Creating a collection: Difference between revisions
(→Formatting content: link to Data file formats, remind users to try rotating the screen and e-book mode) |
(→File formats: clean up) |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
===File formats=== |
===File formats=== |
||
The first step of this process is to make sure that your collection is saved in a file format that is supported by the library. (Other file formats may be supported on the XO, but not within the library). The following |
The first step of this process is to make sure that your collection is saved in a file format that is supported by the library. (Other [[data file formats]] may be supported on the XO, but not within the library). The following file formats are supported by the library: |
||
; Text |
; Text |
||
: <tt>.txt</tt>, <tt>.doc</tt>, <tt>.abw</tt> - These formats can be read by the [[Write]] activity |
: <tt>.txt</tt>, <tt>.doc</tt>, <tt>.abw</tt> - These formats can be read by the [[Write]] activity. |
||
:<tt>.pdf</tt> - This can be read by the [[Read]] activity. |
:<tt>.pdf</tt> - This can be read by the [[Read]] activity. |
||
; Multimedia document with layout |
; Multimedia document with layout |
||
: <tt>.html</tt> - |
: <tt>.html</tt> - Rendered by [[Browse]], and users can view source. |
||
; Formatted text |
; Formatted text |
||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
; JavaScript |
; JavaScript |
||
: This will be viewable the same way page source can be viewed through the browser. |
: This will be viewable the same way HTML page source can be viewed through the browser. |
||
; Etoys projects |
; Etoys projects |
||
Revision as of 04:37, 30 October 2008
See also: creating an activity
If you would like to package a collection of mostly-static content for use on the XO, follow the instructions below to create a collection (sometimes called a library or content bundle). When you're done, you can add your new bundle to the collections page so that it can be viewed and downloaded by children worldwide. Upon installation it will appear in the Library.
If you'd like to suggest a collection for inclusion in the core library, nominate it. Please note that some suggested collections, specifically those in languages other than the current targets of English, Spanish, Portuguese, Arabic, French, Thai, and Urdu, are linked on this site but have not yet been incorporated beyond the wiki.
If you'd like to help out by creating collections but are unsure of where to begin, see the list of new bundle ideas.
Overview
The OLPC Library is the set of content and materials (outside of the core OS and Activities) that ships with the XO laptops and school servers. In order to add your content to this repository, you must create a self-contained bundle for your content. This page is a proposed spec for such a bundle, providing the information you need to select, format, and package a collection.
Note: These instructions explain how to package browsable content for the OLPC library. Materials in a collection that need to be run by an Activity other than Browse will have to have a mime-type registered with the Browse activity so they can launch from there. Activities may be part of content packages for the library as well, for instance as sample code to be read. For more information on packaging source code, as well as other questions you may have, skip down to the #FAQ.
Collections currently unpack into a directory under /home/olpc/Library. Future improvements to the current bundle format are intended to allow a single bundle to contain both an activity and a collection (including, for instance, default help/readme materials).
'If you plan to host your own bundles, please note the #bundle hosting guidelines.
Feedback
As you create your bundle, please note any puzzles or problems you encounter, as well as any thoughts for improvement that you might have.
The process and format is a new one, and feedback helps improve it. One place to do that is on the Talk:Creating a collection page.
Selecting content
The first step to creating your collection is to determine what content should be included. In some cases, this is easy: everything! In other cases, there are additional considerations:
- Size
- How big is your collection? If the size of your entire collection is between 5-20MB, you're all set. Otherwise, you'll need to make two bundles-- one bundle of 5-20MB for use on individual laptops, and a second bundle of unlimited (but reasonable) size for inclusion on each school's library server.
- Note: The XO's filesystem invisibly compresses files to save space, so you may be using less disk space than you think. Text files are compressed about 50%. Other file formats are basically unchanged. If you are curious, there are (somewhat difficult to apply) instructions in JFFS2 to measure likely disk usage.
- Quality
- Does your collection have a rating system in place? If so, consider including only top-rated material in your collection. Otherwise, think about "curating" a selection of high quality material to be included in your bundle (or bundles).
- Relevance
- Is your entire collection relevant to children? If so, terrific! If not, consider including only material that will help children learn, explore, and expand their worlds.
- Language issues
- Does your collection contain material in multiple languages? We hope it does! To the greatest extent possible, please give preference to materials that exist in multiple languages, or that can be easily translated by our localization team.
- Licensing issues
- What kind of copyright exists on the material in your collection? Do you have legal permission to archive and distribute it? Please be sure to review the licensing terms of your collection. For guidance on licensing, see licenses.
Formatting content
Once you've determined the material you'd like to include in your collection, you'll need to format it for use on the XO.
File formats
The first step of this process is to make sure that your collection is saved in a file format that is supported by the library. (Other data file formats may be supported on the XO, but not within the library). The following file formats are supported by the library:
- Text
- .txt, .doc, .abw - These formats can be read by the Write activity.
