Atualizando para LinuxBIOS
| Tradução de Upgrading to LinuxBIOS | probable original version |
| english | português +/- | alterações |
Contents
- 1 Introdução
- 2 Cuidados
- 3 Procedimento de instalação do OLPC LinuxBIOS
- 4 Solução de problemas e informações adicionais para os curiosos
- 4.1 Continuar com uma instalação
- 4.2 Continuar com uma instalação completa do Fedora Core
- 4.3 Continuar com uma instalação para o flash NAND
- 4.4 Notas de Lançamento
- 4.5 Nomes para dispositivos USB no Linux
- 4.6 Detalhes da sequência de inicialização (Boot)
- 4.7 Detalhes do olpcflash
- 4.8 Recuperação de desastre
- 5 Créditos
Introdução
Este é o procedimento de instalação do LinuxBIOS no flash SPI de uma placa de desenvolvimento OLPC, substituindo o BIOS Insyde instalado de fábrica, se estiver lá. O BIOS Insyde expirou em 23 de Agosto de 2006.
Este processo trabalha carregando umas das build images do OLPC, as quais incluem os utilitários necessários para carregar o LinuxBIOS na memória SPI flash das placas. A imagem da build pode carregar tanto o BIOS Insyde quanto o LinuxBIOS. Uma vez que o flash foi atualizado, você pode optar por continuar a instalar a imagem de build na memória NAND interna, ou a instalação completa do Fedora em um disco rígido USB.
Cuidados
- Este é um procedimento de sentido único. Uma vez que você instalou o LinuxBIOS e reiniciou, voltar para o BIOS Insyde requer outras ferramentas e procedimentos.
- Se você instalar a versão CL 2.0 do BIOS em uma placa com memórias RAM Infineon, você pode ter problemas em iniciar (ou reiniciar). Por favor, seja cuidadoso na escolha da versão correta do BIOS.
- Nós recomendamos fortemente que você instale uma nova imagem (de build) do sistema operacional ao mesmo tempo que você atualiza para o LinuxBIOS. Entretanto, você pode também usar uma nova imagem do sistema operacional unicamente para atualizar seu BIOS de Insyde para LinuxBIOS.
- O LinuxBIOS não é compatível com o BIOS Insyde. Depois que o LinuxBIOS estiver instalado, as instalações antigas de software que foram usadas para trabalhar sobre o BIOS Insyde podem não carregar mais. Se você deseja continuar usando sua instalação existente, você precisará atualizar tanto o seu kernel quanto o driver do X, como descrito abaixo.
- The Geode processor on the OLPC boards does not have VESA console graphics hardware built in: instead, the Insyde BIOS has code that emulates VESA hardware. This emulator is not owned by AMD, and we prefer to use the BIOS space for other capability. We could also not maintain this binary blob should it require maintenance. This means that DOS or Windows will not boot under LinuxBIOS directly, as they expect to find VESA graphics present.
- If for some reason you are not using the Fedora builds, you should first update your kernel to our latest kernel, and use the gxfb driver as your console. You will also need the amd X driver. To boot a Linux kernel on OLPC on the graphics console, you must use the gxfb driver. Note that the VESA X driver will also no longer function: you should be using the new "amd" X Window System driver as well, which has much higher performance.
Procedimento de instalação do OLPC LinuxBIOS
Antes de Você Começar
Se você tem um UPS (uninterruptible power supply - sistema ininterrupto de energia, um No Break) acessível, você deve plugá-lo em seu sistema OLPC para usá-lo; você não vai querer perder energia durante essa parte desta operação. Durante o processo de apagamento e reescrita da memória flash SPI (que dura cerca de um minuto) você está vulnerável a falhas de energia que podem causar "quebra" do seu sistema (jargão para sem utilidade).
Você precisará de um chaveiro USB (ou disco USB), uma placa de desenvolvimento OLPC com um hub (concentrador) USB 2.0 energizado e um teclado USB (importante), e um sistema anfitrião Linux.
Exigências de Hardware - Detalhes
- An OLPC development board - this is the machine whose SPI flash you will update.
- Antennae for your board, if you plan to ever enabling the on-board wireless.
- A powered USB 2.0 hub attached to the OLPC board.
