VistA Monograph Wiki
== Introduction ==
VistA AND HEALTHeVET-VistA
VA'S CURRENT AND FUTURE COMPUTERIZED PATIENT RECORD SYSTEM
'VistA'(Today)
The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has had automated information systems in its medical facilities since 1985, beginning with the Decentralized Hospital Computer Program information system, including extensive clinical and administrative capabilities. The Veterans Health Information Systems and Technology Architecture (VistA), supporting ambulatory and inpatient care, delivered significant enhancements to the original system with the release of the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) for clinicians in 1997. CPRS provides a single interface for health care providers to review and update a patient's medical record and to place orders, including medications, special procedures, x-rays, patient care nursing orders, diets, and laboratory tests. CPRS is flexible enough to be implemented in a wide variety of settings for a broad spectrum of health care workers and provides a consistent, event-driven, Windows-style interface.
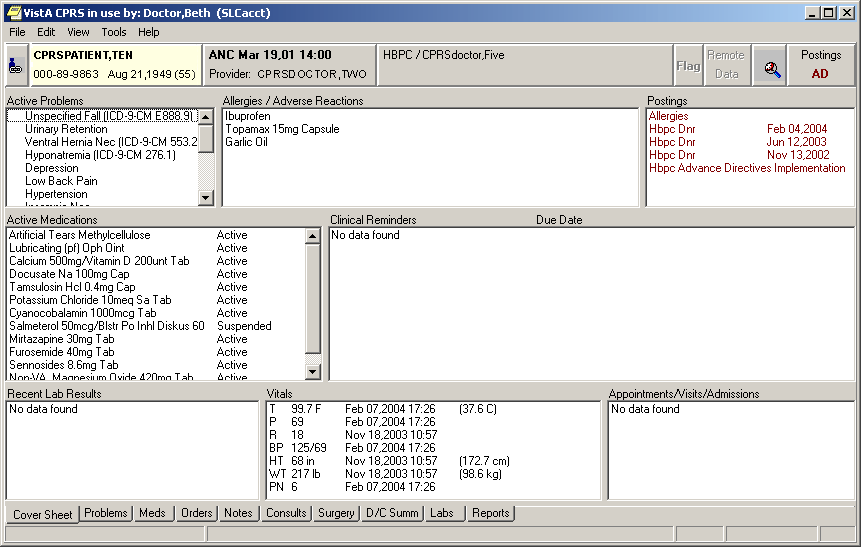
CPRS organizes and presents all relevant data on a patient in a way that directly supports clinical decision-making. The comprehensive cover sheet displays timely, patient-centric information, including active problems, allergies, current medications, recent laboratory results, vital signs, hospitalization, and outpatient clinic history. This information is displayed immediately when a patient is selected and provides an accurate overview of the patient's current status before clinical interventions are ordered. CPRS capabilities include:
- A Real-Time Order Checking System that alerts clinicians during the ordering session that a possible problem could exist if the order is processed;
- A Notification System that immediately alerts clinicians about clinically significant events;
- A Patient Posting System, displayed on every CPRS screen that alerts clinicians to issues related specifically to the patient, including crisis notes, warning, adverse reactions, and advance directives;
- The Clinical Reminder System that allows caregivers to track and improve preventive health care for patients and ensure timely clinical interventions are initiated.
- Remote Data View functionality that allows clinicians to view a patient's medical history from other VA facilities to ensure the clinician has access to all clinically relevant data available at VA facilities.
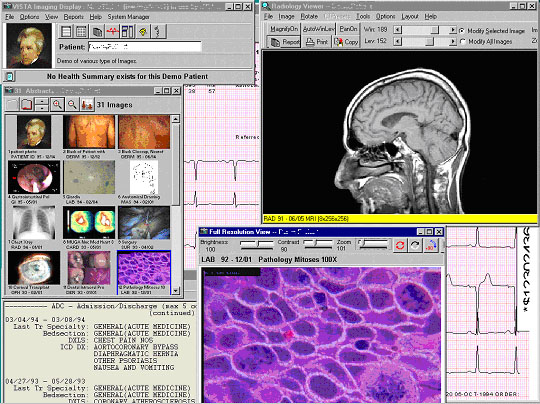
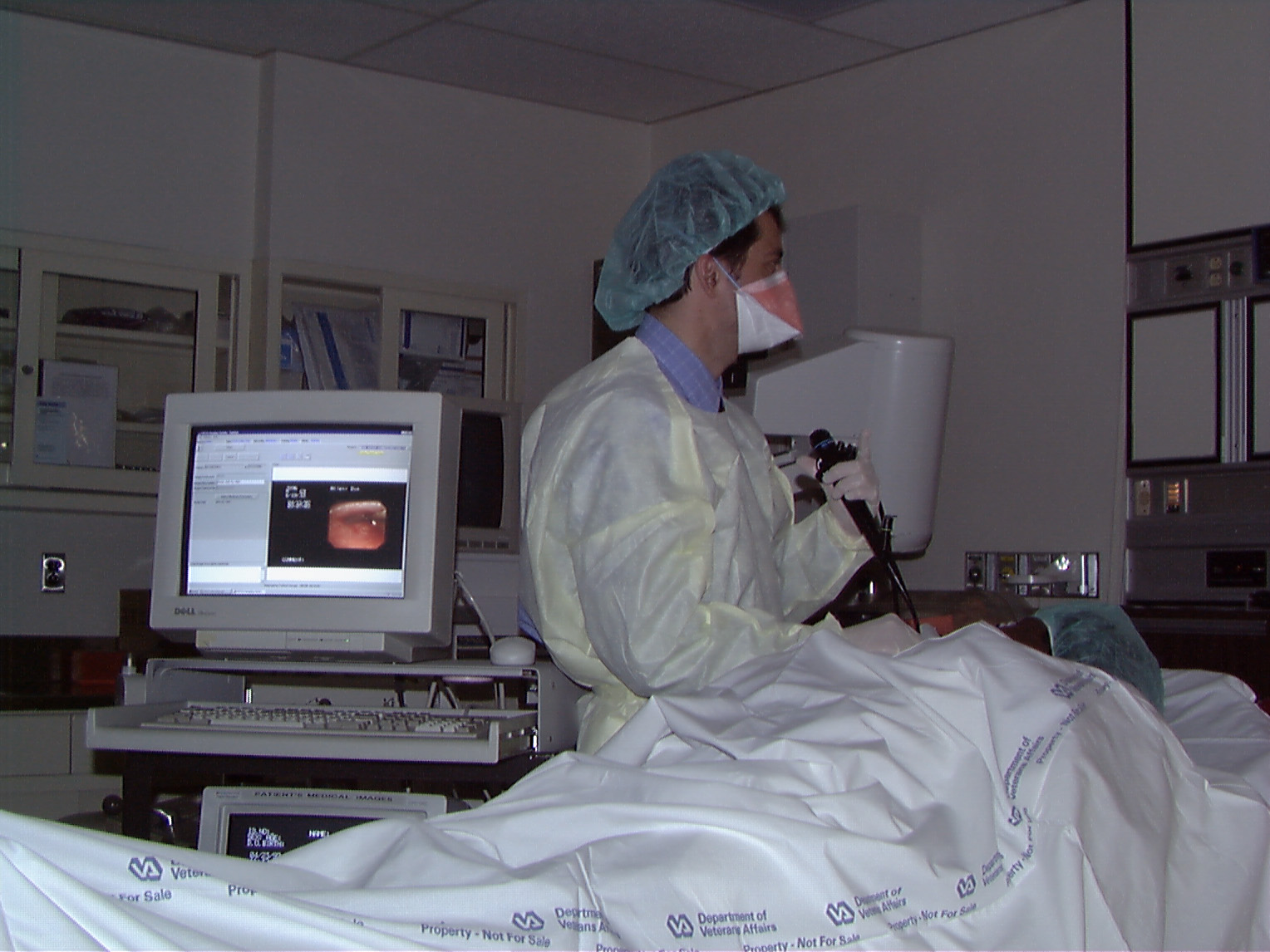
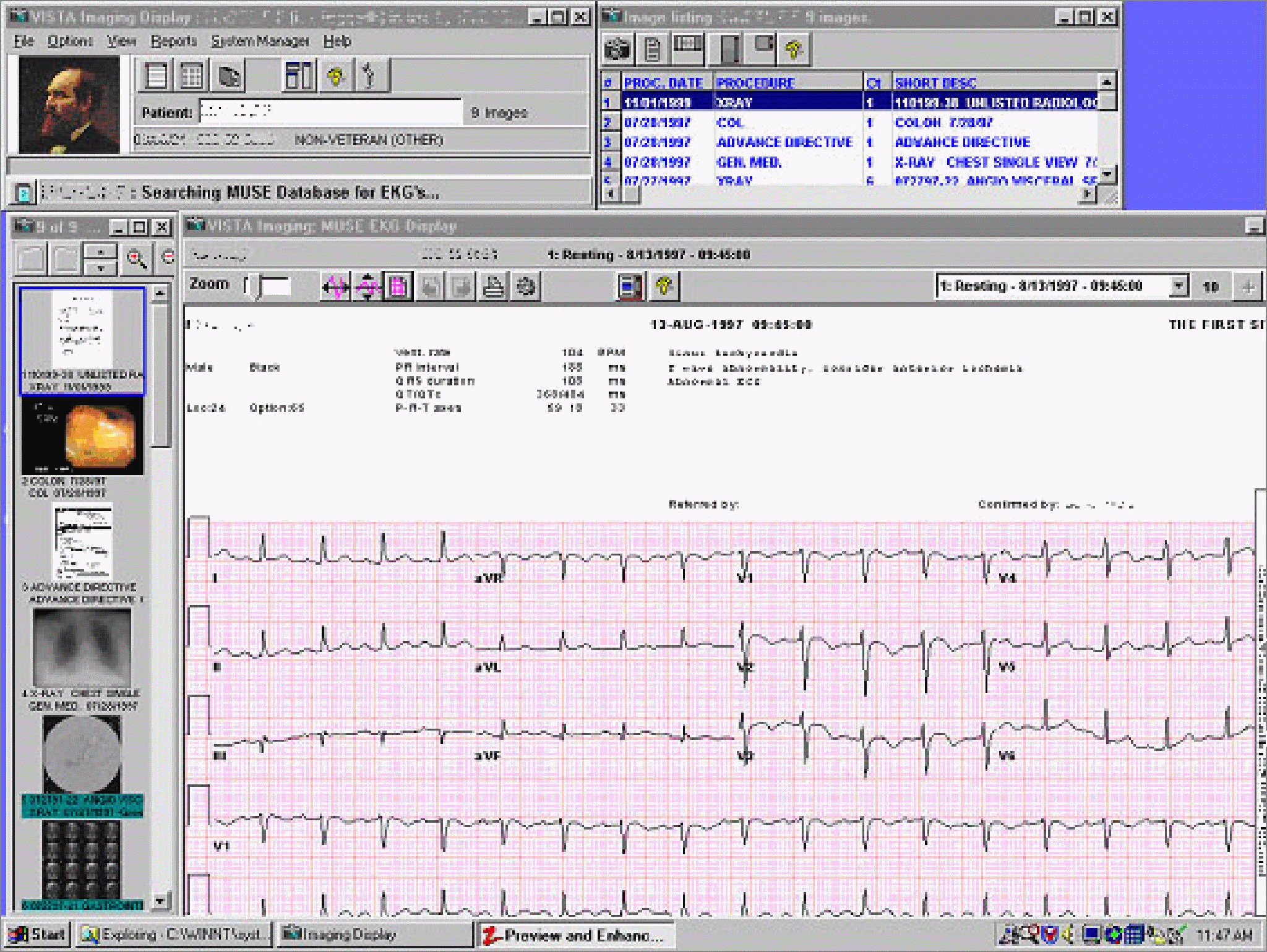
VistA Imaging is also operational at most VA Medical Centers. VistA Imaging provides a multimedia, on-line patient record that integrates traditional medical chart information with medical images, including x-rays, pathology slides, video views, scanned documents, cardiology exam results, wound photos, dental images, endoscopies, etc. into the patient record.
Bar Code Medication Administration addresses the serious issue of inpatient medication errors by electronically validating and documenting medications for inpatients. It ensures that the patient receives the correct medication in the correct dose, at the correct time, and visually alerts staff when the proper parameters are not met.
HealtheVet Desktop is an application framework that will host the new generation of Veterans Health Administration (VHA) clinical applications. Care Management is the first application to run on the new HealtheVet Desktop and is an enhancement of CPRS designed to assist health care providers to follow-up on clinical interventions that might otherwise be missed. Care Management provides an automated method for tracking follow-up actions/tasks for a panel of patients for a designated period of time. The four perspecitives of Care management are the Clinician Dashboard, the Nursing Dashboard, the Query Tool and the Sign List. Implementation of the Care Management project will improve patient care by:
- Ensuring that appropriate clinical interventions are provided on a timely basis;
- Ensuring that clinical notifications are processed on a timely basis;
- Reducing the amount of time primary care providers spend reviewing individual patient records; and
- Reducing the risk of erroneous data entry
HealtheVet-VistA (Future)
A strategy has been developed to move the Veterans Health Information Systems toward �€œHealtheVet,�€ an ideal health information system to support the ideal veterans health system. Collaboratively among the Department, field, and central office leadership and the Chief Information Officer, a proposed strategy has been developed for both VA and Veterans Health Administration needs. The strategy is built around five major systems and integrates five cross-cutting issues:
- The Health Data System [health data repository (HDR)] will create a true longitudinal health care record including data from VA and non-VA sources. The health data system will support research and population analyses, facilitate patient access to data and sharing of information across VHA, and improve data quality and data security.
- Provider Systems support healthcare providers' care for veterans and feed information to VistA today and the HDR in the future. These include CPRS, VistA Imaging, Blood Bank, Pharmacy, Laboratory, Federal Health Information Exchange (FHIE), and Scheduling.
- Management/Financial Systems include four applications that are each ten or more years old and will be replaced: the Financial Management System, Billing and Accounts Receivable (AR), and Fee Basis (paying providers).
- Information and Education Systems with an emphasis on �€œeHealth�€ include prescription refills, appointments, fillable forms online, and My HealtheVet (access to health record, on-line health assessment tools; and high quality health information).
- Registration, Enrollment, and Eligibility Systems will be developed as a single, department-wide data system and demographic database that supports registration and eligibility for the three Administrations and makes this information more accessible and consistent.
- Cross-Cutting Issues include the VA and VHA architectures, information security, data quality, and leadership and management. These issues cut across all systems and ensure effective implementation and operations of the major systems.
Graphical Illustration of the HealtheVet �€" VistA Strategy
(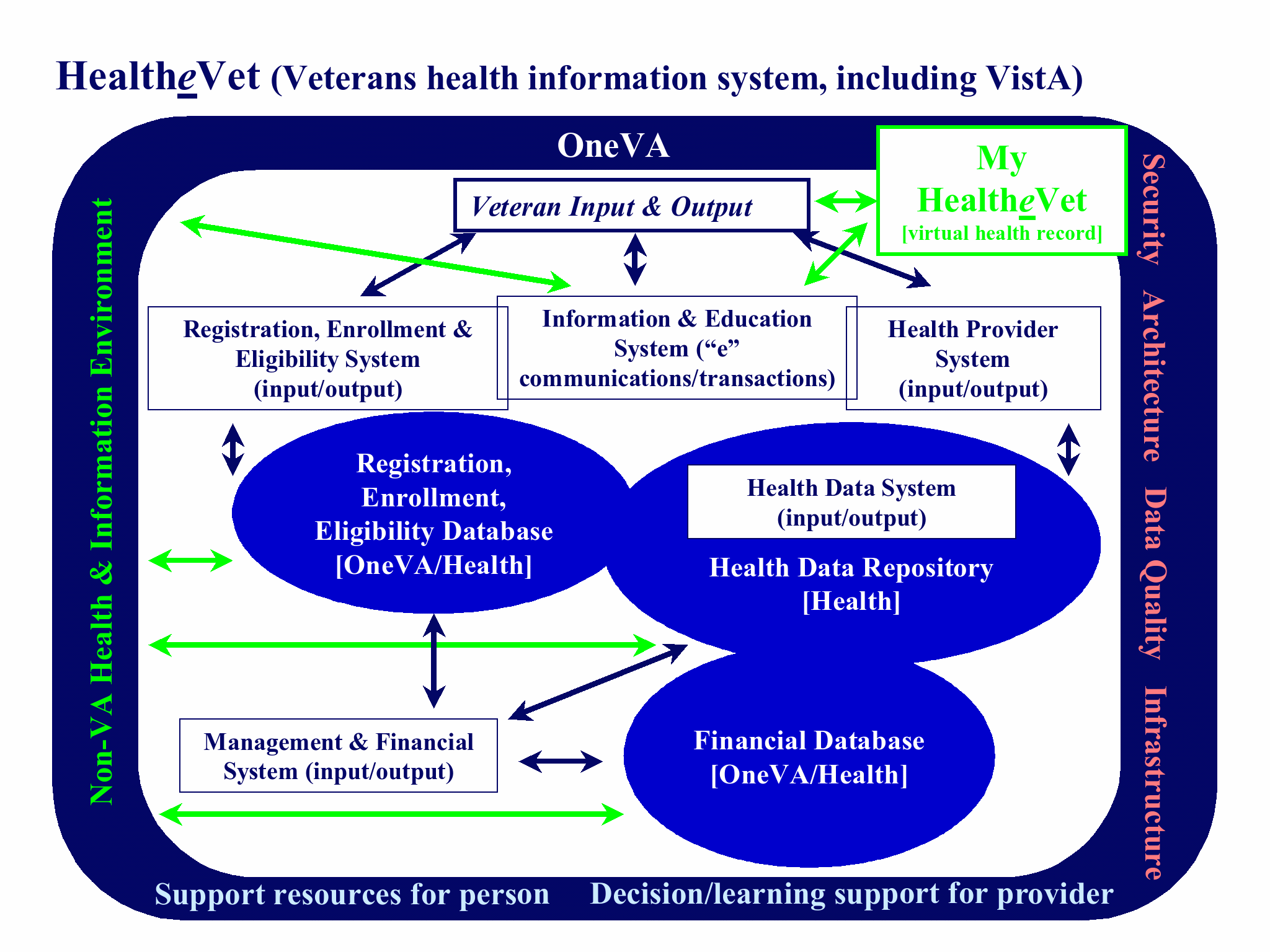
Veterans Health Information System, including VistA)
VistA SOFTWARE PACKAGES
Health Data Systems
The Health Data Repository (HDR) is the cornerstone of the Health Data Systems (HDS) portfolio. The HDR will serve as an operational clinical repository�€"a collection of clinical information, from VA and non-VA sources, residing on one or more independent platforms�€"to be used by clinicians and other personnel to facilitate longitudinal, patient-centric care. Data in the HDR will be organized in a format supporting the delivery of care regardless of the physical location of a patient's clinical information. The HDR will provide additional significant benefits including providing information to support research and population analyses, facilitating patient access to data and sharing information across VHA, improving data quality and data security, and reducing the burden on local VistA systems.
