Activity sharing: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Overview == |
== Overview == |
||
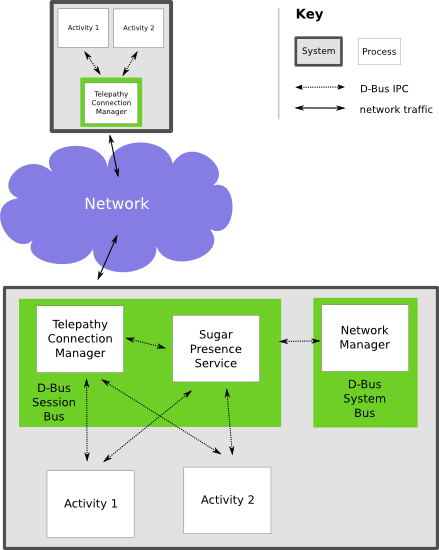
Collaboration in Sugar activities works using a set of services that run on the laptop, and APIs in the Sugar Python modules that wrap those services. The main services are the '''Telepathy connection managers''' and the ''' |
Collaboration in Sugar activities works using a set of services that run on the laptop, and APIs in the Sugar Python modules that wrap those services. The main services are the '''Telepathy connection managers''' and the '''[[Presence Service]]''' that coordinates them. |
||
[[Image:shared activites.png|right]] |
[[Image:shared activites.png|right]] |
||
[http://telepathy.freedesktop.org/ Telepathy] is a system describing a generic interface for various kinds of communication. It is the underlying infrastructure used by Sugar for collaboration. Currently, two Telepathy implementations are used: [[Telepathy Gabble|Gabble]], for Jabber, and [[Telepathy Salut|Salut]] for serverless Jabber (a.k.a. link-local XMPP). The former is used when the school server is reachable; the latter in the simple mesh case. |
|||
== Telepathy == |
|||
== Advertisements and invitations == |
|||
[http://telepathy.freedesktop.org/ Telepathy] is a system describing a generic interface for multi-user chat (MUC), instant messaging (IM) and voice/video applications. It is the underlying infrastructure used by Sugar for collaboration. |
|||
Shared sugar activities are discovered in two different ways: through broadcast advertisements, and through invitations. |
|||
== Presence Service == |
|||
Advertisements are made when the user tells the activity to share itself with the entire network. Anybody on the network can see the activity. |
|||
The [[Presence Service]] performs a number of functions: |
|||
Invitations are send to particular users. Only those users who are sent an invitation see the activity (unless the activity has also been advertised). When Sugar recevies an invitation, it asks the user whether they want to accept or reject it. |
|||
* it starts the Telepathy services on startup |
|||
* it registers the laptop with the Jabber server |
|||
* it reconnects Telepathy connections when they are disconnected |
|||
* it collates activity and buddy information from the Telepathy services, and re-exports it over D-Bus |
|||
To make activity authors' lives easier, there is a class that takes care of |
|||
talking to the D-Bus presence service |
|||
(<tt>sugar.presence.PresenceService</tt>). Most activities can use this class |
|||
for all their Presence Service needs. |
|||
The Presence Service uses two Telepathy connection managers: |
|||
* '''Gabble''', that provides server-based Jabber/XMPP functionality. It talks to a [[Jabber server]] (e.g. <tt>olpc.collabora.co.uk</tt>) and sets up different chat rooms through which activities talk to each other. |
|||
* '''Salut''', a link-local Connection Manager using reliable multicast over the local network |
|||
Only one connection manager is used at a time. The [[Presence Service]] will |
|||
use Gabble when it has Internet access (a valid IPv4 address) and has connected |
|||
to a [[Jabber server]], otherwise Salut. |
|||
== Tubes == |
== Tubes == |
||
[[Tubes]] |
[[Tubes]] are a means for shared activities to exchange data. There are currently two types of tubes: |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* D-Bus Tubes |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* Stream Tubes |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
The [[Presence Service]] creates connection manager objects (Gabble and/or |
The [[Presence Service]] creates connection manager objects (Gabble and/or |
||
Salut). It gets a Connection object (to the [[Jabber server]] in the case of |
Salut). It gets a Connection object (to the [[Jabber server]] in the case of |
||
Revision as of 19:25, 27 March 2008
Overview
Collaboration in Sugar activities works using a set of services that run on the laptop, and APIs in the Sugar Python modules that wrap those services. The main services are the Telepathy connection managers and the Presence Service that coordinates them.
Telepathy is a system describing a generic interface for various kinds of communication. It is the underlying infrastructure used by Sugar for collaboration. Currently, two Telepathy implementations are used: Gabble, for Jabber, and Salut for serverless Jabber (a.k.a. link-local XMPP). The former is used when the school server is reachable; the latter in the simple mesh case.
Advertisements and invitations
Shared sugar activities are discovered in two different ways: through broadcast advertisements, and through invitations.
Advertisements are made when the user tells the activity to share itself with the entire network. Anybody on the network can see the activity.
Invitations are send to particular users. Only those users who are sent an invitation see the activity (unless the activity has also been advertised). When Sugar recevies an invitation, it asks the user whether they want to accept or reject it.
Tubes
Tubes are a means for shared activities to exchange data. There are currently two types of tubes:
- D-Bus Tubes provide a D-Bus bus service that is shared between the participants in a shared activity, providing signals to all participants, and methods called on a particular participant.
- Stream Tubes provide a socket-like connection set up via XMPP, for data streaming like HTTP, between two participants.
Using tubes in Sugar activities
The Presence Service creates connection manager objects (Gabble and/or Salut). It gets a Connection object (to the Jabber server in the case of Gabble). PS creates or gets a Tubes channel. For Python Activities, Sugar creates or joins a D-Bus tube automatically.
The initiator of the activity should then call Tubes.OfferDBusTube to offer a Tube with a specific service name. When a buddy joins an activity, he will try to figure out which Tubes are available by calling Tubes.ListTubes() on the tubes channel (which he doesn't have to create anymore). Both OfferDBusTube and ListTubes result in a callback when the Tube becomes really available. Only then a working Tube is handed to the (shared) activity and it is possible to export objects on that bus and subscribe to signals etc.
See Tubes Tutorial for more on using Tubes.
Who's who?
Buddies/nodes within an activity are currently identified with different handles by different components. The following handles can be distinguished:
- Dbus name. If you have a Dbus related function with the “sender” argument specified, this is what you'll get. To buddy object:
sugar.presence.PresenceService.get_buddy(buddy's public key)
- Telepathy handle. To buddy object:
sugar.presence.PresenceService.get_buddy_by_telepathy_handle(tp_conn, tp_conn_path, handle)