- A USB keyboard attached to that powered hub. Don't use a PS/2 keyboard; it won't work right with this procedure because of a hardware interaction between the PS/2 and SPI programming circuits.
- A USB flash key or USB disk drive, minimum size of 512Mb. Note that we often refer to a flash key when any USB storage device, flash or disk, will do. I tested with a SanDisk Cruzer Mini 1.0GB device. Any existing data on that device will be overwritten.
- A working Linux-based "host system" to copy the software image to a USB key (or see #Using Windows as a Host system).
- Remember to plug into a UPS if you have one.
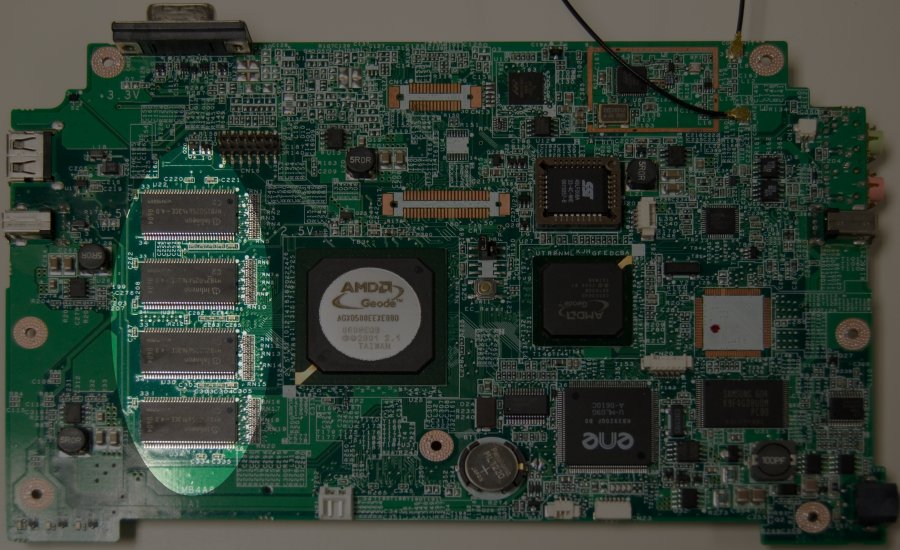
Verificando seu tipo de DRAM
OLPC ATest boards were shiped with DRAM from 3 different manufacturers. Hynix, PSC, and Infineon. The infineon RAMs are the wrong part. They are CL3 parts and the OLPC runs at CL2. Running the Infineon parts at CL2 can cause your board to fail to boot. The Geode does not have a setting for CL3 so there is no "safe" speed for the Infineon. However, after a reasonable ammount of analysis and testing we have found that the Infineon parts will operate at CL2.5 without problems.
Therefore we provide 2 different LinuxBIOS images for upgrade. One that operates at CL2 and another at CL2.5.
Your RAM can be identified by looking at the following picture:
The 4 highlighted chips are the DRAM.
The labeling on the Infineon chips looks like this:
If your RAM matches the above then you need to use the CL2.5 version of the LinuxBIOS upgrade.
Instalando o LinuxBIOS
Download build image 91 from here. This OS image has the following checksums:
$ md5sum olpc-redhat-stream-development-ext3.img.bz2 c37b4fc8b9af3ec119b7f522fd66933c olpc-redhat-stream-development-ext3.img.bz2
$ sha1sum olpc-redhat-stream-development-ext3.img.bz2 91ff00676ed5c14848626adec18f535ab0bad3a9 olpc-redhat-stream-development-ext3.img.bz2
Check that the checksums match! You don't want to flash garbage into your flash. You can use the md5sum and sha1sum utilities on your Linux host system to do the check.
Plug your USB key or disk into the host system, and verify that /dev/sda is its correct name (Alternative names for /dev/sda...). Make sure you do the verification, since SATA hard drives are becoming more common, so using the wrong device name here might overwrite your own hard drive! Now type the following, replacing /dev/sda with the appropriate device if needed:
$ bunzip2 olpc-redhat-stream-development-ext3.img.bz2 $ dd bs=1M if=olpc-redhat-stream-development-ext3.img of=/dev/sda $ sync
When the dd command finishes (it gives no progress indication, so wait until you return to the prompt!), run 'sync' as above, then move the USB key to the OLPC board (connect it via the powered USB 2.0 hub).