Automated Medical Information Exchange (AMIE)
Overview
The Automated Medical Information Exchange (AMIE) module facilitates the electronic interchange of veteran information between Veteran Benefits Administration (VBA) Regional Offices (ROs) and VA medical facilities. The comprehensive module provides an accurate audit trail to track most requests for information.
The module is composed of two components: Facility administrative options and VBA Regional Office options. Each area has individual items to maintain daily, and its own reports to print. RO staff access VA medical facility computers through VA national telecommunications network, and exercise their options on each local medical facility's system as necessary.
Features
- Provides access to local databases for identification of a veteran's admission, discharge, outpatient treatment, patient care, and other information that may require adjudicative actions.
- Reduces overpayments previously caused by lost, misrouted, or improperly processed admission notifications.
- Provides on-line status determinations of pending compensation and pension examinations (requesting, scheduling, tracking, and updating results).
- Provides RO on-line access to the local databases for the confirmation of the propriety of payments based on hospitalization.
- Improves timeliness of the RO benefits adjustment processing.
- Allows medical centers to electronically access sections of the Physicians Guide for Disability Evaluation Examinations.
- Provides tracking of insufficiently completed compensation and pension examinations.
Incident Reporting
Overview
The Incident Reporting module supports VHA policy by compiling data on patient incidents. It organizes the data into defined categories for reporting and tracking at medical facility level and for transmission to the National Quality Assurance Database for Headquarters review and tracking.
Features
- Provides options to simplify the setup of the software.
- Allows for the entry of all required incident information plus descriptive data and actions taken on all reportable and/or locally defined incidents.
- Prints out a Pseudo 10-2633 Incident Worksheet.
- Provides an ad hoc reporting mechanism that uses VA FileMan modifiers for sorting or printing the following data fields:
Patient Type of Death
Patient ID Level of Review
Date of Admission Date of Incident
Patient Type Incident Case Status
Ward/Clinic Severity Level
Treating Specialty Fall Assessment Score
Service Person Reporting the Incident
Responsible Service Patient Diagnosis
Medication Errors Medical Center Action
Case Number Incident Description
Incident Pertinent Information
Incident Location National Case Status
Lexicon Utility
Overview
The adoption of a standardized reference for clinical terminology across VHA enables clinical information to be recorded, transmitted, retrieved, and analyzed in a precise manner independent of clinic or medical center.
The scope of the Lexicon Utility is to express diagnostic clinical problems in easy-to-understand terminology and associate these terms to coding systems such as ICD, DSM, NANDA, etc. It works in conjunction with VistA applications such as Problem List, Encounter Form, and Text Integration Utility (TIU) and provides a comprehensive API so that any application that needs to use standardized terminology can be interfaced.
Features
- Provides a basis for a common language of terminology so that all members of a health care team can communicate with each other.
- Provides terminology that is well defined, understandable, unique in concept, and encodable by multiple coding schemes.
- Provides for site modification of text presentation, term definitions, synonyms, shortcuts, and keywords.
- Provides the ability to upgrade coding systems (e.g., ICD-9-CM to ICD-10) and to add, change, and delete codes.
- Provides for limited views of vocabulary (lexicon subsets).
- Allows each site to add its own vocabulary to the lexicon.
- Accepts the provider terminology if a search of the dictionary does not find a match.
- Uses subsets of terms based on specialty or clinic.
- Allows abbreviations or shortcuts to provide quick access to frequently used definitions.
- Supports CPT terminology and codes.
Occurrence Screen
Overview
The Occurrence Screen module supports VHA policy by providing for the identification of events requiring follow-up review. It generates worksheets used by clinical, peer, management, and committee-level reviewers and identifies practitioner, systems, and equipment-related problems and results. The program enables medical facilities to define site-specific screens and to track events associated with them.
Features
- Provides automatic identification of patients for the following occurrences:
- Readmission within 10 days
- Admission within three days following unscheduled Ambulatory Care visit
- Return to operating room in same admission
- Death anywhere in medical facility, except DNR (Do Not Resuscitate)
- Allows for quick entry of exceptions.
- Provides a tracking and reporting system (ad hoc) for all screens.
- Produces worksheets for clinical, peer, management, and committee-level review.
- Tracks patient occurrences through peer and management-level reviews to final disposition.
- Relates quality of patient care with provider-specific information.
- Tracks problems by provider, systems, and equipment.
- Provides required Summary of Occurrence Screening.
- Compiles numerous reports, including:
- Occurrences by Service
- Review Level Tracking
- Patients Awaiting Clinical Review
- Delinquent Reviews
- Adverse Findings
- System/Management/Equipment Problems
- Occurrence Screen Service Statistics
- Ad Hoc Reports
Patient Representative
Overview
The purpose of the Patient Representative module is to ensure that VA medical facilities respond to patient needs. The software tracks and trends compliments and complaints and measures the facility's types of complaints as they relate to the Customer Services Standards and the National Patient Satisfaction Survey. This package supports the Patient Advocate with the collection and categorization of complaints and compliments that give the medical center an opportunity to meet and exceed the customer's expectations. The issue codes provide the opportunity to track types of complaints and provide trends of specific complaints. Included within the issue codes are the Customer Service Standards. A recent reliability study of the codes has revealed an exceptionally high reliability in the selection of appropriate codes. To help with improving perceptions, the tracking program can also extract data specific for women veterans by eras of service (i.e., Gulf War, Vietnam) as well as clinic, product line, or services.
Features
- Entering and editing contact information.
- Sending Reports of Contact via the Alert system.
- Tracking contacts that have responses due.
- Printing various lists, statistical reports, and ad hoc reports.
Registration, Enrollment, and Eligibility Systems
Registration, Eligibility, and Enrollment Systems will be developed as a single, department-wide data system and demographic database that support registration and eligibility for the three Administrations and make this information more accessible and consistent.
- Strong VHA and OneVA component
- OneVA building common system and demographic database supporting registration and eligibility
- VHA management of companion VHA registration, enrollment, and eligibility through National Health Demographic Database
Admission, Discharge, Transfer (ADT) /Registration
Overview
The Admission, Discharge, Transfer (ADT) module provides a comprehensive range of software dedicated to the support of administrative functions related to patient admission, discharge, transfer, and registration. The functions of this package apply throughout a patient's inpatient and/or outpatient stay, from registration, eligibility determination and Means Testing through discharge with on-line transmission of Patient Treatment File (PTF) data to the Austin Automation Center. The ADT software also aids in recovery of cost of care by supplying comprehensive PTF/RUG-II and Means Test software.
The ADT module functions as the focal collection point of patient information, encompassing demographic, employment, insurance, and medical history data. Many other modules, such as Laboratory, Pharmacy, Radiology, Nursing, and Dietetics, utilize information gathered through the various ADT options.
Several features have been designed to maximize efficiency and maintain control over user access of specified sensitive patient records. The Patient Sensitivity function allows a level of security to be assigned to certain records within the database (i.e., records of employees, government officials, etc.) in order to maintain control over unauthorized user access. The Patient Lookup function screens user access of these records. It also provides for efficient and faster retrieval of patient records and identified potential duplicate patient entries.
The ADT module allows for efficient and accurate collection, maintenance, and output of patient data, thus enhancing a health care facility's ability to provide quality care to its patients.
The functions within ADT currently fall into seven major categories: Application Processing (registration), Bed Control (inpatient movements), Inpatient Care Grouping (DRG)/Long Term Care Grouping (RUG), Data Transmission to National Database (PTF and RUG), Patient Assessment Instrument (PAI), Supervisor Functions (system setup and maintenance), and Local/National Management Reporting.
Features
- Provides on-line patient registration and disposition of applications for medical care.
- Tracks patient movements during inpatient stays.
- Provides up-to-date on-line patient information.
- Generates numerous managerial and statistical reports.
- Performs patient data consistency checks.
- Supports the flagging and monitoring of patient records deemed to be sensitive.
- Enrolls patients in the VA Patient Enrollment System during the registration process.
- Uses industry standard International Classification of Diseases (ICD)/Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes.
- Aids in cost recovery of care by supplying comprehensive PTF/RUG-II, Means Test, and pharmacy copay software.
Clinical Monitoring System
Overview
The Clinical Monitoring System allows the user to design monitors that capture patient data in support of quality management efforts. In most cases, patient data is automatically captured from the existing database and this module allows manual entry of patients into the database for tracking specific events. Statistical data is kept for the number of patients scanned and the number that meet the monitor's criteria, which allows for the trending of data over a user-selected timeframe (daily, weekly, monthly, etc.).
Features
- Enrolls from database, patients/events as defined by each monitor.
- Allows groups of similar items to be scanned as a whole (e.g., ward group, service group, admission type group).
- Allows for manual enrollment of patients/events.
- Warns the user, via MailMan bulletins, when alert levels are reached or time frames are ended.
- Allows comparison of totals for specific time frames.
- Labels each monitor as High Volume, High Risk, Problem Prone, or Other, and allows for further description.
- Allows for entry of a standard of care associated with each monitor.
- Provides for an ad hoc reporting mechanism.
- Provides site parameters allowing Information Resources Management (IRM) staff to control the manual running of the auto enroll function.
Enrollment Application System (EAS)
Overview
Enrollment Application System (EAS) is currently a single module application. It facilitates the processing of a 10-10EZ Application for Health Benefits, which has been transmitted to the VHA site from the On-Line 10-10EZWeb-based software.
This 10-10EZ module allows site staff with enrollment and registration responsibilities to review all data entered by a veteran on the electronic 10-10EZ form before committing the data to the site database. It also provides a basic tracking mechanism in order to follow the progress of the veteran's application and respond to inquiries.
Features
- Automatically receives incoming 10-10EZ data transmissions from the Web-based application into a VistA holding file.
- Provides a List Manager interface that allows the enrollment/registration staff to:
- Match the Applicant with an existing Patient record when appropriate.
- Review all 10-10EZ data and perform corrections as needed.
- Print the 10-10EZ form with data in order to send to the veteran for signature.
- Verify that the veteran has signed the 10-10EZ.
- Commit the 10-10EZ data to the VistA Patient database in preparation for further enrollment and/or registration activities.
- Respond to customer (e.g., veteran) inquiries as to the status of a 10-10EZ Application.
- Provides an audit trail of all significant actions performed in processing a 10-10EZ Application as a basis for management reports.
- Retains a copy of any original Patient database data elements overwritten by incoming 10-10EZ data elements.
Hospital Inquiry (HINQ)
Overview
The Hospital Inquiry (HINQ) module provides the capability to request and obtain veteran eligibility data via the VA national telecommunications network. Individual or group requests are sent from a local computer to a remote Veterans Benefits Administration (VBA) computer where veteran information is stored. The VBA network that supports HINQ is composed of four computer systems located in regional VA payment centers.
HINQ interfaces with other modules to allow users to make eligibility requests. An on-line suspense file stores requests for later transmission and records HINQ responses, thus creating a log of HINQ activity.
The HINQ module provides facilities with the ability to obtain veteran eligibility information quickly, accurately, and efficiently, allowing medical center personnel to act expeditiously on patient requests for medical treatment and other benefits.
Returned HINQ data may be loaded directly into the local Patient file through various screens. The screens display both the data in the HINQ message and what is currently in the Patient file for comparison.
Features
- Sends on-line requests individually and forwards multiple requests in batch mode.
- Tracks and updates requests.
- Establishes real-time links between VHA and VBA computers to service time-of-the-essence requests.
- Processes routine requests in background, allowing requesters to perform other tasks.
- Alerts requesters when responses are received from VBA computers.
- Alerts requesters when there is a discrepancy found between the returned HINQ information and what is in the Patient file.
- Provides the capability to update returned HINQ data directly into the Patient file.
Income Verification Match (IVM)
Overview
The Income Verification Match (IVM) module is designed to extract patient-reported Means Test data and transmit it to the Health Eligibility Center (HEC) located in Atlanta, Georgia. IVM allows Veterans Health Administration (VHA) to accurately assess a patient's eligibility for health care when the eligibility criterion is income-based.
IVM electronically transfers patient income and demographic data for eligible veterans whose VA health care is based on income and for whom a Means Test has been completed. It also sends automatic updates if pertinent patient data is edited at the medical center.
As part of this process, HEC compares the extracted data with earned and unearned income data retrieved from Social Security Administration (SSA) and Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Patients with reported income in the mandatory category, but whose actual income has been proven to be above that level, will have their eligibility for health care changed to the discretionary category and are subject to back billing.
The HEC sends the updated demographic and insurance information to the medical facilities for upload. The IVM module allows the HEC data to be compared with locally collected data and selectively uploaded. An invoice is then generated by MCCR to insurance companies for patients who had not previously reported health insurance coverage. Updated and verified income information from the HEC is automatically uploaded upon receipt at each VA facility, which updates the veteran's eligibility for health care and creates co-payment charges for previous episodes of care.
The software provides inquiries and reports that track all IVM activity.
Features
- Transmits data for basic demographics, next-of-kin, income, temporary address, eligibility, guardian, and employer information to the HEC for patients who meet the IVM criteria. Automatically transmits an updated message if this information is changed.
- Allows the HEC to query the medical facility for the most up-to-date patient information.
- Allows updated demographic and insurance information from the HEC to be uploaded into the patient's record.
- Automatically loads updated income information from the HEC and updates the veteran's eligibility for health care.
- Allows generation of status inquiries, statistical Means Test, and data transmission reports.
Record Tracking
Overview
The Record Tracking module provides for the maintenance and control of medical records and x-ray films to facilitate availability to a variety of users. The system offers a wide range of individual site-definable parameters such that it may be custom- tailored to specific needs and used in any type of file setting. The Record Tracking module is integrated with other associated modules such as Radiology and Patient Information Management System.
The module automates file room functions in support of the following activities. The module also supports requisitioning activities for individual records within a facility and between facilities, including:
- Creation of new records/volumes
- Charge-out/check-in of records
- Inactivation/reactivation and deletion of records
- Printing of bar code labels
- Transfer of records to other facilities
- Recharging records to other borrowers
- Flagging a record as missing
- Record retirement
Features
- Uses bar code technology, prints bar code labels for the charts, and uses bar code equipment to charge records.
- Displays informational bulletins when a record is checked into a file room. Bulletins may include the following information: pending requests for the record, the record has previously been flagged as missing, loose filing exists, the patient is currently an inpatient, or the record is being checked into a file room other than its home.
- Offers a complete system for maintenance and control of records that may be used with ease in any type of file setting.
- Produces a variety of reports associated with the module that may be used to assist management in workload analysis and control of records.
- Creates pull lists to provide requests for records in conjunction with clinic scheduling and record retirement.
Resident Assessment Instrument/Minimum Data Set (RAI/MDS)
Overview
The Resident Assessment Instrument/Minimum Data Set (RAI/MDS) provides a standardized assessment tool supporting the completion of a comprehensive, accurate, and reproducible patient assessment, and serves as the basis for developing the patient's plan of care.
The RAI/MDS aligns the VA's data collection processes with private sector skilled nursing facilities. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and the States require that long-term care facilities implement the RAI/MDS in order to receive Medicare and/or Medicaid reimbursement. Use of the RAI/MDS in VA long-term and Nursing Home Care Unit programs provides a structure for meeting JCAHO long-term care accreditation standards. It also provides opportunities for data comparison of patient outcomes within and across VA and with non-VA long-term care and/or nursing home programs.
The VA purchased the Accu-Med Services (AMS) Clinical Software suite, which has been implemented nationally, with a gateway interface to import patient data from VistA using standard HL7 messaging. The Clinical Software suite consists of the Minimum Data Set (MDS) Version 2.0 as defined by CMS, Resident Assessment Protocols (RAPs) triggered by specific responses to the MDS, multidisciplinary Care Plans, and electronic transmission of the MDS to the national database at the Austin Automation Center (AAC). The AAC in turn utilizes the MDS to produce Resource Utilization Groups (RUG-III) and Quality Indicator reports.
Features
- Admissions module with display of demographic and patient movement information interfaced from VistA using standard HL7 messaging.
- Assessments module based on the MDS Version 2.0, a core set of preliminary screening and assessment elements including common definitions and coding categories.
- Specific responses to MDS questions trigger one or more of eighteen potential problem areas�€"known as Resident Assessment Protocols�€"identifying residents who have, or are at risk for developing, specific functional problems.
- Triggered RAPs signal the need for additional assessment and evaluation using RAI guidelines as defined by CMS. RAP summary notes are used to document analysis of the assessment findings and identify resident problems, some of which may be reversible.
- Resident Care Plan and Report Writer modules.
- Electronic signature and electronic transmission of assessments to AAC.
- Audit controls for HIPAA privacy and security compliance.
- Integration Gateway with HL7 standard messaging and monitoring tools.
- MDS 2.0 with Version 1.2 data specifications and fatal error checks.
- Contains complete on-line help manuals for all modules of the CMS RAI/MDS manual.
