2008
see more templates or propose new |
Description & Goals
Summary
Currently, the Web browser uses the same Gecko browser engine as Firefox. However, our browser is simpler than Firefox and is not directly compatible with Firefox add-ons. Applications can also use xulrunner which includes Javascript capability. An alternate, more complex browser for the OLPC is Opera.
Goals
- display web pages
- display images, like, for example, png files
- provide a place to share browsable information
Web Sessions
The laptops employ a new approach to Activities and Objects, as described in the Journal . This suggests that we rethink the basic browsing model and consider "browsing sessions" as the basic Object format. These sessions should work like the session restore features do in some modern browsers, e.g., Firefox, only each instance of the Browse activity will maintain its own session data within the Journal.
For instance, a child may create one stored session containing tabs for each page he visits daily, and another session containing tabs related to research on his science report. This alternative approach to sessions goes hand in hand with the collaborative aspects of the Browse activity. The child's daily reads session may remain private, while her research session can be shared with the classmates in her study group. Sessions provide a level of organization above what most browsers now provide, separating recreation and work, private and shared.
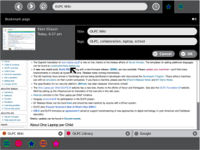
How do I bookmark a website and browse it later?
- Open the Browse activity and go to the website you'd like to bookmark.
- Click the star (☆) in the upper-right corner to bookmark the website.
- Close (Stop) the Browse activity.
- Open your Journal activity.
- Click on the Browse icon at the very top of the list entries; this is a record of the Browse activity in which you just made a bookmark. You will be taken to the detailed view of the entry.
- For later reference, rename the session by typing in the field just to the right of the Browse icon; it should say "Browse Activity", but you can rename it to refer to your bookmark.
- Click the "Resume" icon at the upper-right corner.
- The Browse activity starts again and takes you to the bookmarked page.
A shortcut would be to resume the Browse activity associated with this bookmark without going to the detail view: just click on the "Resume" icon on the far right of the Browse entry that you have renamed (in Step 6) above in the primary Journal view.
Alternative Suggestions
Instead of just renaming the "Browse Activity", in the tag section, add the tag "bookmark" to the journal entry. Then from the journal, you can search for "bookmark" to see all your bookmarks.
Smart Caching
Since we will deploy the laptops in many areas that don't have persistent connectivity, we will create full local caches of the pages opened within a session, saving the associated data within the session's entry in the Journal. This will allow a child to load several pages that will assist her with homework, and others that she intends to use for a school project, while still at school where a stronger and more reliable network exists. Upon returning home, where no connection exists at all, she may resume those sessions and view all of the pages she loaded previously in full.
When these sessions resume, the Browse activity will alert her that the page she is viewing was "last updated 3 hours ago," for example. It will also provide the options to continue reading the cached version, or reload the page. Before providing this message, the Browse activity will attempt to locate the servers of the pages presently displayed. If it cannot locate a connection to these servers, it will provide the alert as usual, but it will also indicate to the child that she may not reload at present.
Of course, when a child views cached versions of pages within the Browse activity, links will not function properly. Therefore the activity will intercept these events, notifying her that they cannot be followed. In all cases, the browser will store the most recently loaded version of the page.
Powerful History
Future Feature
Despite the core focus on sessions (or perhaps more importantly because of them), the Browse activity will support cross-session history and bookmarks. This extensive and easily searchable history will span the gap between various sessions, allowing children to share links they found in a private session with their friends later on.
History Entries
Each entry within the history will have a title, a list of associated tags, and a thumbnail for visual recognition. Additionally, each entry will preserve its creation date and creator. The creation date will have the form "n units ago" (e.g., "11 minutes ago", "5 days ago", "7 months ago"), thus maintaining a logarithmic temporal granularity just as the Journal itself does. This relative measure will function in parallel to the children's memories, proving far more useful than a more discrete yet less meaningful date.
In addition to these common features, each entry will have a specific type which indicates both where it came from and its importance. Entry types include: bookmarks, shared links, unshared links, and searches. Shared links and bookmarks are always placed in the shared link tray for the browser session, and take on the color of the child who posted it. These colors carry over into the histories, providing visual clues about all of the links and bookmarks that your friends have shared with you and vice versa.
Finally, the presentation of the title will also depend upon how an entry was created. Search entries, for instance, will be labeled with the quoted search string. Pages loaded via explicitly typing a URL will likewise have the quoted URL for a title. On the other hand, entries shared by a friend, or browsed to via hyperlinks, will have their actual page titles preserved in the history, since the URL information needn't be exposed and wouldn't likely be remembered anyway.
