Pippy
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
see more templates or propose new |
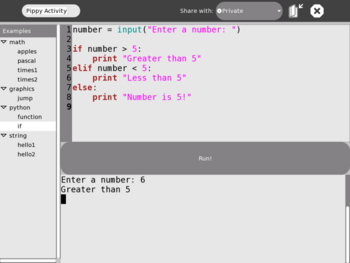
The Pippy interface
Examples
Please add examples here, or modify the existing ones!
Math
Apples
Author: Madeleine Ball
print "Let's do math!" print "On Monday I picked 22 apples. On Tuesday I picked 12." print "Now I have: ", 22 + 12 print "My brother says he picked twice as many apples last week." print "This means he picked: ", (22 + 12) * 2 print "I have 3 friends I would like to give apples." print "One third of my apples is about: ", (22 + 12) / 3 print "Or, more exactly: ", (22.0 + 12.0) / 3.0
Pascal
Author: Madeleine Ball
# Pascal's triangle
lines = 8
vector = [1]
for i in range(1,lines+1):
vector.insert(0,0)
vector.append(0)
for i in range(0,lines):
newvector = vector[:]
for j in range(0,len(vector)-1):
if (newvector[j] == 0):
print " ",
else:
print "%2d" % newvector[j],
newvector[j] = vector[j-1] + vector[j+1]
print
vector = newvector[:]
Sierpinski triangle
Author: Madeleine Ball
Modification of the Pascal's triangle program to produce Sierpinski triangles.
size = 5
modulus = 2
lines = modulus**size
vector = [1]
for i in range(1,lines+1):
vector.insert(0,0)
vector.append(0)
for i in range(0,lines):
newvector = vector[:]
for j in range(0,len(vector)-1):
if (newvector[j] == 0):
print " ",
else:
remainder = newvector[j] % modulus
if (remainder == 0):
print "O",
else:
print ".",
newvector[j] = vector[j-1] + vector[j+1]
print
vector = newvector[:]
Times1
Author: Chris Ball
for i in range(1,13):
print i, "x 4 =", (i*4)
Times2
Author: Chris Ball
number = input("Which times table? ")
for i in range(1,13):
print i, "x", number, "=", i*number
Fibonacci Series
Author : Rafael Ortiz
a, b = 0, 1
while b < 1001:
print b,
a, b = b, a+b
Pythagoras
Author : Rafael Ortiz
import math
from math import sqrt
print "This is the Pythagoras Theorem"
a=float(raw_input("Type a ="))
b=float(raw_input("Type b ="))
c=sqrt((a*a)+(b*b))
print "c =",c
Factorize
Author: Reinier Heeres
import math
import sys
orignum = input("Enter a number to factorize ")
factors = []
num = orignum
i = 2
while i <= math.sqrt(num):
if num % i == 0:
factors.append(i)
num /= i
i = 2
elif i == 2:
i += 1
else:
i += 2
factors.append(num)
if len(factors) == 1:
print "%d is prime" % orignum
else:
sys.stdout.write("%d is %d" % (orignum, factors[0]))
for fac in factors[1:]:
sys.stdout.write(" * %d" % fac)
print
Zeros of a second degree polynomial
Author: Pilar Saenz
import math
from math import sqrt
print "These are the zeros of a second grade polynomial"
a=float(raw_input("Type a ="))
b=float(raw_input("Type b ="))
c=float(raw_input("Type c ="))
aux=b*b-4*a*c;
if aux>0:
x1=(-b+sqrt(aux))/(2*a)
x2=(-b-sqrt(aux))/(2*a)
print "x1= " , x1 ,", x2=" ,x2
elif aux==0:
print "x= " , -b/(2*a)
else:
x1=(-b+sqrt(-aux)*1j)/(2*a)
x2=(-b+sqrt(-aux)*1j)/(2*a)
print "x1= " , x1 , ", x2" , x2
Factorial of a number
Author: Pilar Saenz
def factorial(a):
fac=a
for i in range(1,a):
fac=fac*i
print a,"!=",fac
a=int(raw_input("Type a="))
factorial(a)
Greatest common divisor
Author: Pilar Saenz
n= input("Enter a number ")
m= input("Enter another number ")
r=n%m
if r!=0:
while (r!=0):
n=m
m=r
r=n%m
print "The greatest common divisor is ", m
Python
Function
Author: Chris Ball
def square(x):
print x * x
square(3)
square(4)
If
Author: Chris Ball
number = input("Enter a number: ")
if number > 5:
print "Greater than 5"
elif number < 5:
print "Less than 5"
else:
print "Number is 5!"
Recursion
Author: Mel Chua
# Note this assumes you understand functions and if-else.
def countbackwards(number):
print "I have the number", number
if number > 0:
print "Calling countbackwards again!"
countbackwards(number-1)
else:
print "I am done counting"
number = input("Enter a number: ")
countbackwards(number):
While
Author Pilar Saenz
n=input("enter a number")
while n>0:
print n, " ",
n=n-1
print "Surprise!\n"
String
Hello1
Author: Chris Ball
print "Hello everyone!"
Hello2
Author: Chris Ball
name = raw_input("Type your name here: ")
print "Hello " + name + "!"
Graphics
Jump
Author: C. Scott Ananian
# both of these functions should be in the 'basic' package or some such
def clear_scr():
print '\x1B[H\x1B[J' # clear screen, the hard way.
def wait():
import time
time.sleep(0.1)
# jumping man!
# was having to escape the backslash which was rather unfortunate,
# now using python's r" strings which were meant for regex's
# i didn't have to do that in C64 BASIC
for i in xrange(0,50):
clear_scr()
print r"\o/"
print r"_|_"
print r" "
wait()
clear_scr()
print r"_o_"
print r" | "
print r"/ \"
wait()
clear_scr()
print r" o "
print r"/|\"
print r"| |"
wait()
clear_scr()
print r"_o_"
print r" | "
print r"/ \"
wait()
Games
Guess a number
Author: Pilar Saenz
import random
from random import randrange
R = randrange(1,100)
print "Guess a number between 1 and 100!!!"
N = input("Enter a number: ")
i=1
while (N!=R):
if N>R :
print "Too big... try again"
else :
print "Too small.. try again"
N = input("Enter a number: ")
i=i+1
print "You got it in ", i, "tries"