- .pdf - This can be read by the Read activity.
- Multimedia document with layout
- .html - Rendered by Browse, and users can view source.
- Images
- .jpeg, .gif, .png - These can be viewed by many applications, including Browse.
- .svg - 99% supported in Browse.
- Music
- .csound - This will be playable by TamTam... in early 2008 its XO build doesn't provide a way to save or load sound files, however.
- .ogg - can be played in Browse by the Totem plugin.
- .mp3, .wav - These can be played by [[Helix media activity|Helix], standalone or as a browser plugin, when installed.
- .rm, .ra - This can be played by the Helix plugin when installed with a RealAudio codec.
- Video
- .ogg - Can be played in Browse by the Totem plugin.
- .mpeg, .mov, .wmv, .rm - Playable by Helix media activity, which can be downloaded in a few steps. To play video, please download this activity along with some videos (see for instance this video).
- Python
- Browse will display .py files as text. The Develop activity provides one way to view python files; the 'view source key' another.
- JavaScript
- This will be viewable the same way HTML page source can be viewed through the browser.
- Etoys projects
- .pr files automatically launch Etoys from the browser.
If you have a question about a file format that is not listed above, ask it on the talk page.
Visual formatting
The second step of the formatting process is to make sure that your collection displays correctly on the XO. The small screen can sometimes lead to unexpected formatting and display issues. Also test it with the screen rotated and in e-book mode (with the screen rotated and lowered).
The easiest way to test the visual display of your material is to view it on an XO. If you don't have access to an XO — or to another person who has one — you can install and run the Sugar emulator on your computer. Emulating the XO has installation instructions.
Packaging content
Once you've selected and formatted your content, the last thing to do is to package it as a bundle.
Bundle structure
A collection or library bundle is a directory compressed as a .zip file renamed to end in .xol. (.xo and .xol formats are planned to merge, in which case a collection in a bundle will be identified by the "library" subdirectory and its "library.info" file.)
Each bundle must contain a single top-level directory which has the same name as the bundle (minus the ".xol" extension). All other files in the bundle must be within this directory. The top-level directory must also contain a subdirectory called library that contains certain configuration files.
Here is an example of a library bundle for a collection called "dictionary.xol":
dictionary/
A/
aardvark.html
abacus.html
acacia.html
...
B/
balloon.html
...
C/
...
library/
library.info
library-dictionary.jpg
contents
contents.sig
index.html
- dictionary/
- The top-level directory, which has the same name as the bundle itself (minus the ".xol" extension).
- library/
- This directory contains all the metadata associated with the collection. It includes several configuration files which are discussed below in configuration files.
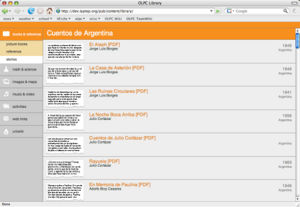
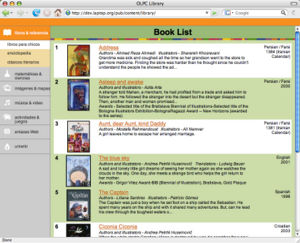
- index.html
- This is the top-level navigation page for the collection. The index.html page is the page that is displayed in the main frame of the reader when a child selects the collection from the library sidebar.
- Need to update with info about templates...
- At right are two examples of index.html pages. The first is a standard index page that uses the default library template. The second is an index page adapted from a pre-existing digital collection that uses its own organization scheme and style sheets. For additional examples of index pages, visit the online version of the OLPC Library.
Configuration files
The "library" directory contains all the metadata associated with the collection. It includes the following files:
- library.info
- The library.info file is a text file that follows a key/value pair format. It contains information about the source, version, language, and subject of the collection (among other things). Sample library.info file is an example, with information about required and optional entries.
- You can use this web form to create a library.info file for your bundle.
- library-dictionary.jpg (optional)
- This is the icon that represents the collection in the library navigation sidebar. The icon should have the same name as the collection's .xol file, except with library- at the front. The icon can be in any number of supported file formats, including SVG, JPEG, PNG, and GIF. See Choosing image formats for more information.
- Note: This may not need to exist since icons appear at the category level, not the level of individual collections.
- contents (not yet required)
- See below.
- contents.sig (not yet required)
- The
contentsandcontents.sigare manifest and credential files for the entire bundle contents (excepting thecontentsandcontents.sigfiles themselves), as described by the Manifest Specification. Their relation to library bundles has not yet been defined.
Localization
Library bundles aren't internationalized quite the same way that activity bundles are. We are working on a spec to support simple localization without requiring existing repositories to change their existing formats, and to enable people without access to other localization tools to use pootle for full document translations and rebuild a set of html pages from the results.