Veteran Identification Card (VIC)
Overview
The Veteran Identification Card (VIC) replaces the embossed data card as a means of identifying veteran patients entitled to care and services at Veterans Affairs (VA) health care facilities.
The replacement VIC displays a larger color photograph of the veteran and the veteran's name. There is no embossed information on the card. A VistA print option provides labels with the patient's identifying information. The labels can be affixed to medical record forms in lieu of using the embossed cards to imprint this information when pre-printed forms are not available.
A color photograph of the veteran is taken at the local medical center using the Patient Image Capture Software (PICS) on a Clinical Context Object Workgroup (CCOW) enabled workstation. The photograph is sent to the local VistA Imaging server, making it available to the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) and other VistA applications. The photograph and VistA patient data is also transmitted to the National Card Management Directory (NCMD) in Silver Spring, MD (a repository of VIC data). Once the Health Eligibility Center (HEC) has verified the patient's eligibility, the veteran has been assigned an appropriate enrollment status, and also assigned a national Integration Control Number (ICN), the VIC data and images are transmitted to the external card vendor using secure protocols. The external card vendor creates the VIC cards and mails them to the veterans. For homeless veterans, the external card vendor mails the cards to the appropriate medical center, which then issues the cards to those veterans.
Features
- Veteran's picture, name, and care type (i.e., service connected) on card face.
- Magnetic stripe on card encoded with the patient's name, social security number, date of birth, sex, patient type, veteran status, and service-connected indicator.
Health Provider Systems
Health Provider Systems are information systems supporting health care providers in the care of veterans by feeding information to main systems such as VistA today and the Health Data Repository (HDR) in the future. Key HPS systems include:
- VistA Imaging
- Blood Bank
- Pharmacy
- Laboratory Services
Care Management
Overview
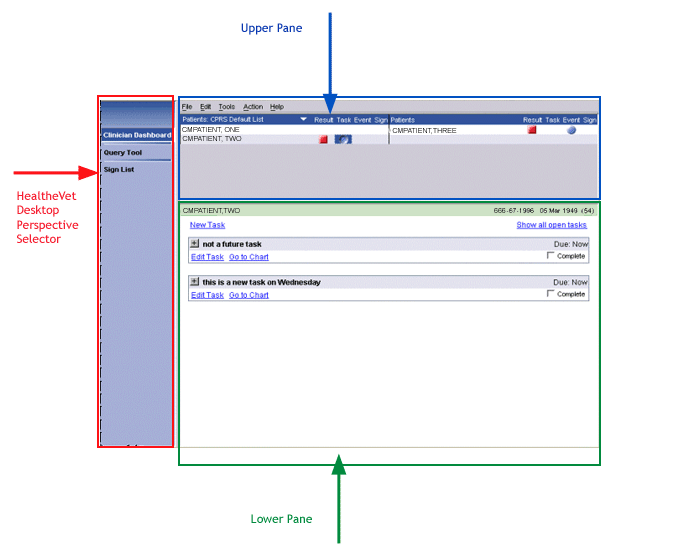
Care Management is the first application to run within the HealtheVet Desktop (the VHA's new Java application framework) and the first to offer a convenient way for healthcare providers to view on a single screen pertinent information about multiple patients. With Care Management, users can see at a glance multiple patients for whom they have items that require attention. The current distribution of Care Management offers the following four perspectives (which are similar to applications):
- Clinician Dashboard�€"Provides an easy-to-read table of patients for whom clinicians have unacknowledged results or event notifications (such as hospital admissions, discharges, or unscheduled clinic visits), unsigned documents, or uncompleted tasks.
- Nurse Dashboard�€"Provides an easy-to-read table of patients for whom nurses have unacknowledged results, unviewed events, uncompleted tasks or text orders, unverified orders, or recent vitals.
- Query Tool�€"Enables authorized users to create reports based on the most current patient data available. The Query Tool offers five pre-defined reports and also enables users to create their own customized reports.
- Sign List�€"Enables users to sign multiple items for multiple patients. For example, using the Sign List, a clinician can sign a discharge summary for John Smith and notes for Jane Smith simultaneously.
This distribution of Care Management also includes the Task Editor, which enables users to create patient-related tasks.
Features
Care Management comprises an extensive set of features designed to simplify and improve patient care.
These features include (but are not limited to) the following:
- Colored-coded icons that indicate the priority status of dashboard items
- A default patient list that is based on users' Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) default patient list
- A dynamically generated, user-based patient list
- Custom patient lists
- Checkboxes for acknowledging and verifying individual or multiple dashboard items
- The ability to set date ranges for dashboard items
- The ability to link tasks to other tasks or to events
- The ability to prioritize, edit, and delete tasks
- Text boxes that expand to provide detailed information about dashboard items
- A variety of predefined reports, including the following:
- Abnormal Results
- Consult Status
Care Management �€" continued
- Incomplete Orders
- Recent Activity
- Scheduled/Due Activity
- Custom reports with a wide selection of criteria, including (but not limited to) the following:
- Screen by Inpatient, Outpatient, or Pharmacy Visits
- Screen by Primary Outpatient Provider
- Orders/Results
- Consults/Procedures
- The ability to print and export reports
Care Management is tightly integrated with CPRS. As a result, from within Care Management, users can:
- Go directly to a patient's chart in CPRS
- Clear selected result notifications in CPRS, including notifications in the following categories:
- Events
- Results
- Actions
Care Management's intuitive Graphical User Interface (GUI) includes an extensive selection of clickable items from which users can:
- Select a default perspective
- Select dashboard preferences
- View demographic information for individual patients
- View details about specific action items
- And much more
Care Management �€" continued
Care Management Clinician Dashboard running in the HealtheVet desktop.
Clinical Procedures
Overview
Clinical Procedures (CP) passes final patient results, using Health Level 7 (HL7) messaging, between vendor clinical information systems (CIS) and VistA. Patients' test results or reports are displayed through the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS). The report data is stored on the Imaging Rapid Application Interface Development (RAID) and, in some instances, discrete data is stored in the Medicine package.
CP works with the Consult/Request Tracking, Text Integration Utility (TIU), CPRS, Patient Care Encounter (PCE), and VistA Imaging packages. In conjunction with CPRS, CP also provides a method for clinicians to document findings and to complete final procedure reports generated by medical devices. There are no specific procedures tracked through this application, nor are management workload reports generated. Links to dSs and other databases through PCE are supported through existing pathways in appropriate VistA applications. The CP functionality is not available in the List Manager (LM) version of CPRS.
CP provides features that can be used across clinical specialties such as Medicine, Women's Health, Surgery, Dental, Rehabilitation Medicine, and Neurology. Its functionality supports clinical practice in all patient care settings including clinics, Home Based Health Care (HBHC), and in-patient units.
Features
- Allows clinicians to enter, review, interpret, and sign CP orders through one application, CPRS.
- Accepts a variety of file types for result report files.
- Allows images to be acquired, processed, stored, transmitted, and displayed by the VistA Imaging package.
- Defines the Hospital Location where the procedure is performed. This location determines which Encounter Form is presented to the end user.
- Electronic transfer of patient reports from medical devices to VistA.
- Bi-directional interface capabilities.
- Easy to use user interfaces, including CP Manager, CP User, and CP Gateway.
- Improved internal communication between the proceduralist and the primary care physician.
- Improved patient education through use of reports.
- Improved medical record keeping.
Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS)
Porting to OLPC XO
There are several options for Porting Clients to the XO
Alternative OpenVista CIS
OpenVista CIS is a rewrite of CPRS in C#, using GTK# as the UI toolkit. It is freely available under the MSPL.
I don't know if the MSPL conflicts with the OLPC Project_hosting agreement.
At the recent Community Meeting I heard the Medsphere was going to relicense under the GPL. Does that apply to this software?
Are the licenses for C# and GTK# compatible with the OLPC requirements?
I'm going to ask the OLPC folks take a look at this issue.
Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) continued
Overview
CPRS enables clinicians to enter, review, and continuously update all order-related information connected with any patient. With CPRS, you can order lab tests, medications, diets, radiology tests and procedures, record a patient's allergies or adverse reactions to medications, request and track consults, and enter progress notes, diagnoses, and treatments for each encounter, and enter discharge summaries. Close integration with the Clinical Reminders and Text Integration packages allows better record keeping and compliance with Clinical Guidelines and medical record requirements.
CPRS not only allows hospital personnel to keep comprehensive patient records, it also enables clinicians, managers, and QA staff to review and analyze the data gathered on any patient in a way that directly supports clinical decision-making.
Features
Improves the efficiency of entering orders, progress notes, encounter data, and other clinical information in the patient chart and helps clinicians comply with legislative mandates and clinical practice guidelines, through features such as:
- Order checking for:
- Out-of-range values
- Duplicates
- Maximum order frequency
- Allergies
- Potential drug-drug, drug-dosage, drug-overlap, drug-lab, and drug-allergy interactions, with appropriate warnings issued
- Orders integrated with progress notes, results, procedures, diagnosis, and problems
- Templating utilities for speedy point-and-click composition of notes
- Interdisciplinary notes enable a single parent note to contain multiple clinicians' notes for their disciplines to make them easier to find
- Tools to create Reminder dialogs for point-and-click resolution of clinical reminders to meet Clinical Guidelines
- Quick orders
- Order sets
- Event-delay orders (for admission, discharge, or transfer orders)
- Clinical Context Management to synchronize multiple applications to the same patient
- Accessibility support for disabled users in accordance with Section 508
- Code Set Versioning that ensures current codes to comply with HIPAA legislation
Computerized Patient Record System�€"continued
Improves the accessibility of online clinical information and results via integration with:
- Clinical Reminders
- Adverse Reactions
- Discharge Summary
- Progress Notes
- Inpatient and Outpatient Pharmacy
- Dietetics
- Radiology
- Laboratory
- Notifications
- Health Summary
- Problem List
- Consult/Request Tracking
- Patient Record Flags
Provides access to clinical information from other VAMC and Department of Defense sites through Remote Data Views.
- Displays other VAMCs where the patient has been seen
- Displays a small subset of data from Department of Defense medical facilities
- From the listed VAMCs, provides the capability to view Clinical reports, nationally released Health Summary components, and results for many lab tests
Graphical User Interface (GUI) provides a consistent, event-driven, windows-style clinical user interface.
- Follows the VistA GUI Guidelines, as well as the common standard for Windows
- List Manager Interface allows Windows-like actions for terminal-based users:
- Provides parameters and defaults that allow VAMC administrators and CPRS users to fine-tune the functionality and processes specific to their needs.
- Provides communication among VistA packages participating in CPRS through event-driven HL7 messaging.
Computerized Patient Record System�€"continued
CPRS Cover Sheet Example
CPRS: Adverse Reaction Tracking
Overview
The Adverse Reaction Tracking (ART) program provides a common and consistent data structure for adverse reaction data. This module has options for data entry and validation, supported references for use by external software modules, and the ability to report adverse drug reaction data to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Features
- Documents patient allergy and adverse drug reaction data.
- Provides the functionality for other VistA modules to extract and add patient reaction data.
- Provides a reporting mechanism that supports VHA Directive 10-92-070 which specifies reporting of adverse drug reactions to the FDA.
- Includes ART event points in an Application Programmers Interface (API) allowing other VistA packages to know when specific ART events take place so package tasks can be performed.
- Alerts the Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee each time the signs/symptoms are modified for a patient reaction.
- Generates progress notes. Displays all information at the time of an ART event on the Progress Notes API and allows editing of the note prior to sign off.
- Allows the site to track whether the patient has been asked if he/she has allergies.
- Tracks when the patient chart and ID bands have been marked indicating a particular reaction.
- Differentiates between historical and observed reactions.
- Tracks the particular signs/symptoms for a reaction.
- Allows for configuration of allergy files.
- Allows for editing and verification of reaction data.
- Allows for the addition of comments for each reaction to ensure completeness in reporting.
- Contains extensive reporting capabilities.
- Contains an online reference guide.
CPRS: Authorization/Subscription Utility (ASU)
Overview
The Authorization/Subscription Utility (ASU) provides a method for identifying who is authorized to perform various actions on clinical documents. These actions include signing, co-signing, and amending. ASU originated in response to Text Integration Utilities' document definition needs. Current security key capabilities were unable to efficiently manage the needs of clinical documentation (Discharge Summaries, Progress Notes, etc.).
Features
- Defines, populates, and retrieves information about user classes. User classes can be defined hospital-wide or more narrowly for a specific service and can be used across VistA to replace and/or complement keys.
- Links user classes with Text Integrated Utilities (TIU) document definitions and document events.
- Allows sites to maintain membership of users in User Classes and to distribute such maintenance tasks.
- Lists class members as active or inactive.
- Allows infinite hierarchies of subclasses.
- Defines business rules to further manage document activities.
CPRS: Clinical Reminders
Overview
The Clinical Reminders package is a valuable aid in patient treatment. Reminders assist clinical decision-making and educate providers about appropriate care. Electronic clinical reminders also improve documentation and follow-up, by allowing providers to easily view when certain tests or evaluations were performed and to track and document when care has been delivered. They can direct providers to perform certain tests or other evaluations that will enhance the quality of care for specific conditions.
Clinical Reminders may be used for both clinical and administrative purposes. However, the primary goal is to provide relevant information to providers at the point of care, for improving care for veterans. The package benefits clinicians by providing pertinent data for clinical decision-making, reducing duplicate documenting activities, assisting in targeting patients with particular diagnoses and procedures or site-defined criteria, and assisting in compliance with VHA performance measures and with Health Promotion and Disease Prevention guidelines.
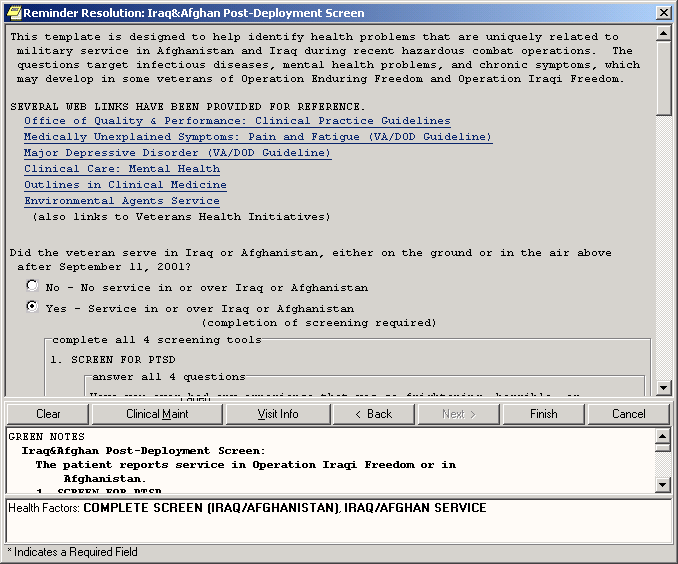
The Quality Enhancement Research Initiative (QUERI), a Health Services Research and Development (HSR&D) program, and the National Clinical Practice Guidelines Committee have joined with the Office of Information, System Design & Development office (SD&D) in designing national reminders and dialogs that will help promote informed decision-making and consistency of health care practices. Cooperatively developed reminders include: Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD), Major Mood Disorder (MDD), Hypertension, Iraq and Afghan Post-Deployment Screen, Race and Ethnicity, Women's Veterans Health, My HealtheVet, and VA Geriatric Care Referral (GEC) reminders.
Version 2 of Clinical Reminders contains many enhancements to improve processing and management of reminders. Performance has been enhanced through the creation of an index of all clinical data used in reminder findings. All enhancements are intended to help the Reminders functionality smoothly transition to CPRS Reengineering.
Features
- Allows results that are unique for each patient, by basing reminder evaluation on the patient's clinical data.
- Allows clinicians to resolve reminders through dialogs within the CPRS GUI. Using point-and-click techniques, a clinician can generate text for progress notes, update current and historical encounter data in Patient Care Encounter (PCE), update vital signs, update mental health test results/scores, and place orders.
- Allows facilities to copy, create, and customize their own reminder definitions, based on local needs.
- Provides components that can be displayed on Health Summaries.
- Provides reminders reports for summary or detailed level information about patients' reminders that are due. Reports allow providers to verify diagnoses, verify that appropriate treatment was given, identify patients requiring intervention, and validate effectiveness of care. Combined reports for multiple facilities or multiple locations can now be generated.
- Provides an enhanced Exchange Utility that allows exchange of reminder definitions and dialogs among sites and Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs).
CPRS: Clinical Reminders �€" continued
Clinical Reminders Example: Reminders Resolution Dialog
CPRS: Consult/Request Tracking
Overview
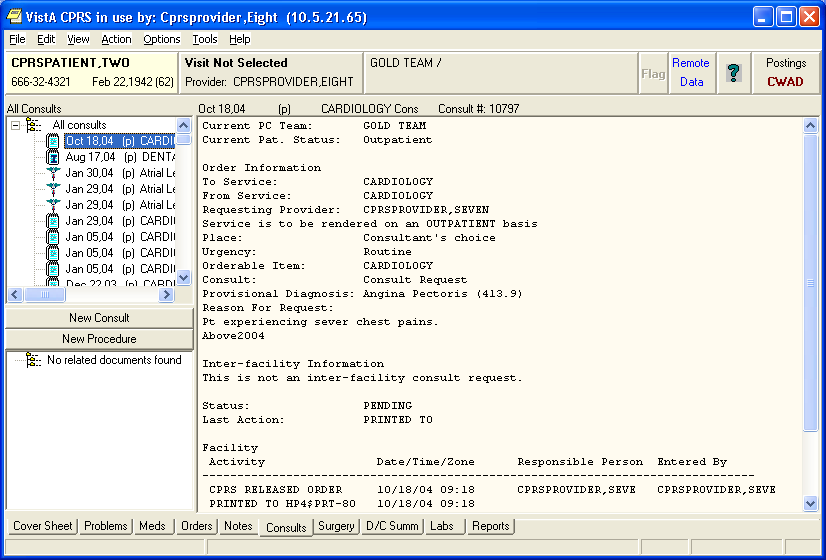
The Consult/Request Tracking package provides an efficient way for clinicians to order consultations and procedures from other providers or services within the hospital system, at their own facility or another facility. It also provides a framework for tracking consults and reporting the results. It uses a patient's computerized patient record to store information about consult requests.