If you have ddrescue installed you can use:
ddrescue olpc-redhat-stream-development-ext3.img /dev/sda
ddrescue has progress indication.
If you are still using Insyde BIOS, you will likely have it complain that it has expired. Set the date back to sometime in the summer, for example, August 1, 2006.
Boot the OLPC board (Boot sequence details...), and be sure to choose the second option in the green grub boot menu (don't accidentally boot the OLPC qemu target!).
When it finishes booting, you should see the sugar login prompt. Press ctrl+alt+F1 to get to a console, and login as 'root' with no password.
Now depending on what DRAM type you have you should flash in one of 2 different images. See Checking your DRAM type for help on figureing out what DRAM mfg you have.
For Hynix and PSC DRAM use:
$ olpcflash -r insyde.rom $ olpcflash -w /var/lib/olpc/linuxbios.rom
For Infineon DRAM use:
$ olpcflash -r insyde.rom $ olpcflash -w /var/lib/olpc/linuxbios.rom.cas25
These take of order a minute each to execute. (Details of what olpcflash does...)
If the flashing is successful, the last line of the output from the last command you executed above will be "- VERIFIED". If something went wrong, or verification failed, see #Disaster Recovery, and do not power cycle or reset the board.
It is important to shutdown the system cleanly as LinuxBIOS is currently picky about finding a clean file system for boot.
$ shutdown -h now
At this point you MUST power cycle the board to make sure it is fully reset. If you do not then your PS/2 keyboard and mice will not work.
Please unplug the board from the wall power wait 10 seconds and then reapply power.
If all goes well and the machine eventually loads the Sugar login prompt after you've power cycled it, you can upgrade some more OLPC boards by repeating this procedure.
This is the end of the procedure. The sections below contain additional information that may be useful if you have problems or are just curious.
Solução de problemas e informações adicionais para os curiosos
Continuar com uma instalação
If you installed the image onto a flash key or disk, and are happy to run off of that, guess what? You are running the OLPC Fedora distribution with Sugar, and have nothing more to do.
If you want to install some other system, a full Fedora installation, or install the image onto the internal flash (which is quite slow, by the way; this is why we are building the CAFE chip), then you can follow the directions below.
Continuar com uma instalação completa do Fedora Core
The Installing Fedora Core page describes how to continue with a full Fedora installation, once you have installed LinuxBIOS, if the minimal OLPC installation is insufficient.
Continuar com uma instalação para o flash NAND
The Installing to NAND page describes how to install a build image to the internal NAND flash on the board and boot from it.
Notas de Lançamento
- The LinuxBIOS buildrom package is very sensitive to the compiler toolchain used to build it; we found that FC6 rawhide would build a broken ROM (now being investigated). Ubuntu Edgy unstable has other problems building buildrom head. We strongly recommend against trying to rebuild the LinuxBIOS rom yourself. Please only use binaries that OLPC has tested and do not attempt to build your own BIOS image unless you are a serious LinuxBIOS developer.
- The X server have been configured to use 1024x768x16@60hz, by default, to maximize the chance of it "just working" on as many panels and monitors as possible. Feel free to tune for your own use. Note the OLPC panel is 1200x900 resolution, so if your flat panel or monitor will support that resolution, you may want to choose that size during your development, though we highly recommend using scalable graphics libraries based on Cairo to keep independent of display resolution.
- The Marvell firmware is not yet included in the distribution, but must be separately installed. The firmware should be downloaded and installed as the file /lib/firmware/usb8388.bin.
- LinuxBIOS won't boot to an unclean filesystem. Be sure to shut down the OLPC board cleanly after using it (running 'init 0' in the shell will do the trick).
Nomes para dispositivos USB no Linux
On many Linux systems, USB mass storage devices (e.g. USB key drives) have device names like /dev/sda, /dev/sdb, etc. Those are the same names that are used for SCSI disks, because USB mass storage devices use SCSI-like commands at one level of their software protocol.