Collections tend to rely much more heavily on text than code, and often the right way to localize something fully is to make a separate bundle for each language (even for some of the activity bundles that now have twenty localizations, the bulk of their size is taken up by their locale materials). The recommended process will provide a facility for localizing navigation, headers and tables of contents; and allows for (but does not recommend) the use of pootle to translate longer documents, for collection creators without access to any other translation management.
While library localization is still in development, simply indicate the language(s) of your collection in the locale field of the library.info file.
Packaging a collection
Step by step
- Make sure that no top-level directories in your content are named library/.
- Make a directory for your content, with the name you want to give your collection. (Let's call it omnium/ for the sake of example.)
- Copy your content files (with any folder structure you like) into omnium/.
- Within omnium/, make a second directory called library/.
- Within library/, create a text file called library.info and give it content as in the sample library.info file.
- If you would like to supply an icon for your collection (see configuration files above), copy this icon (.svg, .jpg, .gif, or .png) into the library/ directory and put the icon's name into the library.info file.
- Decide whether:
- You want to use standard OLPC formatting (possibly with minor changes to colors and styles) in displaying your content on the XO.
- You want to customize the display children see when using the XO to view your content.
- If you want to use standard OLPC formatting:
- Create a text file library.xml within library/.
- For every item in your collection that you want displayed to students, include items in your library.xml file that mirror those in the example Library.xml file.
- If you want to change the colors and styles of the OLPC formatting, create a text file library.css within library/that gives your preferred css.
- If you want to use your own customized formatting:
- Create a text file index.html in omnium/.
- In index.html, write html code providing links to all your content items.
- Zip up omnium/, with all its subdirectories into a .zip file with the same name as your bundle (eg omnium.zip).
- Rename the zip file as a .xol file (e.g. omnium.xol).
Voila! The .xol file is your collection's library bundle.
A note on redirection, index pages, and standard formats
If you are running a build prior to 660, and want to create a bundle without a navigation frame, rename your index page to something else, and make the index page a redirect to it. Earlier 6xx builds generated a bundle_index.html page from the index pages with additional navigation.
This wasn't a good idea[1], and in recent builds bundle_index.html isn't a special file. On older builds, if you want to avoid the navigation frame, you can make your index page a redirect (to the proper index page, which can be named anything /other/ than bundle_index.html)
- [1] design goals : accept existing bundle formats without modification. preserve the integrity of a chosen/installed bundle revision. implementation : avoid modifying bundles in place unless there's a foolproof way of unwinding any changes.
- (corollaries : any superposition of navigation or context should be minimal and reversible. similarly, requiring internal library/ and activity/ directories within a bundle is a bad idea, as that is wrapper information that should change with sugar's needs and not with the bundle curator's design)
Using a setup.py script
see Talk:bundles and the bundler.py script for more. In principle, the bundlebuilder function from the sugar.activity library should generate bundles for you.
This needs testing and updating... and related codepaths in sugar should use the same functions , if with different arguments, for all bundle types
Bundle hosting
To host your own bundles, you must tell your web server about the bundle mime types Sugar expects. You need to add the following to your web-server configuration (/etc/apache/mime.types, or /etc/mime.types on Ubuntu systems):
application/vnd.olpc-sugar xo application/vnd.olpc-content xol
If you want to host your bundles elsewhere, you are welcome to upload them to this wiki or to dev.laptop.org (you can [[requesting an account|request an account] there if you need shell access), which will set the mime-type properly when they are later downloaded.
FAQ
Can I repackage an activity as a library bundle?
Yes. Collections and activities are intended to coexist. To package your activity as a library bundle, you just need to add the index.html page and the library directory (including relevant configuration files) to your existing activity bundle. Then, rename it as a .xol file, and you should be all set. If you are modifying a bundle on an XO, you will also need to move it from /home/olpc/Activities to /home/olpc/Library . As mentioned above, there are plans to merge the xo and xol formats, so that no repackaging is needed for a bundle to be interpreted in both ways.
How do you open an XOL file?
An XOL file is a zip file with .xol extension instead of .zip. You can extract the contents using any unzip utility. If you want to install a content bundle, you do it just like any other activity. Download it with the browser, the resume it from the Journal. The new bundle will show up the next time you open the Web Activity or if you refresh the browser's homepage.
How do you uninstall a collection?
If you downloaded it to begin with, you will have a Journal entry for it. Open the journal, and delete that entry; this will permanently uninstall the collection as well.
Otherwise, open the Terminal activity and stay as the "olpc" user. Delete the bundle's directory found in /home/olpc/Library/. Then, update the browser's index file by running python /usr/share/library-common/make_index.py
How do I upload my collection to this wiki, and host it here?
You can upload it by clicking "Upload file" in the left margin, and entering the filename and description on the page that comes up. Then, after you hit the upload button, it'll be hosted on the OLPC Wiki. Then, to get it into the index of Collections, you can edit that page by hand as well. (you can also try using Semantic Mediawiki to add your entry to the table.)