Features
- Allows direct access to Consults functions through menu options in CPRS.
- Uses Consults' own menu options for managing the system, generating reports, tracking consults, or entering results for an existing consult request.
- Allows staff to set up consults as CPRS Quick Orders, streamlining the ordering process.
- Integrates with Prosthetics to track Home Oxygen, Eyeglasses, Contact Lenses, and other Prosthetics services.
- Produces a permanent record of the request and resolution for the patient's medical record.
- Allows all relevant parties to see the consult report in the context of the patient's record.
- Allows use of TIU templates and boilerplate to report findings.
- Allows display of Consult reports through TIU and CPRS.
- Enables clinicians to order a consult at another facility, using HL7 Messaging and the VA Intranet.
CPRS: Consult/Request Tracking �€" continued
Consults Example
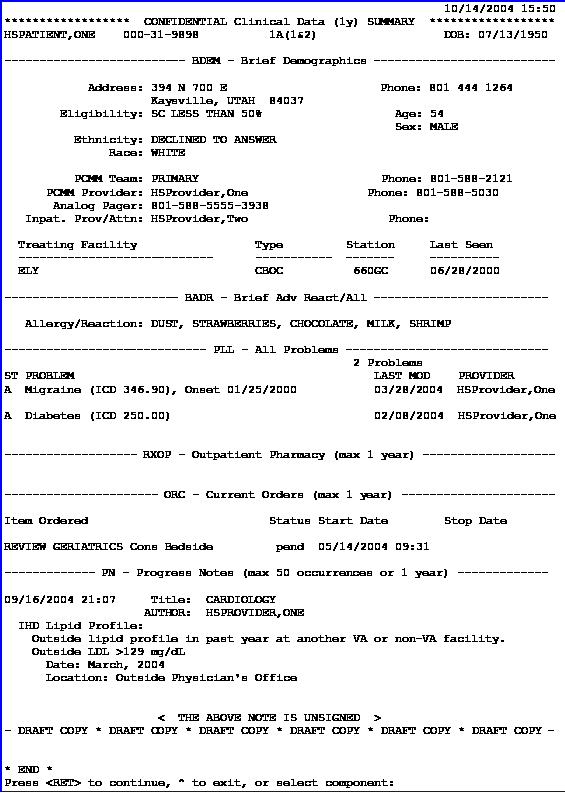
CPRS: Health Summary
Overview
A Health Summary is a clinically oriented, structured report that extracts many kinds of data from VistA and displays it in a standard format. Health summaries can be printed or displayed for individual patients or for groups of patients. The data displayed covers a wide range of health-related information such as demographic data, allergies, current active medical problems, and laboratory results.
Features
- Integrates data from the following packages:
Adverse Reaction Tracking Nursing (Vital Signs)
Automated Medical Information Outpatient Pharmacy
Exchange (AMIE) Patient Care Encounter (PCE)
Clinical Reminders Problem List
Computerized Patient Record Progress Notes
System (CPRS) Radiology
Consults/Request Tracking Registration
Dietetics Scheduling
Discharge Summary Social Work
Inpatient Medications Spinal Cord Dysfunction
Laboratory System Surgery
Medicine VistA Imaging
Mental Health
- Health Summary users can print an Outpatient Pharmacy Action Profile with bar codes in tandem with a health summary.
- Health Summary now exports components that allow staff to view remote patient data through CPRS. Additionally, remote clinical data can be viewed using any Health Summary Type that has an identically named Health Summary Type installed at both the local and remote sites.
- Clinical Reminders work with Health Summary to furnish providers with timely information about their patients' health maintenance schedules. Providers can work with local coordinators to set up customized schedules based on local and national guidelines for patient education, immunizations, and other procedures.
- Health Summary components 'Progress Notes' and 'Selected Progress Notes' can display the new interdisciplinary progress notes and all of the entries associated with the interdisciplinary note.
Health Summary Example
CPRS: Problem List
Overview
Problem List is used to document and track a patient's problems. It provides the clinician with a current and historical view of the patient's health care problems across clinical specialties and allows each identified problem to be traceable through the VistA system in terms of treatment, test results, and outcome.
This application supports primary care givers, such as physicians, nurses, social workers, and others, in inpatient and outpatient settings. It is also designed to be used by medical and coding clerks. A variety of different data entry methods are possible with this application.
Use of Problem List varies from site to site, depending on the data entry method a facility has chosen. Many sites use Encounter Forms, with clerks entering most of the data in the encounter forms. Encounter forms are generated from patient data in the system and added to or modified by clinicians.
Features
- Allows a clinician to view an individual problem list for any given patient.
- Supports a variety of specialized views of a patient's problem list.
- Uses the Lexicon utility that permits the use of �€œnatural�€ terminology when selecting a problem. Each term is well defined and understandable. A user, site, or application may substitute a preferred synonym.
- Can be linked to other sections of the medical record, such as Health Summary, Progress Notes, Order Entry/Results Reporting, Consults, test results, care plans for Nursing and Mental Health, Discharge Summaries, and Billing/Encounter Forms.
- Supports import of problem information from other clinical settings outside the immediate medical facility.
- Allows reformulation of a problem.
- Supports multiple forms of data capture: direct clinician entries, clerk entry, encounter forms, foreign problem lists, scanned encounter forms, hand-held devices, etc.
- Requires minimal data entry.
CPRS: Text Integration Utilities (TIU)
Overview
Text Integration Utilities (TIU) simplifies the use and management of clinical documents for both clinical and administrative medical facility personnel. In connection with Authorization/Subscription Utility (ASU), a facility can set up policies and practices for determining who is responsible or has the privilege for performing various actions on required documents.
The Version 1.0 release included Discharge Summary and Progress Notes. With the release of
CPRS and Consults/Request Tracking, TIU has been upgraded to integrate with these packages.
Features
- Provides boilerplate functionality for the automatic fill-in of information from VistA files into TIU documents. Boilerplates and embedded objects can be set up for specific types of documents for specific clinical needs.
- Interfaces with the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS): the template utilities in the GUI version of CPRS allow speedy point-and-click composition of notes, consults, and summaries. Templates can be set up for specific types of documents for specific clinical needs. Interfaces with Problem List, Automated Information Capture System (AICS), Patient Care Encounter (PCE), Authorization/Subscription Utility (ASU), Incomplete Record Tracking, Health Summary, and Visit Tracking. Uses a standardized and common user interface, which allows clinicians and others to retrieve many kinds of documents from a single source.
- Enables healthcare practitioners to enter interdisciplinary notes regarding a single episode of care for a patient. This is accomplished through the addition of a level to the tree structure where a note can have children (subordinate entries) and each of the children can have a different author. This provides for more complete patient records and facilitates input from a variety of practitioners regarding a single episode of care.
- Interfaces with VistA Imaging allowing clinicians to link TIU documents to all types of clinical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CAT scans.
- Uses an integrated database, which lets clinicians, quality management staff, researchers, and management search for and retrieve clinical documents more efficiently because documents reside in a single location within the database.
- Permits document input from a variety of data capture methodologies such as transcription, direct entry through CPRS or the TIU package, or upload of ASCII formatted documents into VistA.
- Uses a uniform file structure for storage of documents and management of document types.
- Uses a consistent file structure for defining elements and parameters of a document.
- Allows a variety of user actions, such as entry, edit, electronic signature, addenda, browse, notifications, etc.
- Allows a variety of management functions, including amendment, deletion, and identification of signature surrogate, re-assignment, and administrative authentication.
- Follows HL7 interface and other communication standards.
Dentistry
Overview
The Dentistry module is a menu-based system incorporating features necessary for the maintenance of medical center dental records. Users can enter dental treatment data, edit dental records, review and print reports, schedule appointments for patients, perform patient inquiry, and print and transmit data electronically to update the VA central database.
There are two levels of users, general user and manager. General users have limited system access as determined by the manager at a given medical center, while managers have access to all menus and options.
Features
- The package transmits service reports to a VA centralized database on a monthly basis. All service report data may be edited or deleted prior to release.
- Treatment reports can be displayed in four different formats: a provider format, sittings by provider, clinic summary, and individual sittings.
- There is full screen or line-by-line data entry and edit via the Treatment Data Enter/Edit feature. A tailored template/screen is used depending upon the provider selected (e.g., Prosthodontic, Endodontic, Oral Surgery, Periodontic, General).
- Patient inquiries combine Dentistry and Patient Information Management System (PIMS) data for patient information display (e.g., current address, sex, age, ward location).
- The package is integrated with the PIMS Scheduling module to allow users to make appointments, change or delete appointments, print pre-appointment, no-show, and cancellation letters, and generate routing slips and appointment lists.
- It provides a critical path method (CPM) aid to schedule appointments for Dental patients.
Hepatitis C Case Registry
Overview
The Hepatitis C Case Registry contains important demographic and clinical data on VHA patients identified with Hepatitis C infection. The registry extracts VistA pharmacy and laboratory databases to provide key clinical information. Data from the Hepatitis C Case Registry are used on the national, regional, and local level to track and optimize clinical care of Hepatitis C infected veterans served by VHA. National summary information (without personal identifiers) will be available to VA Central Office for overall program management as well as to inform Veterans Service Organizations, Congress, and other federal public health and health care agencies.
Features
This VistA software package provides the following key functions:
- Automatically develops a list of patients with Hepatitis C infection.
- Provides a GUI interface that allows select local facility staff to add to and/or edit the list.
- Identifies patients who are receiving investigational class drugs for Hepatitis C.
- Transmits patient data to a national database, including patient demographic information, the reason(s) patients were added to the registry, pharmacy utilization information, radiology test results, and a limited set of laboratory test results.
- Generates the following local reports:
- A report that lists the patients currently on the registry. Users can filter this report to display a subset of patients based on the date range they were added to the registry.
- A report that lists patients who have received Hepatitis C therapy within a user-selected date range.
- A report that displays local software activity and error report information.
- Technical improvements include:
- Automatic nightly updates to the national registry list.
- Use of a uniform M (formerly MUMPS) program backbone that can be used for other disease case registries.
- The transformation of VistA data into standard Health Level Seven (HL7) formatted messages for transmission, including limited validation checks, error messaging, etc.
Home Based Primary Care (HBPC)
Overview
The Home Based Primary Care module is designed to allow for the local entry and verification of HBPC patient-related data. Individual medical centers can now enter HBPC-related data and maintain, validate, and manipulate the database locally. This local database structure gives the HBPC program greater accountability for the integrity of its data, and eliminates the correction cycle previously required to correct data entry errors at the central database. Each site can now transmit complete records of HBPC patient information monthly to the Austin Automation Center (AAC) for processing. The AAC will continue to generate the same quarterly reports�€"only the source of the data has changed. This system eliminates the paper reporting system between medical centers and the AAC database.
Features
- Uses Appointment Management to handle patient visits and captures that visit data from Patient Care Encounter for transmission to the AAC.
- Provides for the entry and editing of patient evaluations and admission/discharge data.
- Provides automatic transmission of data to the central database.
- Allows data validation and correction to be completed at the individual medical center prior to transmission to the central database.
- Allows for medical center control over the site's HBPC database.
- Enables medical facilities to generate a wide variety of reports covering:
- Visit, admission and discharge data
- Length of stay
- Rejections
- Procedures
- Census for program, team, case manager, and/or provider
- Enables the HBPC program manager to control and assess the staff workload and organizational characteristics.
Immunology Case Registry (ICR)
Overview
The Immunology Case Registry (ICR) contains important demographic and clinical data on VHA patients identified with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infection. The ICR module accesses several other VistA files that contain information regarding diagnoses, prescriptions, surgical procedures, laboratory tests, radiology exams, patient demographics, hospital admissions, and clinical visits. This access allows identified clinical staff to take advantage of the wealth of data supported through VistA.
The key capabilities provided by the ICR to VA facilities that provide care and treatment to patients with HIV infection include the clinical categorization of patients, generation of the Center for Disease Control (CDC) case report form, clinical reports, and automatic transmission of data to the VA's National Immunology Case Registry.
Data from the ICR are used on the national, regional, and local level to track and optimize clinical care of HIV infected veterans served by VHA.
The latest version of the ICR is augmented by the capabilities of the Clinical Case Registries (CCR) software and has been further enhanced by the automation of the data collection system. The enhanced version, referred to as CCR: ICR, is a clinically relevant tool for patient management.
Features
The CCR: ICR software enhancements provide the following capabilities and features:
- New graphical user interface (GUI).
- Robust reporting capability, using both process and patient outcome measures, that allows for tailored local level reporting and divisional level reporting to help monitor the quality of patient care.
- Provides the ability to export report data to spreadsheet applications.
- Facilitates the tracking of patient outcomes related to antiretroviral drug treatment.
- Provides partial automation of HIV case identification.
- Identifies and tracks important trends in treatment response, adverse events, and time on therapy.
- Matches resources to clinical needs and utilization at local, VISN, and national levels.
- Verifies workload for VERA reimbursement.
- Automates notification to HIV coordinators that data was sent to and received by the national database.
- Automates extraction of data to the national registry.
Intake and Output
Overview
The Intake and Output (I&O) application is designed to store, in the patient's electronic medical record, all patient intake and output information associated with a hospital stay or outpatient visit. This application is not service specific and currently is interfaced with the Patient Information Management System (PIMS) (MAS), Nursing, and Pharmacy applications.
Features
Users may electronically document patient intake (e.g., oral fluids, tube feedings, intravenous fluids, irrigations, and other types of intake defined by the facility) and patient output (e.g., excreted patient material such as urine, nasogastric secretions, emesis, drainage, liquid feces/stool, and other types of output defined by the facility).
Intake data can be entered through either a quick or detailed route. The quick route documents the total fluid consumed. The detailed route requests the user to enter information regarding the specific type of fluid intake (e.g., orange juice, water, soup) along with the quantity absorbed.
The Start/Add/DC IV and Maintenance option contains nine protocols associated with intravenous therapy:
- Start IV�€"Start a new IV line or heparin/saline lock/port.
- Solution: Replace/DC/Convert/Finish Solution�€"DC current solution then replace a new solution to the selected IV line, or convert the IV according to the user's choice.
- Replace Same Solution�€"Replace the same solution to a selected IV.
- D/C IV Lock/Port and Site�€"Remove IV/lock/port from a selected IV site.
- Care/Maintenance/Flush�€"Check site condition, dressing change, tube change and flush.
- Add Additional Solutions(s) �€"Add additional solution(s) without discontinuing an existing one.
- Restart DC'd IV�€"Restart an IV that was DC'd due to infiltration or other reasons.
- Adjust Infusion Rate�€"Adjust infusion rate for a selected IV.
- Flush�€"Flush all IV line(s) for a selected infusion site.
The software supports documentation of intravenous intake via both single and multi-lumen catheters and is interfaced with the IV module of the Pharmacy software. The following reports are included:
- Print I/O Summary by Patient (by Shift and Day(s))
- Print I/O Summary (Midnight to Present)
- Print I/O Summary (48 Hrs)
- 24 Hours Itemized Shift Report
- Intravenous Infusion Flow Sheet
The last four reports can be printed for all patients on a ward, for patients in selected rooms on a ward, and for an individual patient.
Laboratory
Overview
The Veterans Health Information System and Technology Architecture (VistA) Laboratory module is a clinically oriented system designed to provide data to health care personnel. It assists the Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Service in managing and automating the workload and reporting process. The Laboratory module supports the following areas: General Laboratory, Microbiology, Histology, Cytology, Surgical Pathology, Electron Microscopy, Blood Donors, and Blood Bank.
Features
Phlebotomy/Ordering
- Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS)
- Supports ward order entry.
- Prints collection lists and labels and supports barcode printing.
- Provides maximum ordering frequency (e.g., daily, user-defined limits).
- Supports immediate request for blood specimen collection.
- Laboratory Electronic Data Interchange (LEDI).
Processing
- Provides worklists by urgency and accession number (instrument-specific).
- Produces lists of incomplete, workload/data capture reports, and lists for verification of data.
- Supports uni-directional and bi-directional Auto Instrument interfacing.
- Supports automatic download to automated instruments.
Verification/Release of Data
- Provides Delta Checks, flagging high/low/critical results.
- Presents critical values to the technologist in reverse video.
- Supports review/verification by group or individual accessions.
- Provides various on-screen alerts.
- Automated electronic result message generation via LEDI.
Reports
- Produces supervisory management, audit trail, data integrity, and quality management and utilization review reports.
Laboratory�€"continued
- Provides searches for specific antibiotic with defined antimicrobial patterns.
- Produces discharge summaries and cumulative and discrete episode reports.
- Produces automatic transmission of verified data to the ordering location.
- Provides quality control/search capabilities (e.g., SNOMED, critical values, and high/low values).
- Produces reports for Laboratory Management Information Program.
- Produces and transmits roll-up reports to national database.
- Produces site-customized management reports.
- Schedules patient cumulative reports based on inpatient or outpatient treatment.
Data Extracts Capabilities for External Databases:
- Laboratory Management Index Program workload data.
- Laboratory Workload for Decision Support System.
- Hepatitis C clinical information.
- Emerging Pathogen clinical data, antimicrobial trend, infection control, and Health Department reports.
- Patient Care Encounter workload.
- LEDI messages to remote Laboratory Information Systems (LIS).
- External LIS.
Laboratory: Anatomic Pathology
Overview
The VistA Laboratory Anatomic Pathology module automates record keeping and reporting for all areas of Anatomic Pathology (i.e., Surgical Pathology (SP), Cytopathology, Electron Microscopy (EM), Autopsy). The module provides valuable quality management features, increases productivity, provides comprehensive search and reporting capabilities, and facilitates the gathering of workload statistics.
Features
Provides quality management features, including:
- Access to historical pathology data during microscopic examination of current specimens.
- Lists of incomplete cytology, surgical pathology, EM, and autopsy reports.
- Turnaround time reports for all anatomic pathology sections.
