XO Monitor: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TOCright}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Image:Xo-monitor 002.png]] |
[[Image:Xo-monitor 002.png]] |
||
== |
== Features == |
||
* Get XO basic information as: build, kernel, firmware, model, serial number, etc |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* Trace system CPU usage |
|||
* Log viewer |
|||
* Simple network stats |
|||
* List XOs in the local network |
|||
== Getting XO Monitor == |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
== Installing XO Monitor == |
|||
=== Requirements === |
|||
* [[Git]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* PyGtk |
* PyGtk |
||
* PyCairo |
* PyCairo |
||
* FUSE |
* FUSE |
||
* sshfs |
* sshfs |
||
* Avahi (in fc6, rpm avahi-tools is needed for python2.4/site-packages/avahi) |
|||
* Avahi |
|||
* python-crypto |
* python-crypto |
||
=== Apt-get based Linux system === |
|||
== Download == |
|||
For Debian-based Linux systems (Ubuntu, etc). |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
<pre> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
git clone git://dev.laptop.org/users/edsiper/xo-monitor |
|||
cd xo-monitor |
|||
sudo apt-get install python python-gtk2 python-cairo sshfs python-avahi python-setuptools |
|||
sudo easy_install pexpect |
|||
</pre> |
|||
=== Yum based Linux system === |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
For Fedora-based Linux systems, including XOs. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
<pre> |
|||
git clone git://dev.laptop.org/users/edsiper/xo-monitor |
|||
cd xo-monitor |
|||
sudo yum install python python-gtk2 python-cairo sshfs python-avahi python-setuptools |
|||
sudo yum pexpect |
|||
</pre> |
|||
=== Other operating systems === |
|||
There is no support for other operating systems (in particular, Windows and Mac OS X) at this time. |
|||
== Using XO Monitor == |
|||
In a terminal window, type: |
|||
<pre> |
|||
./xo-monitor.py <ip-address-of-the-XO-you-want-to-connect-to> -u <username> -p <password> |
|||
</pre> |
|||
[[category:software development]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 16:21, 24 October 2008
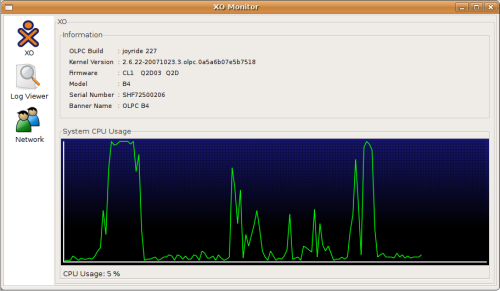
This is an external program to watch the XO resources through the network. It uses ssh + FUSE to mount the XO root filesystem in a local directory, most of the information comes from the remote procfs.
Features
- Get XO basic information as: build, kernel, firmware, model, serial number, etc
- Trace system CPU usage
- Log viewer
- Simple network stats
- List XOs in the local network
Getting XO Monitor
The first alpha snapshot can be found here:
http://dev.laptop.org/~edsiper/projects/xo-monitor-alpha-0.1.tar.gz
or you can get the latest development version from the git repository:
$ git clone git://dev.laptop.org/users/edsiper/xo-monitor
Installing XO Monitor
Requirements
- Git
- Python
- PyGtk
- PyCairo
- FUSE
- sshfs
- Avahi (in fc6, rpm avahi-tools is needed for python2.4/site-packages/avahi)
- python-crypto
Apt-get based Linux system
For Debian-based Linux systems (Ubuntu, etc).
git clone git://dev.laptop.org/users/edsiper/xo-monitor cd xo-monitor sudo apt-get install python python-gtk2 python-cairo sshfs python-avahi python-setuptools sudo easy_install pexpect
Yum based Linux system
For Fedora-based Linux systems, including XOs.
git clone git://dev.laptop.org/users/edsiper/xo-monitor cd xo-monitor sudo yum install python python-gtk2 python-cairo sshfs python-avahi python-setuptools sudo yum pexpect
Other operating systems
There is no support for other operating systems (in particular, Windows and Mac OS X) at this time.
Using XO Monitor
In a terminal window, type:
./xo-monitor.py <ip-address-of-the-XO-you-want-to-connect-to> -u <username> -p <password>