Grouping
A primary reason for the uselessness of many browser histories is the sheer number of entries that fill it up all too quickly due to most of our browsing habits. While sessions and tabs should, in theory, limit this phenomenon, a better approach is needed. For this reason, the history will support smart grouping of entries. All pages visited in succession within a single top-level domain will be grouped together in collapsed form within the history, making quick scans for any given entry much quicker. Of course, a child may expand any of these groups to reveal the individual pages visited within the domain as well.
Searching & Filtering
A searching and filtering system will allow children to quickly locate entries by name, tags, date, type and creator. By specifying any combination of these parameters, the results list will update to reveal all matching entries.
Collaboration
The web-activity does feature collaboration. To share your session you select the scope in the Activity tab of the web-activity. The icon will be visible in the mesh view and the session can be joined by others. What is shared in the case of the web-activity are links and their information. To share a link you have to hit the 'star button' in the Browse tab right to the entry for the URL. This will generate a link from the currently visited URL, creates a thumbnail of the visible page and add it to a tray at the bottom of the page. The link contains the thumbnail the title of the page and the owner of the link which is displayed in the palette visible when you hover over the link. The same information will be visible to the other members of this shared session. They can then decide whether they want to follow the link (browse to the web-page associated with it) or not.
We decided to implement the friends or trust model. This means that any member of the shared session can add a link. This is different than a possible teachers model, where the owner of the shared activity browse links and the members of the session have to follow these actions. The issue of someone adding garbage or undesired information to the session has been taken care of by displaying information about the creator of a link, so we make this a social problem. The name and the XO colors are displayed with the link in the tray. You can remove a link from your tray as well. This happens locally since we want to avoid someone removing links from all the members in the session.
Since bundle version 42, you can hide and show the tray to not use so much space from the actual canvas. This can be toggled with the ctrl+v keystroke. Since image 581, a button to show and hide the tray of the shared links has been added as well.
With bundle version 47 we are introducing the syncing of the shared links when members leave and rejoin (with possible changes in their set of links). Member A might add links when member B is not around and B might do the same. When both then come together again a syncing of their state needs to be done. When you delete a link from your tray it will not be added when you meet with another member where this link is still present in his tray. Below we describe scenarios which should work by now.
Scenarios
- a)
- A opens an instance and shares it
- B joins this instance
- they share information A<->B
- B quits
- A changes his information
- B resumes from journal (A's mesh view instance is still available)
- ---> B joins and gets synced
- b)
- A opens an instance and shares it
- B joins this instance
- they share information A<->B
- B quits
- B resumes from journal (A's mesh view instance is not available anymore)
- ---> B will share his instance, C joins and gets synced
- c)
- A opens an instance and shares it
- B joins this instance
- they share information A<->B
- A quits (modifies his version)
- B quits (modifies his version)
- A and B resumes from journal and they get synced
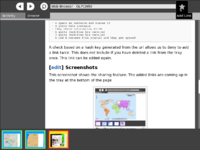
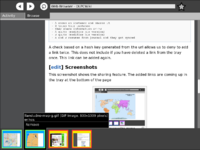
A check based on a hash key generated from the url allows us to deny to add a link twice. This does not include if you have deleted a link from the tray once. This link can be added again.
These screenshots show the sharing feature. When you share a link it will be added to the tray at the bottom of the page. Your shared links are saved to the journal as well. You can resume the shared session and it will be synced with the other members of the session.Link Sharing
Each browsing session will have a tray at the bottom for shared links. This tray will be shared among all of the participants of the activity, and anything shared through it will automatically appear within their histories. Every bookmark that a child makes (with the star button) will automatically be added to the shared links tray; Children may also share links (with the globe button) )that they don't wish to bookmark.
This simple interaction mechanism will provide an entirely new collaborative browsing experience. It could be useful in a classroom setting, allowing a teacher to simply share the links for the day's lessons instead of writing long and complicated URLs on the board. It can also provide a valuable resource for group projects, where each child researches various aspects of a topic and shares the most relevant links with the group. All of the shared links within a session will be preserved with that session. Essentially, any shared link becomes a bookmark unique to that session.