- Generation of defined groups of cases requiring additional review, as defined by the accrediting agencies.
- Compilation of all information (e.g., special stains, immunopathology, or electron microscopy studies) in a single cumulative patient summary.
- On-command printing of laboratory test results of specified tests.
- Tracking outcomes of Quality Management review.
Increases productivity through:
- On-line access to historical anatomic pathology data (diagnosis and SNOMED codes only).
- Immediate availability of information regarding surgical pathology, cytology, electron microscopy specimens, and autopsy.
- Access to verified/released reports by non-laboratory personnel.
- Generation of labels for both specimens and slides.
- Interface with Kurzweil Voice Recognition Systems.
Provides comprehensive searching/reporting capabilities, including:
- Final pathology, autopsy, cytology, and EM reports.
- A log of all specimens accessioned, including final diagnoses.
- A variety of reports based on morphology, procedure, and etiology disease field entries, including:
- List of patients with a particular diagnosis.
- List of specimens from a particular site.
- List of specimens from a particular procedure (e.g., biopsies, frozen sections).
Provides workload statistics for:
- Number of specimens accessioned by area.
- Number of blocks, slides, and stains prepared.
Laboratory: Blood Bank
Overview
The VistA Laboratory Blood Bank module uses data that can be tied primarily to a donor, a patient, or a unit of blood/blood component. Information about a blood donation or a donation attempt revolves around the name of the blood donor. Similarly, information about a unit of blood/blood component, once it appears in inventory, revolves around the donor unit identification, while information involving transfusion and testing of patient samples revolves around the patient name and social security number.
Features
- Improves the safety of blood/blood component transfusions by decreasing the number and severity of human errors through:
- Retrieval of previous records and verification of current results.
- Detection of inconsistencies and flagging results that require corrective action before release of the unit.
- Bar code entry of donor unit information.
- Computer-assisted labeling of donor units.
- Improves the quality of patient care by allowing an evaluation of the appropriateness of all transfusions and specific blood components through integration with other portions of the system. Integration is accomplished by:
- Comparison of current lab values with established standards and screening criteria for each of the various components to allow concurrent audits.
- Delta checks for pre-transfusion and post-transfusion values to determine if the increments are within the established range.
- Decreases clerical workload through:
- Bar code entry from donor unit information.
- Transfer of information via pointers to reduce duplication.
- Preparation of labels following data entry.
- Generation of consultation reports.
- ility to perform searches for generating call lists.
- Generation of workload statistics for a given collection site for use in future planning.
- Automated blood donor recruitment and thank you letters.
- Improves utilization review/resource management through:
- Workload and transfusion statistics, and cost accounting by ward, treating specialty, and physician.
- Workload statistics, including variables by time of day and day of week.
- Access to information for medical and nursing staff.
Laboratory: Electronic Data Interchange (LEDI)
Overview
The Veteran Integrated Service Network (VISN) mission is to consolidate electronic lab test ordering and lab test result reporting throughout all Veterans Affairs (VA) medical care facilities laboratories within a VISN, between VISNs, and for non-VA organizations (i.e., commercial reference laboratories). The LEDI software reduces or eliminates the need for manual ordering and reporting of laboratory results to interface laboratories. The software minimizes the amount of manual labor associated with preparing samples for delivery and processing at the host lab facility.
The VistA Laboratory Electronic Data Interchange Phase II (LEDI II) software application provides electronic messaging for Lab Test Ordering and Lab Test Results Reporting between VA health care facilities laboratories based on the Health Level Seven (HL7) Version 2.3 Standard Specification and VistA Health Level Seven (HL7) Version 1.6 Standard Specification. These Specifications are used as the basis for defining VistA Laboratory Universal Interface (UI) and LEDI HL7 Interface Standard Specification Version 1.2.
Features
- Addresses the electronic lab test order transfer from the host facility laboratory to collection facilities laboratories.
- Provides for the automated transfer of verified test results from the host facility back to the collection facility's laboratory for release to the patient electronic medical record.
- Provides storage of lab test results in the clinical database at the collection facility laboratory. The LEDI software electronically returns test results to the collection facility laboratory using the HL7 protocols. Results returned to the collection facility laboratory would be processed and verified as if completed by an auto instrument. This eliminates manual entry of results at the collection facility laboratory.
- Creates the automation of shipping lists to process the laboratory work at the collection and host laboratories.
- Provides the capability to interface non-VistA laboratory information systems. This includes university hospitals, commercial reference laboratories, other government agencies and centralized clinical patient record systems.
- Sends/Receives Laboratory HL7 Messages.
- Utilizes TCP/IP Protocol as a Communication Protocol.
- Builds lab test orders.
- Processes NTE Segments.
- Stores test reference ranges.
- Specifies final or incomplete lab test results.
- Provides new SM40 shipping codes.
- Builds and closes a Shipping Manifest.
- Generates Result (ORU) Messages.
- Referral Patient Multi-purpose Accession.
Medicine
Overview
Medicine is designed to serve clinical services and maximize the use of the VAMC database. The module allows entry, edit, and viewing of data for many medical tests and procedures. The Summary of Patient Procedures allows the clinician to view a two-line summary of all medical procedures for each patient. These summaries are most often presented in descending order from most recent to oldest. Details of the procedures can be viewed by selecting the summary of interest. Medicine currently has six components: Cardiology, Pulmonary, Gastrointestinal, Hematology, Pacemaker, Rheumatology, and Generalized Procedure.
Features
- Provides a Summary of Patient Procedures for all procedures performed on a particular patient with simple drill downs for further information. Reports for all procedures are menu options.
- Provides both scroll mode and screen entry features for all components and provides word processing-based consult software for all procedures.
- Features an extensive screen entry system for Cardiac Catheterization Lab, Holter, Electrophysiology, Exercise Tolerance Test, Echo, and Electrocardiogram. Standards-based electronic transfer of ECG and Holter data to VistA is available.
- Allows the entry and edit of Esophageal Gastroduodenoscopy (EGD), Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiogram and Pancreatogram (ERCP), Colonoscopy, and Laparoscopy findings or data.
- Allows the entry, edit, and printing of endoscopic data and Pulmonary Function test data.
- Contains a diagnosis filter that allows the separation of primary and secondary diagnoses, a consult component, and an automatically-generated recall list within both the Gastrointestinal and Pulmonary components.
- Allows data entry and edit for Generator and Lead implants, and follow-up surveillance within the Pacemaker component. The software also permits the direct electronic transfer of a report to the National Pacemaker Centers using VA network mail.
- Permits data entry and edit of Bone Marrow Aspirates (BMA) and Bone Marrow Biopsies (BMB).
- Allows the tracking of Rheumatology visits and is based on standards developed by the American Rheumatology Associations Medical Information System (ARAMIS).
Mental Health
ASI-MV
I believe it is missing from WorldVistA because of copyright issues. Perhaps something similar to the agreement with AMA allowing use of the CPT procedure codes can be worked out.
Mental Health (continued)
Overview
The Mental Health module provides computer support for both clinical and administrative patient care activities associated with mental health care. Psychiatrists and psychologists have directed its design with active input from all health care disciplines, guided by the principle of creating software that makes the clinician's job easier and leads to better patient care. A by-product of this approach has been the creation of a clinical database, which is useful to mental health program managers in many ways, including evaluating clinical productivity, monitoring and improving the quality of care, and trending various patient care events. This clinical database package is comprehensive and accessible from workstations throughout medical facilities.
Features
Provides a mini clinical record that includes:
- A patient profile with demographic information and a brief index of the clinical database, including physical examinations, psychological tests, clinical interviews, problem list, and diagnoses.
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV) and International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9) diagnoses.
- Psychological test and interview results, reviews of systems, past medical histories, crisis notes, clinical patient messages, and progress notes.
- A Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF) Case Finder Report, which lists all patients that have not been given a GAF score within the last 90 days.
- The ability for patients to undergo psychological tests and clinical interviews at a workstation, saving considerable clinician time. Psychological tests are automatically scored for retrieval, with access governed by the guidelines of the American Psychological Association.
VistAMental Health (MH) Addiction Severity Index Multimedia Version (ASI-MV):
- Introduces the new functionality required to run the commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) Addiction Severity Index Multimedia Version (ASI-MV) software.
- Allows clinicians and patients to enter demographics and self-administered ASI-MV interviews via a workstation using video and audio technology.
- Is a significant time-saver for clinicians, because clinicians need not be present during the interview.
- Provides the patients with privacy and appropriate time to complete an interview.
VistA Mental Health Assistant (MHA) Graphical User Interface (GUI):
- Provides a crash recovery file.
- Displays patient demographics data, which can be printed, copied to the Windows clipboard, or saved to a text file.
- Context-sensitive help is available for most items, with suggestions for test administration and interpretations.
- Provides a user-friendly interface for entering interview data for ASI.
Mental Health�€"continued
- Enhances the ability of both staff and patients to enter psychological test data.
- Creates reports and graphical displays of complex tests by sub-category or scales.
- Creates psychological test order windows that display tests that can be ordered based on the provider privileges.
- Provides a text report of selected tests and graphs of numeric scores.
Nursing
Overview
The Nursing application is a component of the Department of Veterans Affairs VistA program. It is comprised of multiple modules (i.e., Administration, Education, Clinical, Quality Assurance, and Package Management).
Features
The nursing software includes the following functionalities:
Administration:
- Tracks staff information.
- Generates management reports on employees.
- Accumulates daily statistics on the number of patients treated.
- Generates daily, monthly, quarterly, and yearly AMIS Reports.
- Provides workload statistics based on AMIS data.
- Provides miscellaneous patient acuity reports.
Clinical:
- Contains a patient classification system which generates reports by bed section and ward.
- Includes nationally developed standard nursing care plans for initiating patient care plan generation.
- Allows nurses to generate a patient care plan based on patient problems, identified goals, and specified nursing interventions.
- Allows a staff nurse to update a patient's nursing ward location and/or nursing AMIS bed section to insure accurate patient classification entries.
- Allows users to enter vital signs, height, and weight for patients.
- Allows users to generate Intake and Output reports, an End of Shift Report, and a Health Summary Report by patient or ward.
Package Management:
- Allows sites to modify data in specified nursing files.
- Provides special ADP Coordinator functions for executing nursing options that affect patient acuity, manhours, FTEE status, etc.
- Provides ADP Coordinator options for admitting/transferring/discharging patients within the Nursing system when the MAS System is off-line.
Nutrition and Food Service (N&FS)
Overview
The Nutrition and Food Service (N&FS) software integrates the automation of many Clinical Nutrition, Food Management, and Management Reports functions. The Clinical N&FS activities of Nutrition Screening, Nutrition Assessment, Diet Order Entry, Tube Feeding and Supplemental Feeding Orders, Patient Food Preferences, Specific Diet Pattern Calculations, Nutrient Analysis of meals, Consult Reporting, Encounter Tracking, and Quality Care Monitoring are all available in this program. The Food Management function has complete automation of food production activities; Service and Distribution, Inventory and Cost Management, Recipe Expansion, Menu and Recipe Nutrient Analysis, Meal and Diet Pattern Development and Implementation, Diet Card and Tray Ticket Printing, and Quality Service Tracking are available. The Management Reports include the Served Meals, Additional Meals, Cost Per Meal, Tube Feeding Cost, Supplemental Feeding Cost, Staffing Data, Encounter Data and Annual Management Reports.
Features
- Allows the building of a site-specific listing of patient food preferences that can be incorporated in meal production calculations and the printed diet card and tray tickets programs.
- Manages patients' requests or dietary requirements for specific food items or utensils, allowing the selection of standing orders for any patient, for any meal or quantity.
- Controls all aspects of ingredient usage.
- Develops a list of site-specific recipes that includes portion size, preparation area and time, equipment and serving utensils, recipe category, ingredients, and directions for preparation. Recipes can be quickly analyzed for their nutrient value.
- Creates multiple meals and menu cycles. Meals can be used in different patterns by creating menu cycles or by creating special holiday dates within a cycle. It allows for the nutrient analysis of meals or daily/weekly menus.
- Controls quantities produced in the Food Management program. Specific patient diet orders are reorganized into production diets and diet patterns that reflect the foods to be served. This information is used along with data from the meal file to generate production reports, diet cards and/or tray tickets. A forecasting tool also exists in this section that allows the manager to anticipate, by percentage of total census, the type and quantity of various production diets that will be needed by any selected service point.
- Allows the entry of information required by the Annual Report that is not automatically retrieved from the program.
- Prints a patient-specific record of all diet order entry information.
- Controls the order entry activity.
- Manages food items and their nutrients using the latest USDA data, food items from Bowes and Church, and additional data from research.
- Handles N&FS consults and allows the reassignment of active consults from one staff member to another.
- Manages the supplemental feeding food items and menus. A supplemental feeding menu automatically goes into effect at the time of diet order entry and changes automatically with new orders.
Oncology
Overview
The Oncology module automates the tumor registry and supports tumor registrars in abstracting cancer cases, following up on cancer patients and producing the Hospital Annual Report. Functions are grouped according to order of use: Case Finding and Suspense; Abstracting, Printing and Quality Management; Follow-up; Registry Lists; Annual Reports; Statistical Reports; and Utilities.
The Oncology application functions in accordance with the current editions of American College of Surgeons (ACOS). It contains required data standards and data sets necessary to bring the tumor registry module into compliance with the Facility Oncology Registry Data Standards (FORDS) 2003 specifications approved by the Commission on Cancer (COC); Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Reporting (SEER) Extent of Disease for site-specific surgery; International Classification of Disease�€"Oncology 3rd Edition; and American Joint Commission on Cancer (AJCC) Manual for the Staging of Cancer, 1st through 6th Editions.
Features
- The software supports multi-divisional sites.
- The program automatically finds cases by searching the database from Anatomical Pathology (Surgery, Cytology, Electron Microscopy, and Autopsy), Radiology, and Patient Treatment File (PTF). Cases can be entered into the Suspense File by date of diagnosis, and chart request pull lists can be printed.
- Demographics are drawn directly from Patient Information Management System (PIMS) patient file and stored permanently. Cancer identification data is obtained from the local database (e.g., laboratory and radiology test results).
- The program accessions and abstracts with extensive on-line help and stages extent of disease automatically.
- It produces a wide range of follow-up lists and registry lists needed for accreditation and allows entry of contacts directly into Oncology Contact File.
- Professional letters covering diverse situations and customization of letters are available.
- Predefined annual reports can be generated and the user can create specialized reports using VA FileMan.
- Reports to the Associate Chief of Staff (ACOS) can be generated using special routines that extract data onto floppy disk. The same functionality is available for state reporting.
- The database can be customized to suit the individual hospital.
- The full set of TNM codes is included from the appropriate edition of the AJCC Manual on Staging of Cancer.
- The program allows on-line completion of Patient Care Evaluations (PCEs) during the abstracting function if the case being abstracted fulfills the selection criteria for the PCE.
Pharmacy: Automatic Replenishment/Ward Stock (AR/WS)
Overview
The Automatic Replenishment/Ward Stock (AR/WS) package provides a method to track drug distribution and inventory management within a medical center. The AR/WS module is designed to allow each medical center to adapt the system to its own needs.
Features
The AR/WS package:
- Provides inventory management capabilities for clinical care locations and drug crash carts.
- Allows easy drug item inactivation for inventory locations.
- Provides tools to develop medication storage areas with lists of drugs to be maintained in that area. Drugs are classified by inventory type and assigned storage location and stock level.
- Groups medication storage areas together by inventory group name. Grouping may be by location, date (time or frequency of inventory), or inventory type.
- Provides tools to conduct inventory: prints inventory sheets and/or pick lists to determine stock to be replenished in medication storage areas and, by a selected method, replaces needed inventory items.
- Maintains backorder totals if a physical inventory is conducted and entered into AR/WS software.
- Provides inventory management reporting capabilities for clinical care locations and drug crash carts.
- Provides ability to select by inventory group on all reports.
- Supplies a report to fill on-demand requests for out-of-stock items or items not part of the standard inventory.
- Provides various printouts as well as several management statistical reports for the creation and maintenance of the system.
Pharmacy: Bar Code Medication Administration (BCMA)
Overview
Bar Code Medication Administration (BCMA) software provides a real-time, point-of-care solution for validating the administration of Unit Dose (UD) and Intravenous (IV) medications to inpatients in Veterans Administration Medical Centers (VAMCs). BCMA uses a Graphical User Interface (GUI), MS Windows-based Client/Server architecture, designed to improve the accuracy of the medication administration process, and to increase the efficiency of the administration documentation process. The end result is enhanced patient safety and patient care at VAMCs. As a clinician scans each patient wristband and medication using a bar code scanner, BCMA immediately validates the patient and their medication, and that the medication is ordered, timely, and in the correct dosage. At the same time, BCMA electronically updates the patient's Medication Administration History (MAH). The software is fully compatible with other VistA applications.
Features
The BCMA software provides the following features:
- Medication Tabs on a patient's Virtual Due List (VDL) are designed for separating and viewing the different types of active Unit Dose, IV Push, IV Piggyback, and large-volume IV medication orders. Each Tab provides an �€œalert�€ light, which turns green only when the patient has active medication orders for that Tab.
- Patient safety tools include a Missed Medications Report, an alert when due medications are not administered, a notification when a patient is transferred, and an alert light to indicate that a medication order exists for the Schedule Type and Start/Stop Date and Time selected on the VDL. Other tools include a listing of Allergies and Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) that are documented for a patient in the Allergy/Adverse Reaction Tracking (ART) package.
- A Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) Med Order Button (or �€œHot Button�€) on the BCMA Tool Bar streamlines the workflow in ICU-type environments. This button links nurses directly to CPRS for electronically ordering, documenting, reviewing and signing verbal and telephone STAT and NOW (One-Time) medication orders already administered to patients.
- BCMA increases the amount and type of information available to nurses at the point of care, improves communications between Nursing and Pharmacy staff, records Missing Doses for patients, sends an electronic Missing Dose Request to the Pharmacy, and supports Health Level Seven (HL7) messaging.