In the common case where there is only one USB key drive and no "real" SCSI hard disks, the device name will be /dev/sda. If there are multiple USB mass storage devices or some SCSI hard disks, the USB key might be /dev/sda, /dev/sdb, /dev/sdc, etc. Make sure that you find the right one, because you don't want to overwrite the wrong drive.
On some Linux systems, USB mass storage devices have names like /dev/uba, /dev/ubb, etc. ("ub" instead of "sd").
Detalhes da sequência de inicialização (Boot)
This section describes what you should see while the OS image is booting under Insyde BIOS.
A few seconds after power on, the white Insyde BIOS banner screen will appear. A little later, the top of that screen will show the results of USB probing. Those results should include your USB key.
Then the screen will switch to white text on a black background. Eventually it will boot GRUB (the intermediate bootloader). After a brief timeout, GRUB will then start Linux. When Linux takes control of the screen, the font size will decrease and you'll see a lot of Linux startup messages.
X should start, showing a login prompt in a window titled 'Sugar'. At this point, you can press ctrl+alt+F1 to see a login shell.
Detalhes do olpcflash
The steps that occurs during the execution of the instructions above are as follows.
- (-r) Make a backup copy of the SPI FLASH in insyde.rom
- (-E) Erase the SPI FLASH
- (-w) Write the contents of /var/lib/olpc/linuxbios.rom to the SPI FLASH
- (-v) Verify that the newly-written data matches the file
Recuperação de desastre
If the reflashing process fails, Don't power off or reset the OLPC board. Here are some things you can try that might be helpful. These are just suggestions, because I've never seen any failures - recovery procedures for hypothetical failures are inherently speculative.
Retrying the write command
You can retry the command that writes the SPI FLASH, i.e.
$ olpcflash -w /var/lib/olpc/linuxbios.rom
Retrying might conceivably be of some use if the failure was transient.
Restaurando o BIOS Insyde
You might be able to restore the Insyde BIOS with
$ olpcflash -w insyde.rom
This only works if you haven't powered off or otherwise reset the OLPC board since you loaded LinuxBIOS into FLASH. The reason is because LinuxBIOS cannot boot the software that we use in this procedure, which is set up to be booted by Insyde BIOS.
If something went wrong with the olpcflash process, it's possible - perhaps even likely that the same problem might also affect writing the insyde.rom back. So don't expect miracles; this is suggested "just in case it helps". It might help, for example, if the flash has a single bit error that Insyde BIOS's code has happened to hide.
("olpcflash -w insyde.rom" was helpful in the testing of this procedure, allowing me to test the procedure several times before committing to the "one way" nature of the upgrade.)
Se você ainda estiver com algum problema
Don't power off or reset the OLPC board and please get in contact with us, on IRC or via email, so that we have a chance to see what has gone wrong. If you power off or reset the board, we will have no way to diagnose the problem short of returning the board to OLPC and time consuming hardware diagnosis, and even then, may not be able to figure out what went wrong.
Utilizando o Windows como sistema anfitrião
http://www.chrysocome.net/dd has a version of the "dd" command that runs under Windows. The command line arguments are compatible with the Linux version, but you have to use the Windows form of the USB device name (not /dev/sda). The Windows "dd" has a "--list" command to help you discover the right device name.
Créditos
- LinuxBIOS: Ron Minnich, Richard Smith, Mitch Bradley, Li-Ta Lo and the LinuxBIOS project
- Linux: Cast of thousands
- gxfb driver: Jordan Crouse
- amd EXA X driver: Jordan Crouse
- Libertas Marvell 8388 wireless driver: Ronak Chokshi, Aswath Mohan, Michailis Bletsas, Marcelo Tosatti
- Distro hacking, and initramfs goodness: David Zeuthen
- Kernel hacking: David Woodhouse, Marcelo Tosatti
- JFFS2: David Woodhouse
- Sugar: Dan Williams, Marco Gritti, Chris Blizzard, Walter Bender
- Amazing Sleuthing: Mitch Bradley
- Testing: Chris Ball, Ivan Krstić, Ray Tseng
- Lots of information: Ray Tseng
- Installation directions: Mitch Bradley, Ivan Krstić, Jim Gettys, Chris Ball, Carl-Daniel Hailfinger
- Official OLPC virgin (tester): Léandra King