Handheld Mode
Button Mapping
As of build 650, scrolling buttons work, but the sharing link and select link buttons are not implemented.
| Button | Press | Hold |
|---|---|---|
| LEFT | focus previous link | focus previous link |
| RIGHT | focus next link | focus next link |
| UP | page up | scroll up |
| DOWN | page down | scroll down |
| NORTH | share link | shared link overlay |
| SOUTH | panning overlay | |
| EAST | select link | TOC overlay |
| WEST | back | navigation overlay |
LEFT, RIGHT, UP, DOWN are the keypad to the left hand side of the screen.
NORTH, SOUTH, EAST, WEST are the buttons on the right hand side of the screen.
Hold overlay
In the table above, the overlays activated by holding are navigable using the arrow buttons in two different ways. The first button can be held while the option is chosen with the arrow keys; when the first button is released, the option is activated. Alternatively, the first button can be held down until the overlay appears, then released. The arrows are then used to choose an option and any of the NSWE buttons select that option.
Basic navigation of a page is supported by the directional buttons in conjunction with the EAST and WEST buttons. UP and DOWN buttons page or scroll the view vertically — the primary direction of scroll — and the RIGHT & LEFT buttons jump to the next and previous links on the page, respectively. Note that the selection focus should remain visible on screen at all times; When the focused link scrolls off of the page, the last or first selectable link in the viewable area should be selected automatically, when scrolling/paging up and down, respectively. The EAST button will follow the currently focused link, while the WEST button will navigate backward. Note that this configuration lacks an explicit forward functionality. In practice, the forward button is used much less than the back button; Here we also make the assumption that a child may navigate forward by selecting the same link again. In order to facilitate this, the scroll position and focused link state will be stored in the navigation stack, such that the link she selected will be auto-focused when she navigates backward. Thus, in effect, the EAST and WEST buttons will function just like forward and back buttons when no intermediate navigational keys are pressed in between.
Panning
Due to the small size of the display, some pages will inevitably require horizontal scrolling. Since the LEFT and RIGHT buttons map to link selection, another means of spatial navigation is required. The SOUTH button, which has no immediate action on press, will activate a panning mode when held. A visual indication of up, down, left and right arrows on the screen will indicate that the child may use these buttons to scroll in each of these directions. When the SOUTH button is pressed momentarily, a short overlay message will appear briefly, informing her that she may hold the button to scroll in all directions.
The EAST and WEST buttons also have overlays when held down. These overlays always act as modifiers for the directional buttons, allowing selections from menus that appear on screen. Since these buttons both serve navigational functions, so too do their overlays. The EAST button, associated with following the selected link, will provide a dynamically generated table of contents (based upon the semantic definitions provided within the HTML) for the active page. Essentially, this will provide a list of anchor links which may or may not actually exist within the page itself, or may exist at the very top, far from the current visible portion of the page. While many pages may not have support for this at all, it will prove invaluable in many instances, such as reading long wikipedia articles. The WEST button, otherwise associated with backward navigation, will provide a navigation overlay. This overlay will operate in two dimensions. Vertically, a list of visited pages in the forward/back queue will appear, with the current page selected at the center. Horizontally, a child may navigate left and right to switch the currently selected tab, allowing them to switch easily between several documents or pages without exiting Handheld Mode.
Link Sharing
Finally, the NORTH button associates with the sharing functionality. Pressing the button will share the link for the currently selected page, effectively bookmarking it within the current Browse session. Since the keyboard is inaccessible in this mode, bookmarks cannot be created. Of course, once shared, any important pages will remain in the shared link bar and can be bookmarked once out of Handheld mode. Holding the NORTH button down will reveal the shared link overlay. This list of all links will indicate visually who posted them and their Title, and allow selection of them at any time during the browsing session.
Explore
A main feature in the OLPC project is the possibility to explore the laptop. For Trial-3 the possibility to show the source of a web page has been added. When the desired page is displayed use the ctrl+u or fn+space shortcut to display the source. This will open a write activity and display the content. This generates an item in the journal as well, which allows use of another activity to display the plain text content. (Added since image 575)
There are some shortcuts to facilitate navigation in the web-activity. Please note that the shared link tray will only appear when there are bookmarks to display.
| Add a link to the shared link tray | ctrl+l |
| Toggle the visibility of the shared link tray | alt+space (this is a global keystroke that works in other activities as well) |
| Show the source | ctrl+u |
| Show the source | fn+space |
| View > Fullscreen/Return from Fullscreen | alt+enter |
Visual Design
Media
| Document | Description |
|---|---|
| Activity Mockup (216KB) history | Adobe Illustrator file containing mockups for each toolbar |
Screenshots
Development
Discussion
Feature Requests
Clearing History and Cookies
The ability to clear the history and cookies would be very useful and appreciated.