- Management and accountability tools identify PRN entries that require effectiveness comments and pain scores, list medications that were not scanned as administered during an administration time window, list early/late administration variances, and allow nurses to set site-specific parameters and defaults on their systems.
- Compiles reports by Patient or by Ward for Nursing, Pharmacy, and Information Resources Management (IRM). Reports available for printing include: a Medication Administration History, Medication Log, Missed Medications, Missing Dose Request, PRN Effectiveness Log, Medication Due List, Medication History, Medication Variance Report, Cumulative Vitals/Measurement Report, and Administration Times Report.
Pharmacy: Consolidated Mail Outpatient Pharmacy (CMOP)
Overview
The Consolidated Mail Outpatient Pharmacy (CMOP) package provides a regional system resource to expedite the distribution of mail-out prescriptions to veteran patients. CMOP host facilities, regionally located, receive data from medical centers within the area of service. Current CMOPs are designed to handle the dispensing and mailing of between 20,000 and 40,000 prescriptions in an 8-hour workday.
Features
The CMOP package provides the following features:
- Patients submit medication requests via telephone, mail, or in person at each medical facility. When necessary, pharmacy personnel enter the orders into the patient database.
- Each area CMOP host facility establishes a schedule for the electronic transmission of the prescription data.
- Prescriptions are transmitted electronically from the medical facility to the automated prescription dispensing equipment, checked by a pharmacist, mailed to the patient, and information on the prescription filled is returned to update the medical center database.
- The process is highly integrated with the Outpatient Pharmacy software and requires no additional processing by pharmacy personnel responsible for entering the prescription.
- All prescriptions are automatically screened by the CMOP software and set for transmission if appropriate.
- The user is then notified that the prescription will be dispensed by the CMOP. Once the prescription is processed by the CMOP, the prescription file at the medical center is updated accordingly.
- Pharmacy staff may view the prescription at any time to determine if it has been transmitted to CMOP, dispensed, not dispensed, etc.
- Upon fulfillment of the medication order by the CMOP, any applicable pharmacy prescription co-payment is billed as the medical center files are updated with the release information.
- The software provides order tracking and operational data for the CMOPs.
- The software allows prescriptions written for schedule III-V controlled substances to be electronically transmitted to the CMOP facilities.
Pharmacy: Controlled Substances
Overview
The Controlled Substances package provides functionality to monitor and track the receipt, inventory, and dispensing of all controlled substances. This software provides the pharmacy with the capability to define a controlled substance location and a list of controlled substances to maintain a perpetual inventory. The capability for Pharmacy personnel to receive a controlled substance order, which automatically updates the quantity on hand and receipt history, is also available. Nursing personnel can request orders for controlled substances via on-demand requests and receive these orders when delivered from Pharmacy. Pharmacy may dispense controlled substances, using the automated VA forms 10�€"2321 and 10�€"2638, to complete an order request.
Features
The Controlled Substances package provides the following features:
- Monitors/tracks the receipt, inventory, and dispensing of controlled substances.
- Allows management inspections to automatically identify discrepancies in stock levels.
- Allows nursing to place orders for controlled substances via on-demand requests.
- Provides AMIS and cost reporting data.
- Maintains perpetual vault inventory balances.
- Provides the functionality to return to stock, transfer between locations, cancel orders, and log outpatient prescriptions.
- Automates current inventory requirements that allow medical facilities to detect discrepancies or diversions of controlled substances, thereby improving overall drug accountability.
Pharmacy: Drug Accountability/Inventory Interface
Overview
The Drug Accountability/Inventory Interface works toward perpetual inventory for each VA medical facility pharmacy by tracking all drugs through pharmacy locations. Drugs are added to the pharmacy location as they are received from the Prime Vendor and CoreFLS. Both methods allow sites to receive invoice information containing data for confirmed orders. The files are uploaded into Drug Accountability, processed, and upon verification, the pharmacy locations or master vaults are updated. Dispensing data is collected from pharmacy packages to decrement balances. Drug Accountability also provides the capability for Pharmacy personnel to display or print procurement history, drug balance adjustments, and order data.
Features
There are two primary methods of receiving invoice data into Drug Accountability:
- Prime Vendor Data
- CoreFLS Data
Both methods involve having the user place the invoice orders with the appropriate company. With the prime vendor, the data is uploaded into VistAusing a Graphical User Interface to perform the upload. With CoreFLS, the data is automatically shipped to VistA upon receipt at the warehouse.
The Prime Vendor Interface includes the following features:
- It automatically updates the Drug Accountability pharmacy locations based on dispensing and receiving information, and it also updates master vaults based on receiving information.
- Drugs are added as the invoice data is received.
- If the invoiced drug's order unit and dispense units per order unit are the same as the information currently contained in the local DRUG file, the NDC field in the DRUG file is overwritten with the most recent National Drug Code (NDC) number.
- The reorder quantities for the pharmacy locations and master vaults are provided on a daily basis by way of a mail message.
CoreFLS Interface includes the following features:
- When a pharmacy order invoice is received and entered into the CoreFLS purchasing system, the receipt data will be collected and compiled to an Health Level Seven (HL7) message and transmitted �€˜real time' to VistA Drug Accountability. Upon receiving the message, the receipt data will be stored in a temporary global, and Drug Accountability will alert the user about the Pharmacy receipt.
- After receiving invoice data into the warehouse, the transmission from CoreFLS will place data into a temporary global.
- When Pharmacy personnel sign into the Drug Accountability package, the program will check for the existence of orders to process.
- If the orders exist, and the user has the proper security key, the data can then be received into Drug Accountability.
Pharmacy: Drug Accountability/Inventory Interface �€" continued
- Each Purchase Order received will be for a specific pharmacy location. If items are to be shipped/received at different pharmacy locations, a different purchase order will be created/shipped for each location.
Both Interfaces include the following features:
- Vendor-specific information and procurement history is displayed for a selected drug.
- Pharmacy locations are established and populated.
- A purge capability with scheduling queuing is provided.
- Supports NDC code set and pricing for Electronic Claims Management Engine pharmacy electronic billing.
Pharmacy: Electronic Claims Management Engine (ECME)
Overview
The Electronic Claims Management Engine (ECME) package provides the ability to create and distribute electronic Outpatient Pharmacy claims to insurance companies on behalf of VHA Pharmacy prescription beneficiaries in a real-time environment. The application does not impact first party co-payments and minimizes the impact on legacy pharmacy workflow. This system meets the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of 1996 mandate, specific to the Electronic Transactions and Code Sets rule. The rule mandates VHA must submit claims electronically to insurance companies via the National Council for Prescription Drug Programs(NCPDP) v5.1 standard transmission format. The system, developed from a version currently utilized by Indian Health Service, has been modified to support the VHA Pharmacy Order Entry model.
ECME receives a billing determination by Integrated Billing (IB) if an Outpatient Pharmacy order is billable. If so, ECME builds a NCPDP v5.1 electronic claim transaction using data required by the insurance company for claim adjudication, as defined within the company's individual payer sheet. Claims are submitted during the Outpatient Pharmacy finish process, and again during the Outpatient Pharmacy release process if the claim was initially rejected. If any additional edits or other events occur to the prescription, such as a return to stock, ECME generates additional electronic claims to payers updating them on the prescription billable status and updates IB with any claim specific information.
Features
The ECME application provides the following features:
- Creation of outpatient pharmacy electronic claims for real-time submission to third party insurance companies for adjudication utilizing billing activities within the VHA prescription fill process.
- Utilization of information provided by a subscription with First DataBank to create electronic claims.
- Support and integrated functionality for TRICARE/CHAMPUS, ChampVA, and itemized charging methods for prescription pricing.
- Enhancements to VHA revenue cycle management by submitting claims at the point of service while building claim segments using payer-provided transaction formats compliant with the NCPDP v5.1 standard.
- Collection and presentation of DUR information to application users based on information received from payer claim responses.
- Reporting and on-line worklist presentation formats supporting VHA claims adjudication requirements.
- Integration with VistA IB for prescription billing determination and claims tracking.
- Integration with VistA Pharmacy applications when creating claims based on Pharmacy workflow.
- Communication with the VistA Health Level Seven (HL7) application and Vitria BusinessWare to store and forward electronic pharmacy claims for third party insurance adjudication.
Pharmacy: Inpatient Medications
Overview
The Inpatient Medications package integrates functions from the Intravenous (IV) and Unit Dose (UD) modules (described on the following page). This integration provides a comprehensive record of medications utilized during hospitalization of the veteran, the functionality for clinician order entry through Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS), and tailors processes by facility, user, and/or medication.
Features
The Integrated software allows these features, via the List Manager interface, for both IV and Unit Dose:
- Provides the user the capability to
- Browse through a list of orders and take action(s) against those items.
- Print 7-day, 14-day, and 24-hour MARs, labels, and profiles from within the options.
- Select a detailed allergy report, document new allergies or adverse drug reactions.
- Update the Patient's Record from within List Manager.
- Provides Drug/Drug Interaction, Drug/Class Interaction, Duplicate Drug, and Duplicate Class Order checks.
- Allows easier drug selection using Orderable Item.
- Provides on-line order maintenance (for example: edit, renewal, cancellation) and marks orders that need attention.
- Provides on-line order entry with an integrity check for each order type.
- Generates labels containing order and patient information upon the entry/maintenance of an order.
- Provides on-line or printed patient profiles that include a history of medication orders for the current or last medical center visit.
- Displays patient order information and histories of all actions taken on active orders.
- Provides an Action Profile of patient medication orders for use by physicians to cancel or continue medications.
- Provides a Stop Order Notice report to notify users of orders near expiration.
- Cancels/holds medication orders for patients transferred between wards and/or services.
- Provides dispensing cost reports by patient, ward, service, drug, and providers.
- Provides reports and forms by patient, ward, and selected groups of wards.
- Allows electronic entry and inpatient processing of medication orders for an outpatient receiving treatment via a clinic or ancillary service.
Pharmacy: Inpatient Medications - Intravenous (IV)
Overview
Inpatient Medications' Intravenous (IV) module provides pharmacists and their staffs with IV labels, manufacturing worksheets, ward lists for order updates, and management reports. It permits the Pharmacy staff to track the manufacture of IV formulas with greater control than manual procedures allow. Through order entry and ward list updating, the staff can easily establish and maintain an accurate and timely data set of IV orders. A carefully designed set of checks and balances has been incorporated to ensure that the patient is supplied IV solutions quickly and accurately.
Features
The IV module:
- Generates Manufacturing Lists to facilitate maximum efficiency in the preparation and delivery of IV products.
- Generates IV labels containing all necessary patient, drug, and schedule information. Labels provide a bar-coded identifier which when used in conjunction with Bar Code Med Administration greatly enhances patient safety.
- Generates management reports designed to track drug costs and workload by ward, provider, IV room, and patient.
- Provides on-line generation of production reports such as renewal lists, active order lists, and formulary drug reports.
- Discontinues/holds orders for patients transferred between wards and/or services.
Pharmacy: Inpatient Medications - Unit Dose (UD)
Overview
The Unit Dose (UD) module of Inpatient Medications provides a standard computerized system for dispensing and managing inpatient medications. Timely, accurate, accessible, and up-to-date patient medication information is available from any terminal within the facility. Computer-generated working forms allow personnel to dedicate more time to patient care.
Features
The Unit Dose module:
- Allows immediate entry of pre-defined sets of unit dose orders.
- Provides computerized pick lists, which include pre-calculated doses for pharmacists.
- Provides an interface to automated dispensing equipment.
Pharmacy: National Drug File (NDF)
Overview
The National Drug File (NDF) package provides standardization of the local drug files in all VA medical facilities. Standardization includes the adoption of new drug nomenclature and drug classification, as well as linking the local drug file entries to data in the National Drug files. For drugs approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), NDF provides VA medical facilities with the ability to access information concerning dosage form, strength and unit, package size and type, manufacturer's trade name, and National Drug Code (NDC) information. The NDF software also lays the foundation for sharing prescription information among medical facilities.
Features
The National Drug File:
- Standardizes drug file information.
- Standardizes drug classifications.
- Adopts standard nomenclature.
- Provides up-to-date prescription and over-the-counter information.
- Provides available sources for drugs manufactured and approved by the FDA.
- Provides a base for implementation of drug inventory control and management throughout VA (i.e., Consolidated Mail Outpatient Pharmacy and Pharmacy Benefits Management).
- Allows file access by NDC, manufacturer's trade name, ingredient, dosage form, dosage strength, route of administration, and VA drug classification.
- Allows management of drug information, including reports on drugs by classification, ingredient, NDC, trade name, and/or active/inactive status.
- Matches additions to medical center drug files with the national drug database.
- Provides an ingredient file that is an integral component of the Allergy Tracking and Outpatient Pharmacy (drug-drug interactions) modules.
- Provides an enhanced formulary report listing local, VISN, and National Formulary information.
- Includes the Patient Medication Information Sheets that feature the following:
- An explanation of how and why to take a medication and the possible side effects.
- Information supplied by commercial sources.
- Information that is copyrighted and periodically updated.
- Utilizes data provided and standardized by First DataBank for point of sale electronic billing using Electronic Claims Management Engine (ECME).
Pharmacy: Outpatient Pharmacy
Overview
The Outpatient Pharmacy package provides a way to manage the medication regimen of veterans seen in outpatient clinics and to monitor and manage the workload and costs in the Outpatient Pharmacy.
The primary benefits to the veteran are the assurance that he or she is receiving the proper medication and the convenience of obtaining refills easily. The clinicians and pharmacists responsible for patient care benefit from a complete, accurate, and current medication profile available at any time to allow professional evaluation of treatment plans. Utilization, cost, and workload reports provide management cost-controlling tools while maintaining the highest level of patient care.
Features
The Outpatient Pharmacy package:
- Checks new prescriptions against existing prescriptions (for the same medication, therapeutic class, reported allergies, reactions, or drug interactions).
- Allows pharmacists to verify data entered by technicians prior to the printing of labels.
- Allows for the renewal of prescriptions that have no remaining refills. Prints labels for new, renewed, and refilled prescriptions.
- Auto-cancels individual prescriptions for a patient after admission for inpatient treatment.
- Creates medication profiles for patient charts to meet the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO) requirements for a current medication list. Profiles are suitable for counseling patients.
- Allows the Action Profile to be used as a quick renew/cancel request form by clinic providers, which allows for rapid entry of request by Pharmacy staff.
- Provides the Screen Profile for review at several points in the order/entry process.
- Provides basic Drug Use Evaluation (DUE) template generator.
- Provides necessary laboratory checks and reports to meet national requirements for Clozapine dispensing.
- Provides finishing of orders entered through CPRS.
- Provides information for billing any applicable medication co-payment when the prescription is released.
- Allows the user to select a different action without leaving an option.
- Uses List Manager features to allow:
- Pharmacist or technician to browse through a list of actions.
- Pharmacist or technician to take action against those items.
- User to select an action that displays an action or informational profile.
- Works with Integrated Billing (IB) and Electronic Claims Management Engine (ECME) to enable and manage point of sale billing supporting the Healthcare Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Electronic Claims and Code set congressional mandate.
Pharmacy: Outpatient Pharmacy �€" continued
- Allows prescription labels and Prescription Medication Information (PMI) sheets to be printed in another language if the system has the other language fields populated in Pharmacy Data Management and the individual patient is identified with the other language preference flag.
- Allows the ability to print a microchip-embedded label for a prescription. This label can then be read by ScripTalk�, thus improving patient safety for visually impaired veterans.
- Provides display of Herbal, over the counter (OTC), and Non-VA medications documented through CPRS. The data will be used for screening of Drug-Herbal and Drug-Drug Interactions with prescribed medications in VistA.
Pharmacy: Pharmacy Benefits Management (PBM)
Overview
The Pharmacy Benefits Management (PBM) package replaced the Drug and Pharmaceutical Products management (D&PPM) application. The software extracts medication dispensing data elements from the Outpatient Pharmacy, Inpatient Medications IV and Unit Dose, Automatic Replenishment/Ward Stock, and Controlled Substance modules; Procurement information from Drug Accountability, Integrated Funds Control, Accounting and Procurement (IFCAP); and a limited amount of Laboratory data on a monthly basis.
The software makes data extraction reports available at Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Centers (VAMCs) and allows local management to use the data to project local drug usage and identify potential drug accountability problem areas. The Pharmacy Benefits Management Strategic Health Group (PBM) is able to provide information on local facility, Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) and national product use on monthly, quarterly, and annual intervals.
The extracted data is transmitted to the PBM using VA Mailman. The MailMan message headers display how many messages were sent for a particular module along with the facility name and number from which the data was extracted. The header easily identifies the module from which the data was extracted, and confirmation messages include the number of MailMan messages generated for each module.
Features
Pharmacy Benefits Management contains the following:
- Breakout of Inpatient Medications IV and Unit Dose, Outpatient Pharmacy, and Controlled Substance modules by dispensing occurrence.
- Breakout of procurement information by line item.
- Collection of the Prime Vendor Procurement Information (requires implementation of Drug Accountability V 3.0), Pharmacy AMIS data, Laboratory data, and Patient and Provider information.
- Capture of controlled substance dispensing to patients if electronic Controlled Substance Administration Record (CSAR) is implemented with Controlled Substance Version 3.0.
- Extraction of data and generation of drug and statistical data summary reports by inpatient division or outpatient site whenever possible.
- Inclusion of National Formulary Indicator and Restriction.
- Mechanism to monitor the successful completion of the automatic monthly extraction job and to notify users if a problem exists.
Pharmacy: Pharmacy Data Management (PDM)
Overview
The Pharmacy Data Management (PDM) package provides tools for managing site configurable data in pharmacy files. It includes tools for creating the Pharmacy Orderable Items and maintaining files necessary for the Computerized Patients Records Systems (CPRS). PDM consolidates tools for managing the various pharmacy software products, such as Outpatient Pharmacy and Inpatient Medications, to facilitate the maintenance of files used within these applications. Prior to the release of the Pharmacy Data Management (PDM) software, the maintenance of pharmaceutical items within the local DRUG file (#50) was accomplished using application specific options. PDM provides a single option to maintain this file to facilitate this process.
