Inertial navigation peripheral/System design: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
'''Locograph''' |
'''Locograph''' |
||
A Locograph has the following attributes: |
A Locograph has the following attributes: |
||
* '''position''': A tuple of length three - (x, y, z) - expressing coordinate change relative to the laptop in the global Cartesian space. |
* '''position''': A tuple of length three - (x, y, z) - expressing coordinate change relative to the laptop in the global Cartesian space. |
||
Revision as of 23:48, 4 November 2008
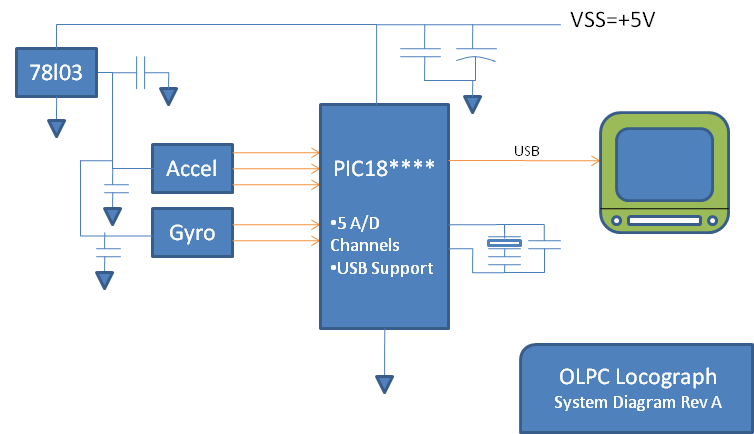
System schematics
note: Greg fails at typing "inertial"
Software Systems
Microcontroller
Python "Driver" Class
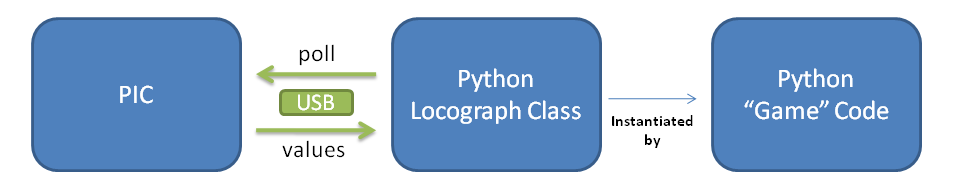
The driver class for the Locograph will be a Python class called "Locograph". Locograph will handle connecting to the USB device using libusb, meaning a user of this class merely needs to instantiate one and start asking it for values.
Here is something like a UML diagram for Locograph:
Locograph
A Locograph has the following attributes:
- position: A tuple of length three - (x, y, z) - expressing coordinate change relative to the laptop in the global Cartesian space.
- bearing: A number - 0 to 1 - expressing how much of a rotation the laptop has completed in the global Cartesian space.
A Locograph offers the following methods:
- getPosition(): returns self.position
- getBearing(): returns self.bearing
- _updateFromDevice(): polls the USB device for new values.
- _mapDevice(): sets up the USB device originally.
- reset(): client asks for coordinate reset.
- _reset(): ask USB device for coordinate reset.
Python "Game" App
Form factor
(insert sketches)
(include sketch model picture)