Pippy: Difference between revisions
m (+OBX pootle) |
(needs an intro) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
[[Image:Pippy.png|thumb|right|350px|The [[Pippy]] interface]] |
[[Image:Pippy.png|thumb|right|350px|The [[Pippy]] interface]] |
||
__TOC__ |
__TOC__ |
||
=Description & Goals= |
|||
===Summary=== |
|||
Teaches Python programming by providing access to a fully |
|||
interactive Python interpreter.? |
|||
The user can type simple expressions with some mathematical functions |
|||
and execute the expression. |
|||
This means that there is some overlap between Pippy and [[Calculate]]. |
|||
?? |
|||
===Goals=== |
|||
? |
|||
===Collaboration=== |
|||
? |
|||
= Examples = |
= Examples = |
||
Revision as of 06:02, 29 October 2007
see more templates or propose new |
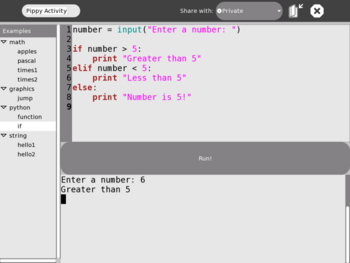
Description & Goals
Summary
Teaches Python programming by providing access to a fully interactive Python interpreter.?
The user can type simple expressions with some mathematical functions and execute the expression. This means that there is some overlap between Pippy and Calculate.
??
Goals
?
Collaboration
?
Examples
Please add examples here, or modify the existing ones!
Math
Apples
Author: Madeleine Ball
print "Let's do math!" print "On Monday I picked 22 apples. On Tuesday I picked 12." print "Now I have: ", 22 + 12 print "My brother says he picked twice as many apples last week." print "This means he picked: ", (22 + 12) * 2 print "I have 3 friends I would like to give apples." print "One third of my apples is about: ", (22 + 12) / 3 print "Or, more exactly: ", (22.0 + 12.0) / 3.0
Pascal
Author: Madeleine Ball
# Pascal's triangle
lines = 8
vector = [1]
for i in range(1,lines+1):
vector.insert(0,0)
vector.append(0)
for i in range(0,lines):
newvector = vector[:]
for j in range(0,len(vector)-1):
if (newvector[j] == 0):
print " ",
else:
print "%2d" % newvector[j],
newvector[j] = vector[j-1] + vector[j+1]
print
vector = newvector[:]
Sierpinski triangle
Author: Madeleine Ball
Modification of the Pascal's triangle program to produce Sierpinski triangles.
size = 5
modulus = 2
lines = modulus**size
vector = [1]
for i in range(1,lines+1):
vector.insert(0,0)
vector.append(0)
for i in range(0,lines):
newvector = vector[:]
for j in range(0,len(vector)-1):
if (newvector[j] == 0):
print " ",
else:
remainder = newvector[j] % modulus
if (remainder == 0):
print "O",
else:
print ".",
newvector[j] = vector[j-1] + vector[j+1]
print
vector = newvector[:]
Times1
Author: Chris Ball
for i in range(1,13):
print i, "x 4 =", (i*4)
Times2
Author: Chris Ball
number = input("Which times table? ")
for i in range(1,13):
print i, "x", number, "=", i*number
Fibonacci Series
Author : Rafael Ortiz
a, b = 0, 1
while b < 1001:
print b,
a, b = b, a+b
Pythagoras
Author : Rafael Ortiz
import math
from math import sqrt
print "This is the Pythagoras Theorem"
a=float(raw_input("Type a ="))
b=float(raw_input("Type b ="))
c=sqrt((a*a)+(b*b))
print "c =",c
Factorize
Author: Reinier Heeres
import math
import sys
orignum = input("Enter a number to factorize ")
factors = []
num = orignum
i = 2
while i <= math.sqrt(num):
if num % i == 0:
factors.append(i)
num /= i
i = 2
elif i == 2:
i += 1
else:
i += 2
factors.append(num)
if len(factors) == 1:
print "%d is prime" % orignum
else:
sys.stdout.write("%d is %d" % (orignum, factors[0]))
for fac in factors[1:]:
sys.stdout.write(" * %d" % fac)
print
Zeros of a second degree polynomial
Author: Pilar Saenz
import math
from math import sqrt
print "These are the zeros of a second grade polynomial"
a=float(raw_input("Type a ="))
b=float(raw_input("Type b ="))
c=float(raw_input("Type c ="))
aux=b*b-4*a*c;
if aux>0:
x1=(-b+sqrt(aux))/(2*a)
x2=(-b-sqrt(aux))/(2*a)
print "x1= " , x1 ,", x2=" ,x2
elif aux==0:
print "x= " , -b/(2*a)
else:
x1=(-b+sqrt(-aux)*1j)/(2*a)
x2=(-b+sqrt(-aux)*1j)/(2*a)
print "x1= " , x1 , ", x2" , x2
Factorial of a number
Author: Pilar Saenz
def factorial(a):
fac=a
for i in range(1,a):
fac=fac*i
print a,"!=",fac
a=int(raw_input("Type a="))
factorial(a)
Greatest common divisor
Author: Pilar Saenz
n= input("Enter a number ")
m= input("Enter another number ")
r=n%m
if r!=0:
while (r!=0):
n=m
m=r
r=n%m
print "The greatest common divisor is ", m
Python
Function
Author: Chris Ball
def square(x):
print x * x
square(3)
square(4)
If
Author: Chris Ball
number = input("Enter a number: ")
if number > 5:
print "Greater than 5"
elif number < 5:
print "Less than 5"
else:
print "Number is 5!"
Recursion
Author: Mel Chua
# Note this assumes you understand functions and if-else.
def countbackwards(number):
print "I have the number", number
if number > 0:
print "Calling countbackwards again!"
countbackwards(number-1)
else:
print "I am done counting"
number = input("Enter a number: ")
countbackwards(number):
While
Author Pilar Saenz
n=input("enter a number")
while n>0:
print n, " ",
n=n-1
print "Surprise!\n"
String
Hello1
Author: Chris Ball
print "Hello everyone!"
Hello2
Author: Chris Ball
name = raw_input("Type your name here: ")
print "Hello " + name + "!"
Graphics
Jump
Author: C. Scott Ananian
# both of these functions should be in the 'basic' package or some such
def clear_scr():
print '\x1B[H\x1B[J' # clear screen, the hard way.
def wait():
import time
time.sleep(0.1)
# jumping man!
# was having to escape the backslash which was rather unfortunate,
# now using python's r" strings which were meant for regex's
# i didn't have to do that in C64 BASIC
for i in xrange(0,50):
clear_scr()
print r"\o/"
print r"_|_"
print r" "
wait()
clear_scr()
print r"_o_"
print r" | "
print r"/ \"
wait()
clear_scr()
print r" o "
print r"/|\"
print r"| |"
wait()
clear_scr()
print r"_o_"
print r" | "
print r"/ \"
wait()
Games
Guess a number
Author: Pilar Saenz
import random
from random import randrange
R = randrange(1,100)
print "Guess a number between 1 and 100!!!"
N = input("Enter a number: ")
i=1
while (N!=R):
if N>R :
print "Too big... try again"
else :
print "Too small.. try again"
N = input("Enter a number: ")
i=i+1
print "You got it in ", i, "tries"