Features
Pharmacy Data Management provides:
- Tools for managing pharmacy orderable items.
- Centralized control of pharmacy files and frequently used options into one location.
- A new drug enter/edit option, which allows the user to edit fields for all pharmacy packages.
- The ability to identify drug interactions.
- Tools for marking drugs to be transmitted to the Consolidated Mail Outpatient Pharmacies.
- Local point-of-sale billing functionality for Electronic Claims Management Engine (ECME) electronic claim submission.
Pharmacy: Pharmacy Prescription Practices (PPP)
Overview
The Pharmacy Prescription Practices (PPP) package provides VA medical centers with the ability to determine whether a patient has been seen at other VA facilities and to request current pharmacy information from those facilities prior to the patient appearing for a scheduled outpatient visit. This information alerts pharmacy personnel to the existence of medications that may have been prescribed at other VA facilities and prevents possible drug abuse or adverse medication interaction.
The PPP software is integrated with other VistA applications. It interfaces with the Patient Data Exchange (PDX) module to provide a method of extracting pharmacy data from remote hospitals, the Minimal Patient Dataset (MPD) module to provide a history of patient visits, the Patient Information Management System (PIMS) to provide scheduled clinic appointments, and the Pharmacy module to provide active pharmacy data on local patients.
Features
The Pharmacy Prescription Practices package:
- Alerts pharmacy personnel to the existence of medications that may have been prescribed at other facilities.
- Builds a file of all patients currently registered at the medical center who have visited other VA medical centers.
- Allows the software to be tailored specifically to meet the needs of the various sites through a number of site-specific parameters.
- Provides several outputs containing information such as the medication profile, significant events and error conditions encountered while running the software, and statistical data.
- Automatically sends a PDX request for the medication profile to all other facilities visited by a patient scheduled for a clinic appointment.
Primary Care Management Module (PCMM)
Overview
In the outpatient setting, patients are assigned a primary care team and provider who are responsible for delivering essential health care, coordinating all health care services, and serving as the point of access for specialty care. Associate Primary Care Providers (APs) provide primary care to patients under the supervision of the Primary Care Provider (PCP). PCMM supports both primary care and non-primary care teams. The software allows one to create, set up, and define teams; create and assign positions to the team; assign staff to the positions; assign patients to the team; and assign patients to providers' positions.
In PCMM, primary care providers have an assigned �€œnumber of patients allowed�€ which is compared with the �€œnumber of patients actual�€ to determine if more patients may be assigned to the provider. PCMM functionality assists in maintaining accurate, active patient listings for primary care teams and panels. By unassigning patients who have not seen their primary care providers in a specified amount of time, new patients may be assigned. Unassigned patients are readily reassigned to their previous primary care team and provider if they return for care. When a patient cannot be assigned to a primary care team or position, the PCMM software asks if the patient should be placed on the Electronic Wait List. PCMM Wait List reports assist in the management of patients awaiting a primary care team or provider assignment. The amount of time the APs and PCPs spend providing direct primary care is also entered and measures the capacity of each institution (and VHA as a whole) to provide outpatient primary care. PCMM also screens staff assignments to PCP and AP positions to assure the data on providers is correct.
The primary care patient, provider, and team information captured in PCMM is sent to the Austin Automation Center and the National Patient Care Database. Some PCMM information is available in the KLF Reports. Additionally, the Office of Performance and Quality Measures utilizes PCMM data for national reporting and performance measures.
Features
- Uses a graphical user interface (GUI) for creating teams and provider positions as well as assigning staff to the provider positions.
- Ability to assign/unassign patients to primary care and non-primary care teams and providers both in GUI and VistA roll-and-scroll.
- Automates patient unassignment from primary care teams and providers if the patient has not seen their primary care provider for a specified time or when a patient's date of death is entered.
- Screens assignments to PCP and AP positions based on provider type and person class.
- Produces patient-oriented, practitioner-oriented, and team-oriented reports.
- Transmits data for primary care teams, providers, and patients to Austin in Health Level Seven (HL7) message format and provides the ability to receive/process transmission errors.
- Ability to control transmission of MailMan messages to team positions.
Prosthetics
Overview
The Veterans Health Information Systems and Technology Architecture (VistA) Prosthetics package automates purchasing. The Prosthetics module enhances patient care by determining what prosthetic services and devices have been provided to the veteran in the past, and decreasing the time required for the order, delivery, and/or repair of devices. The Prosthetics package provides control and auditing of expenditures and generates management reports.
File:Vista monograph2005 06 html 0.gifFeatures
- The Purchasing module interfaces with IFCAP (Integrated Funds, Distribution, Control Point Activity, Accounting and Procurement). Users enter requests to purchase and repair items or services using online VA forms or Purchase Card that allows tracking of the transactions.
- The Electronic Record of Prosthetic Services (VAF 10-2319) tracks demographics, disability codes, new purchases, repairs/replacements, service cards, clothing allowance, automobile adaptive equipment, and Home Improvement Structural Alterations (HISA).
- The Lab module has Orthotic Lab, Restoration Lab, Shoe Last Clinics, Wheelchair Repair Shops, and the Denver Distribution Center.
- The Inventory module tracks quantities of prosthetic items that facilities have in stock.
- The Administrative Home Oxygen module manages vendor billing and current prescriptions.
- The Suspense module tracks patient requests for prosthetic appliances or services through Prosthetics or Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS).
- The National Prosthetics Patient Database (NPPD) module captures medical center Prosthetic patient transaction data.
Quality: Audiology And Speech Analysis And Reporting (QUASAR)
Overview
Quality: Audiology and Speech Analysis and Reporting (QUASAR) is a VistAsoftware package written for the Audiology and Speech Pathology Service. QUASAR is used to enter, edit, and retrieve data for each episode of care.
Features
- Provides automatic transmission of visit data to the Patient Care Encounter (PCE) program in order to incorporate QUASAR visit data in Ambulatory Care Reporting Program (ACRP) and in the Decision Support System (DSS).
- Produces a variety of reports useful to local managers, medical center management, and central planners.
- Contains a Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) FileMan function that permits users to generate customized reports.
- Produces an automated Cost Distribution Report (CDR) RCS-10-01 41.
- Generates and processes Audiology compensation and pension visits through an agreement with the Automated Medical Information Exchange (AMIE) package.
- Allows input of a patient's audiogram and display of audiometric data in graphical or tabular format. The audiogram may then be signed and transmitted to the VA Denver Distribution Center (DDC) for inclusion in a patient's hearing aid order. The audiogram will also be recorded in the DDC's national database of audiometric data.
Radiology/Nuclear Medicine
Overview
Radiology/Nuclear Medicine is a comprehensive software package designed to assist with the functions related to processing patients for imaging examinations. The Radiology/Nuclear Medicine package automates the entire range of diagnostic functions performed in imaging departments, including order entry of requests, registration of patients for exams, processing of exams, recording of reports/results, verification of reports on-line, displaying/printing results for clinical staff, automatic tracking of requests/exams/reports, and generation of management statistics/reports, both recurring and ad hoc.
Features
Functionality is screened by Imaging Type to make it look as if there are separate sub-packages. Many options are also screened by or allow selection by division and/or imaging location.
- There is on-line patient registration for exams, automatic printing of flash cards and jacket labels, and transcription of patient radiological/nuclear medicine reports.
- Management reports include workload, complications and ad hoc summaries, daily activity logs, examination statistics, and performance indicators.
- Health Level 7 (HL7) (e.g., voice-to-text and PACS equipment) standard for interfacing with non- VistA computer systems is supported for the exchange of radiology/nuclear medicine results.
- There is on-line physician verification of radiological/nuclear medicine exam reports using electronic signatures.
- Stop codes and procedures associated with a radiological/nuclear medicine exam are automatically credited for reimbursement purposes.
- It interfaces with the Computerized Patient Record System module for entry of radiology/nuclear medicine requests and display of results to clinical staff. It interfaces with the Adverse Reaction Tracking (ART) module by allowing users to add contrast media reactions to ART via the Radiology/Nuclear Medicine package. It interfaces with the Women's Health module by automatically adding mammogram and ultrasound procedures for female patients to the Women's Health database.
- It supports entry of multiple diagnostic codes and multiple interpreting by residents and staff.
- There is a single combined report for a set of related procedures. This is a "printset" mechanism for entering a single report for all descendent cases registered from a parent order.
- It provides the ability to enter and edit information specific to radiopharmaceuticals for Nuclear Medicine.
- It allows on-line verification of "STAT" category requests.
- It allows for the selection and printing of multiple reports.
Remote Order Entry System (ROES)
'Overview'
The Remote Order Entry System (ROES) is the front-end of the Denver Distribution Center's (DDC) supply chain/order fulfillment production system. ROES is used by Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) clinicians to place orders for certain types of medical products and services that are maintained under contract by the DDC. The most substantial product line handled through ROES is custom hearing aids. As implied by the name, custom hearing aids are highly specialized devices custom made for individual veteran patients. The ROES application and database are tailored for efficiency in ordering these unique devices and other items available from the DDC. Other product lines handled through ROES include stock hearing aids, hearing aid accessories and batteries, prosthetic items, aids for the visually impaired, and assistive devices. The hearing aid repair is a line of service provided by the DDC and facilitated by ROES. The ROES application and database integrates the DDC enterprise business functions of contracting/acquisition management, order fulfillment, distribution management, finance, and product life cycle support. Extensive order tracking, serialized device registration, patient/device history, and sales/financial reporting are also supported by the database.
'Features'
ROES uses advanced technologies and practices in software design, supporting hardware platform, database management, and network integration. ROES also integrates Web-based application architecture with a VistA environment, obtaining an optimum mix of decentralized VistA interfacing with centralized data management. The database is optimized for the DDC's progressive procurement and distribution practices, advanced general business practices, and current VA regulations.
Scheduling
Overview
The Scheduling module automates all aspects of the outpatient appointment process, including the ability to check in/check out patients, clinic set-up and maintenance, enrollment/scheduling/discharge of patients to and from various clinics, and the generation of managerial reports, statistical reports, patient letters, and workload reporting. It provides for multiple-appointment booking, which enables the user to schedule, at one time, numerous appointments on a consecutive day/week basis. This pattern of scheduling supports requirements for clinics such as dialysis treatment and physical therapy.
The system may display numerous messages when an appointment is scheduled depending on the availability of the slot requested. These include notification that the appointment is an overbook, the patient already has an appointment scheduled for that date and time, or the appointment cannot be made due to previous inactivation of the designated clinic. In addition, certain classification questions are prompted during the check out process (if applicable) to determine if treatment rendered was connected to special circumstances (such as Agent Orange, Ionizing Radiation, Persian Gulf, etc.).
Patient Appointment Information gathers appointment data to be loaded into the National Database in Austin for statistical reporting. Patient appointments are scanned from September 1, 2002 to the present, and appointment data meeting specified criteria are transmitted to the Austin Automation Center (AAC). Subsequent transmissions will update the National Database. This additional data supplements the existing Clinic Appointment Wait Time extracts.
The functions within Scheduling currently fall into four major categories: Appointment Scheduling, Local Reporting (outputs), National Data Collection, and Module Set-Up and Maintenance.
Features
- Creates fixed or variable length clinic patterns.
- Provides on-line clinic availability and system identification of conditions such as first available appointment.
- Interacts with the Record Tracking module allowing chart request at the time of appointment scheduling.
- Generates cancellation, no-show, and pre-appointment letters.
- Provides on-line transmission of pertinent visit information to the national database at the Austin Automation Center.
- Patient Appointment Information functionality collects and formats data for Health Level Seven (HL7) batch transmission. It also utilizes new hardware technologies for transmitting data via the VA's Intranet.
Social Work
Overview
The Social Work package is designed to facilitate the Social Work Service functions within a medical facility and is composed of Case Management, Clinical Assessment, and Community Resource. The Case Management software is used for managing social work cases (e.g., opening and closing cases, recording problems and outcomes, storing referrals) and for generation of reports that are transmitted quarterly to VA Central Office. The Clinical Assessment software provides a method of identifying, upon admission, patients most likely to require social work assistance before or after discharge. The hospital stay may be minimized with the anticipation of patients' domestic or social needs prior to discharge. The Community Resource software allows the social worker to build a network of local community agencies that can serve the veteran. The network enables the worker to expediently match the needs of the client to the existing community resources, thereby increasing productivity and viable referrals.
Features
The Social Work package:
- Features automatic screening that uses predetermined and site-specific criteria (e.g., veteran with no permanent address) to determine if a patient needs the services of Social Work Service prior to discharge.
- Creates networks of local community agencies (e.g., alcohol treatment, housing, health) that can serve veterans.
- Compiles a list of community resources by user-selected category (e.g., name, town, type, zip code).
- Identifies local residential care homes and maintains detailed information on the homes (e.g., rates, vacancies, residents, date home assessed by a VA social worker).
- Allows workers to track patients and homes in the residential care home program by home and patient registry printouts.
- Facilitates mailings to residential care home sponsors by printing address labels.
- Tracks caseloads by recording the openings and closings of cases.
- Compiles and produces monthly and quarterly reports. Transmits data electronically via the network MailMan module.
- Provides patient teaching and monitoring necessary for VHA-wide system of coordination/care management services.
- Provides for standardized Psycho-social Database/Assessment for inclusion in patient medical records. Also, provides mechanism for entering progress notes.
- Provides for automated quality management monitors and reviews.
Spinal Cord Dysfunction
Overview
The Spinal Cord Dysfunction (SCD) package permits the identification and tracking of patients with a spinal cord dysfunction due to trauma or disease and the medical resources utilized during their treatment. The module supports the maintenance of local and national registries. It includes features for clinical, management, and research staff. Clinicians benefit from the ability to see profiles of Spinal Cord Dysfunction patients, and the software helps them ensure that regular annual exams are completed with functionality to measure patient outcomes. Managers have a suite of reports that reflect the resources needed to care for Spinal Cord Dysfunction patients, and researchers have access to a national registry for all veteran Spinal Cord Dysfunction patients and their associated health care events.
Features
- Allows for the entry and tracking of a patient's functional measures over time. This includes the American Spinal Injury Association (ASIA) Impairment Scale, Functional Independence Measure (FIM), Craig Handicap Assessment and Reporting Technique (CHART), Functional Assessment Measure (FAM), Duke University of Illness Index (DIENER, DUSOI), and for Multiple Sclerosis patients, Kurtzke Functional Systems Scales and Expanded Disability Status Scales (EDSS).
- Generates a Health Level Seven (HL7) message to a national registry whenever a new record is created or a current record is edited. The central registry is used to provide VA-wide review of patient demographics, clinical aspects of injury and disease, and resource utilization involved in providing care to patients.
- Provides a link to the Health Summary package.
- Provides a variety of reports, including ad hoc and data filtering capabilities:
- New applications for inpatient care, current inpatient/outpatient activity, and discharges.
- Patient outcome information.
- Registrant injury reports.
- Self reported functional measures and summaries of clinician reported measures.
- Annual rehabilitation evaluations: offered, received and due.
- Mailing labels and Aggregate Outcomes Reports.
Surgery
Overview
The Surgery package is designed to be used by surgeons, surgical residents, anesthetists, operating room nurses, and other surgical staff. This software integrates scheduling surgical cases and tracking clinical patient data to provide a variety of administrative and clinical reports.
In the operating room, the software provides on-line access to the clinical record and automatically generates post-operative reports, including the Nurse Intraoperative Report. Automated scheduling provides better operating room utilization and greater ease in distributing the operating room schedule, and the software generates monthly, quarterly, and annual surgical reports, thus reducing the amount of clinical overhead associated with the management of the Surgical Service. The Surgery software facilitates morbidity and mortality tracking and other complications, providing vital information to the Chief of Surgery and to VA Central Office.
Features
The Surgery package:
- Allows a surgeon to generate requests for surgical procedures.
- Allows operating room scheduling managers to assign operating rooms and time slots and generates operating room schedules.
- Allows for the rescheduling or cancellation of operative procedures.
- Facilitates entry of information specific to an individual surgical case (e.g., staff, times, diagnoses, complications, anesthesia).
- Provides for on-line entry of data inside the operating room during the actual operative procedure.
- Generates patient records and nurse reports.
- Produces management reports (e.g., Annual Report of Surgical Procedures, Attending Surgeons Report, Nurse Staffing Report, Anesthesia Management).
- Produces quarterly and annual reports for VA Central Office.
- Provides secured access to lists of cancellations and the Morbidity and Mortality Report.
- Extracts data necessary to monitor risk management issues.
- Provides additional checks for Transfusion Error Risk Management.
- Includes a generic Health Level Seven (HL7) interface for use with commercial Automated Anesthesia Information Systems.
- Includes an interface to the Patient Care Encounters (PCE) software that allows ambulatory procedure workload information to be transmitted to the National Patient Care Database (NPCD) at Austin.
- Allows for on-line electronic signature of the Nurse Intraoperative Report and the Anesthesia Report
Surgery: Risk Assessment
Overview
The Risk Assessment module of the Surgery software provides medical facilities a mechanism to track information relating to both surgical risk and operative mortality. This information, once downloaded to the VA national database, supports a program of total quality improvement in Surgery in VHA.
The National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) was established to develop distributions of observed-to-expected (O/E) mortality and morbidity ratios (risk-adjusted outcomes) across facilities for all operations, for eight major sub-specialties, and for cardiac surgery. At each of VA's medical facilities
performing surgery, a Surgical Clinical Nurse Reviewer, under the direction of the Chief of Surgery, collects risk and outcome data. All patients undergoing major surgery requiring general, spinal, or epidural anesthesia are assessed. Completed non-cardiac assessments are electronically transmitted to the Hines, IL Center for Cooperative Studies in Health Services (CCSHS), while cardiac assessments are transmitted to the Denver Cardiac Coordinating Center for data analysis. At these centers, models are continually developed and enhanced for the major surgical subspecialties and procedure-specific cardiac surgeries. Managerial reports are prepared at the coordinating centers to provide Chiefs of Surgery with their own risk-adjusted data compared to the VA national averages.