Bookmarks
While the activities pane is great, access to bookmarks make it easier to pre-load a system with sites a child can go to.
View Source
Now implemented via Ctrl-U. This is a key binding currently unique to Browse, as of November 2007.
Supporting Firefox extensions
Specifically wanted: a way to get google gears to work in Browse, as a broadly useful open source project that has been well received and that is being used for many new applications online to make them fast offline.
- people managed to get firefox extensions which doesn't modify the xul UI to run under epiphany/galeon in the past. I don't know exactly how they did that but something similar should also work
for Browse... Christian (chpe@gnome.org) should know about it. - marco
Note: Getting Firefox extensions working in the Browse activity would allow rudimentary parental controls extensions to be installed. Several of the G1G1 users are interested in this. —Joe 20:16, 18 December 2007 (EST)
Also wanted: a way to block out ads/other contents from some sites. Kids should not be exposed to ads at such an early age.
Launching to specific sites from the taskbar
It would be convenient to use the taskbar as a means to launch directly to some favorite sites, such as gmail. This could be achieved either by exposing the Journal entries from the taskbar—so you could resume a gmail session without having to open the Journal and search for it—or by having separate start pages associated with different icons, as per the gmail-activity. The latter is a lot of overhead, but having the icon on the taskbar is quite convenient. But the latter will create a new entry in the Journal each time, when we probably just want to update the existing one—something to revisit when we review the Journal/DataStore API.
Flash in the default web browser
The browser runs Gnash by default as a flash player. You can also install Flash Player plugin 9 for the gecko/xulrunner web browser. See Adobe Flash.
"Find in page" support
The browser should support the ability to search for text in the page as ctrl-f does in Firefox.
Enhanced support for working with URLs
Would be useful for a URL destination to be shown via tooltip, right click menu, or possibly in some activity space (bookmarks bar or top browse bar). Also, right click to copy URL is requested so that links can be shared without the need to first follow them and then cut/paste from the Browse input box.
For example, I was trying to get RSS links from SFGate.com for News Reader. This site instructs you to cut and paste the link into your RSS reader. Links are images, so text of link cannot be seen. When link is clicked on, it takes you to another site where the feed can be properly viewed from within the browser. The only true way to grab the link is 'copy link' from Firefox (or similar) right click menu. Aaronfeibus 14:00, 8 January 2008 (EST)
Implementation Discussion
Possible alternatives
- WebKit
- Dan Winship did a quick and dirty build and port of webkit to use in the web browser activity. It did work but the upstream support for Gtk is in its relative infancy and it was clear due to crashes and other symptoms that it will be a long time before WebKit is ready for primetime for our project. It was, however, a good bit faster and smaller. But not an order of magnitude.
- Dillo
- The small web browser capable of running in an embedded environment
- Dillo website
- Opera
- has been successfully installed.
- Firefox 2.0
- It is also possible to install Firefox2
- Seamonkey
- Seamonkey 1.1.7 can be successfully installed, though a number of dependency .RPMs are required from Fedora 7.
Version History
Known Bugs
Use of "View: + (Increase size)" icon in browser to increase text size on screen has led to browser crashes.
On two or three of occasions I went to the regular BBC news page , and the page loaded properly. Pressing the + icon once caused the text size to increase properly. After waiting briefly for resized page to stabilize, pressing the + icon a second time caused the broswer activity to spontaneously quit. This problem appears to be repeatable on demand.
This problem does not occur when viewing Wikipedia pages, so it may be particular to BBC News, or it may occur in cases where pages have excessive graphical content. I consider this a potentially significant problem since if the font size is too small to be readable, the resulting frustration may discourage reading in general or dampen curiosity to explore.
(Submitted by: G510, not a registered user, but one of the first to order an XO via G1G1)
- (The "known bugs" link was broken by the activity name change—I've fixed it.) The bug you describe appears to have been already found and fixed, but thanks for reporting it: Trac ticket 5639. The fix should be present in the big software update coming early next year. —Joe 18:24, 31 December 2007 (EST)
I've had three problems with Browse:
1. When I hit the back button, sometimes Browse spontaneously quits. This error does not happen every time I hit the back button, however.
2. I have also had the browser quit when I tried to resize a page.
3. Sometimes Browse takes almost 5 minutes to start up (most of the time it is much faster).
Source
http://dev.laptop.org/git.do?p=web-activity
RPMs
none available
Resources
Functional Test
View source : currently via Ctrl-U