Features
The Risk Assessment module:
- Provides for entry of non-cardiac assessment information including pre-operative information, laboratory test results, operation information, and intraoperative and post-operative occurrences.
- Provides for entry of cardiac assessment information, including clinical information, cardiac catheterization and angiographic data, operative risk summary data, cardiac procedures requiring cardio-pulmonary bypass, and intraoperative and post-operative occurrences.
- Creates a Surgery Risk Assessment report on each patient assessed.
- Transmits completed Surgery Risk Assessments to Hines CCSHS and Denver Cardiac Coordinating Center.
- Lists Surgery Risk Assessments by categories, including complete, incomplete, and transmitted assessments, as well as lists of major surgical cases and all surgical cases.
- Generates a monthly Surgical Case Workload Report.
- Prints follow-up letters to patients 30 days after a procedure.
VistA Imaging System
Not in WorldVistA
Uses proprietary components not available outside the VA
Alternative: O3DPACS
Open Source Java based O3 DPACS IHE compliant from O3 Consortium.
VistA Imaging System (Continued)
Overview
The major goal of VISTA Imaging is to facilitate medical decision-making by delivering complete multimedia patient information to the clinician's desktop in an integrated manner. Windows-based workstations, which are interfaced to the main hospital system in a client-server architecture, make images and associated text data available at all times anywhere in the hospital.
VISTA Imaging handles high quality image data from many specialties, including cardiology, pulmonary and gastrointestinal medicine, pathology, radiology, hematology, and nuclear medicine. VISTA Imaging can also process textual reports from the hospital information system, scanned documents and electrocardiograms.
VISTA Imaging is integrated with the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) to provide a comprehensive electronic patient record. VISTA Imaging improves the quality of patient care, enhances clinicians' communication, and is used routinely for daily work, conferences, morning reports, educational seminars, and during ward rounds.
VISTA Imaging's diagnostic display software (VISTARad) can be used for the filmless interpretation of radiology studies and for radiology workflow management.
VISTA Imaging is made up of the following components:
- Core Infrastructure
- Document Imaging
- Filmless Radiology
- Imaging Ancillary Systems
Each component is described in the following pages.
V'istA'Imaging �€" continued
Features
VISTA Imaging:
- Provides display, manipulation, and management functions for a wide variety of medical images such as radiographs, sonograms, EKG tracings, gastroenterology studies, pulmonary bronchoscope exams, podiatry, dermatology and ophthalmology images. Images can be any sort of multimedia data, including digital images, motion video clips, graphics, scanned documents, and audio files.
- Is integrated with CPRS, allowing users to view images automatically for a selected patient. When a user views a radiology report or progress note in CPRS, the associated images are easily available.
- Provides an interface between VISTA and commercial PACS systems using DICOM Gateway software.
- Automatically acquires complete studies from DICOM-compliant modalities (CT, MRI, digital x-ray, ultrasound, etc), associates the studies with the correct patient and report, and stores the studies in VISTA Imaging for inclusion in the electronic patient record.
- Manages image file storage, management, and retrieval from magnetic and optical disk servers and supports data capture, storage, and retrieval over a local or wide area network (WAN).
- Provides access to electronic medical records from remote VA medical facilities over the VA intranet, if appropriate access privileges are assigned.
VistA Imaging: Core Infrastructure
Overview
The Core Imaging Infrastructure includes the components used to capture, store, and display all types of images. Images can be captured using video cameras, digital cameras, document and color scanners, x-ray scanners, and files created by commercial capture software. Images can also be directly acquired from DICOM-compliant devices such as CT scanners, MR scanners and digital x-ray machines.
Captured images are accessible through VISTA Imaging or the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) graphical user interface (GUI) on the clinician's desktop. Viewing a procedure/exam report or progress note in CPRS allows the user to automatically access any associated images.
Core Imaging Infrastructure is made up of the following:
- DICOM text gateways, which provide patient and order information to medical devices (such as CT scanners and digital radiography systems), allowing selection of the examination to be performed. The data provided by DICOM text gateways complies with the DICOM Modality Worklist standard. DICOM text gateways can also be used to communicate patient and order information to commercial PACS (Picture Archiving and Communications Systems).
- DICOM image gateways, which allow VISTA Imaging to receive images from PACS systems or acquisition devices. Image gateways can also be used to transfer images from the VISTA system to any DICOM-compliant storage devices for display, printing, or teleradiology purposes.
- Windows-based workstation software for image display and capture.
- The Background Processor, which manages image storage on various network devices, including magnetic storage (RAID) and optical storage (jukebox) as a long-term archive.
Core Infrastructure �€" continued
- The VISTA Imaging database, which manages the links between images and patient electronic records.
- The commercially available equipment required by VISTA Imaging, including magnetic servers, optical disk jukeboxes, and utility workstations.
Features
The Core Imaging Infrastructure:
- Acquires images and multimedia data.
- Stores images to allow immediate access and long-term permanent storage.
- Communicates and displays images in a timely manner.
- Processes different types of images from different specialties.
- Links images to VistA's integrated patient record so that they can be retrieved by patient or study/progress note.
- Protects security and privacy of images, and prevents alteration of images after capture.
- Enables remote viewing and capture of images.
- Uses non-proprietary hardware.
VistA Imaging: Document Imaging
Overview
Document Imaging allows scanned and electronically generated documents to be associated with the online patient record and displayed on clinical workstations. The benefits of Document Imaging include:
- Online availability of all information in the electronic patient record, including handwritten papers, drawings, signed documents, and medical correspondence.
- Linkage of paper-based patient information to the electronic patient record, making all patient information quickly available and easily retrievable from a single source.
- Immediate availability of critical documents, such as advance directives and informed consent forms, at the time of need.
- Elimination of lost or misfiled medical chart information.
- Potential savings due to reduced medical records staff and file room costs. Possible benefits include decreased retrieval, filing and delivery functions, reduced volume of paper records, and faster retrieval time for clinicians.
Document Imaging will also provide interfaces to commercial document scanning systems and systems that generate documents electronically.
Features
- Scanning and indexing of black-and-white, grayscale, and color documents, including: signed advance directives, consent forms, annotated drawings, outside medical records documents, and administrative documents such as Means Test forms.
- Automatic transmission of signed means test documents to the Health Eligibility Center (HEC), in compliance with VA requirements.
- Document image storage in short and long term storage devices.
- Display of images for clinical and administrative purposes.
- Printing of document images.
VistA Imaging: Filmless Radiology
Overview
Filmless Radiology uses high-resolution workstations and high-speed servers to allow radiology departments to operate without generating x-ray film. Workstations running VISTARad, VISTA Imaging's diagnostic image display software, are used by radiologists for the online interpretation of images acquired by CR, CT, MRI, and other modalities. VISTARad is integrated with the VistA Hospital Information System and with the Radiology Package in particular.
Features
- Exam lists, which are based on exam status or patient name, are used to divide the pool of available exams into useful categories. Exam lists are created using information from the Radiology package and the VISTA patient database.
- Site-specific custom lists can be created to reflect the workflow of individual departments.
- In addition to images, other parts of a patient's medical record, such as laboratory and pathology information, can be displayed using the VISTA Health Summary reporting capability.
'VistA'Imaging: Filmless Radiology �€" continued
- A full range of image display and manipulation features for radiology and nuclear medicine images are provided.
- Multiple exams can be displayed concurrently, allowing for comparisons with prior studies.
- Exam locks are used to prevent duplication of effort.
- Specialized display tools are provided for CT, MRI, and angiography exams, including cine viewing, series linking, and series synchronization.
VistA Imaging: Imaging Ancillary Systems
Overview
VistA Imaging's Ancillary Systems component captures, stores, and displays images for a particular service or specialty. This may be accomplished using the Clinical Capture workstation or by interfaces to commercial systems. These commercial systems are typically small systems, and often incorporate special-purpose hardware. They often have components that assist clinicians in creating exam or procedure reports.
Features
- Allows direct capture of images from a variety of sources, such as standard video outputs from medical devices, and digital cameras.
- Interfaces to a commercial EKG system for display of electrocardiograms on clinical workstations.
- Supports automatic DICOM interfaces for capture of specialty images from compliant systems (DICOM Modality Worklist Conformance Requirements are provided to sites purchasing specialty equipment).
- In the future DICOM and Clinical Workstation support for ophthalmology, dental, endoscopy, pathology, cardiology, and other specialties will be included.
- Support for acquisition of DICOM Structured Report information is planned for the future.
Visual Impairment Service Team (VIST)
Overview
The Visual Impairment Service Team (VIST) program is designed to enhance the efficiency of the Visual Impairment Service Team programs within the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). With this program, Visual Impairment Service Teams are able to easily manage and track activities and services provided to blinded veterans in their service area. This program integrates several fields of patient data to produce a variety of reports. The VIST patient record printout can be used in place of VA Form 10-1371 and is a more versatile document than the card.
Features
- Enhances the efficiency of the Visual Impairment Service Team programs.
- Provides a way to easily track and manage activities and services provided to blinded veterans.
- Provides a wide variety of reports based on patient data.
- Blinded veterans can be quickly added or deleted from the rolls.
The new Blind Rehabilitation V.5.0 will integrate all four segments of Blind Rehabilitation Service, which includes VA Headquarters and Visual Impairment Service Teams (VIST), Blind Rehabilitation Outpatient Specialists (BROS), and Blind Rehabilitation Centers (BRC). It will also store data from surveys on patient demographics, satisfaction, and outcome. The data is expected to determine outcome measures and provide a national information system for the Department of Veterans Affairs.
A few of the main features will be: A Web-based user interface following W3Chtml specifications use of existing VistA tools, HealtheVet architecture and Data Base Integration Agreements (DBIAs) to interface with existing VistA applications for more streamlined data entry, and retrieval and to minimize duplicated data entry. Multi-divisional data capture and reporting will be a new feature, as well as a streamlined centralized database.
Vitals/Measurements
Overview
The Vitals/Measurements application is designed to store, in the patient's electronic medical record, all vital signs and various measurements associated with a patient's hospital stay or outpatient clinic visit. Data can be accessed by several Veterans Health Information Systems and Technology Architecture VistA applications (e.g., Health Summary and Pharmacy) that interface with the Vitals/Measurements application.
Features
- Contains a Graphical User Interface (GUI) to make editing and viewing of data easier.
- Supports documentation of a patient's vital signs (e.g., temperature, pulse, and respiration).
- Tracks a patient's height, weight, central venous pressure (CVP), circumference/girth, and oxygen saturation via oximetry with supplemental oxygen information.
- Supports documentation of detailed or positional blood pressures for a patient (i.e., bilateral blood pressures taken in a sitting, standing, and lying position).
- Associates qualifiers (alpha characters appended to the measurement's numeric value) to provide a more detailed description of the patient's vitals/measurements.
- Prints patient's cumulative measurements on the Vital Signs Record and the Cumulative Vitals Report.
- Displays latest information on all of the patient's vitals/measurements in both metric equivalents and U.S. customary units along with the date/time the information was obtained.
- Prints an expanded vitals graphic report, which includes the patient's intake and output when present in the patient's database (refer to the Intake and Output application).
- Allows facilities to establish hospital-wide high and low values for each vital sign or measurement.
- Identifies abnormal patient values on vitals/measurements reports (those values outside the high and low range).
- Prints the following patient measurements in a linear graphic format when using a Kyocera F-800A or HP compatible (programmable) printer:
- Temperature and pulse
- Blood pressure
- Weight
- Pulse oximetry and respiration
- Pain
- If reports are printed on a dot matrix printer, plotted data values are not connected by a line.
- Supports the archiving and purging of patient measurements, which are no longer required on the production account, through FileMan.
- Passes patient vitals/measurements information (numeric values only) within a specific date range to the Health Summary application.
- Records a reason for the omission of a patient's vitals/measurements.
Women's Health
Overview
The purpose of the Women's Health package is to establish a computerized tracking system that generates aggregate data at the facility level. The product would assist in the assessment of various aspects of care provided to women veterans, such as efficiency of care, outcomes of care, and quality of care for individual patients. It is intended to: provide data to determine if there are differences in disease frequency between women veterans and the general population; provide information for clinical guideline development and determine if preventive health screening guidelines developed for the general population are applicable, or need modification in the women veteran population; and provide workload, preventive screening, women veterans health profile, outcome measurement, and provider profiling data.
Features
The Women's Health software is composed of three main modules: Patient Management, Management Reports, and Manager's Functions.
Patient Management is the portion of the software used to manage individual patient care, that is, their procedures, due dates, and correspondence. Under the Patient Management menu, it is possible to maintain patient data such as the date of the next PAP smear, colposcopy or mammogram, the patient's pregnancy and her EDC (due date), as well as the patient's current PAP regimen. It is also possible to track the patient's individual procedures: the date performed, the provider and clinic, the results or diagnosis, etc. Notifications (letters and phone calls) may also be tracked. A file of form letters has been included in the software, and these letters may be edited and personalized for a clinic's particular needs. Reminder letters can be queued months in advance of a future appointment, then printed and mailed out shortly before the tentative appointment.
Management Reports is the portion of the software used to print epidemiological reports, such as the number of women who received a mammogram for the selected time period or the number of patients having abnormal PAP results during a selected time period. Under the Management Reports menu, it is possible to produce lists of patients who are past their due dates for follow-up procedures. It is also possible to store program statistics by date for later comparison of program trends and progress.
Manager's Functions is that portion of the software that provides the ADPAC with a set of utilities for configuring the software to the specific needs of the site. It also provides utilities for other program needs, such as customizing tables, making special edits to patient data (e.g., pregnancy log, PAP regimen log), printing notification letters, running error reports, and documenting laboratory results. By using the File Maintenance options under the Manager's Functions menu, it is possible to maintain site-specific parameters, such as the text of form letters, the types of notifications and their synonyms, how and when letters get printed, and several defaults relating to dates.
Management and Financial Systems
Management and Financial Systems manages portfolios for the core legacy systems, aids in the planning, development, and implementation of enterprise-wide projects, and provides billing and patient records management solutions to our internal customers and end users, which results in a positive experience for our most prized customer, the Veteran.
The MFS portfolio focuses on:
- Patient Financial Services Systems
- Fee Basis Claims Processing
- Decision Support Systems
- Core Financial Logistics Systems
- Health Revenue Center
- HIPAA
- Future Integration with Commercial Applications
Accounts Receivable (AR)
Overview
The Accounts Receivable (AR) package is a system of accounting and receivables management. The AR package automates the debt collection process and a billing module is available to create non-medical care debts. Functionality is available to establish, follow-up on, collect against, and track all medical facility debts.
Some of the debts owed to a VA facility may include patient care covered by health insurance companies, veteran copayments, pharmacy prescription copayments, employee salary overpayments, lost or damaged property, vendor collectibles, benefit overpayments, and services provided under a sharing agreement with another institution.
Features
- Provides a generic billing system used to generate standardized bills.
- Receives patient and third party billing information passed automatically from the Integrated Billing (IB) package.
- Sends electronic transmissions to the Consolidated Copayment Processing Center (CCPC) in Austin, TX to generate patient statements.
- Automatically processes first party payments received from the Lockbox Bank.
- Calculates interest and administrative charges.
- Records, processes, and tracks payment information from patients, vendors, insurance companies, employees, and institutions.
- Records and tracks credit balances if debtors have overpaid their accounts, and processes refunds as appropriate.
- Updates Financial Management System (FMS) with Accounts Receivable data.
- Updates the Medical Care Collections Fund (MCCF) National Database with Accounts Receivable data.
- Tracks and forwards eligible delinquent patient, vendor, and employee debts to the Treasury Program for offset.
- Tracks delinquent debts for Regional Counsel and Department of Justice for enforced collection.
- Provides the ability to set up repayment plans.
- Provides reports and inquiries for the follow-up and maintenance of outstanding receivables.
- Provides for transmission of certain AR bills over 90 days old to be referred to the Debt Management Center (DMC) for collection action.
- Automatically processes electronic payments and explanation of benefits documents received from third party insurance carriers through the EDI Lockbox bank.
Automated Information Collection System (AICS)
Overview
The Automated Information Collection System (AICS) software supports outpatient clinical efforts through the creation and printing of encounter forms that display relevant clinical information, and provides for the entry of clinical encounter data for local and national needs. These encounter forms are used to display relevant patient data for use during the appointment (e.g., demographics, allergies, clinical reminders, and problems) and to collect data about the appointment (e.g., procedures, providers, and diagnoses), thus providing an organized method of data collection through scanning or data entry. Many of the lists that a user sees in Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) for input of outpatient encounter data are based on lists created when designing encounter forms for clinics.
A form generator is included, which allows sites to design forms which meet local medical facility needs. There is enough flexibility in the software so sites can build forms that meet their individual clinical, billing, and resource requirements. The encounter form may be filed in the clinical record.
A print manager is included that allows sites to define reports to print in conjunction with the encounter form and any supplemental forms for each appointment. Reports can be defined to print at the division, clinic group, or clinic level. Utilities are available to manage when and where forms may print.
Data from encounter forms can be inputted (into VistA) in one of two ways. Forms can be scanned on client workstations with the data is automatically transmitted to the VistA server, or clerks can key in data from forms.
Features
- Provides a form design utility that allows creation of attractive and easy to use forms for each clinic.
- Allows forms to be designed to print with patient data displayed, such as patient demographics, insurance information, allergies, clinical reminders that are due, and active problems.
- Allows for the creation of forms to collect data such as procedures, diagnoses, problems, providers, progress notes, vital signs, and PCE-related data such as exams, health factors, patient education, skin tests, and immunizations.
- Provides a print manager that allows all clinic-specific forms to print with the encounter form for an appointment. The print manager also provides a setup system that, once accomplished, no longer requires daily user intervention.
- Provides an import/export utility that makes it easier for sites to exchange forms they have already created.
- Provides forms tracking to ensure that each form printed is processed or accounted for.
- Manual data entry options are available to allow data to be key entered by a clerk and passed to PCE to be stored.
Beneficiary Travel
Overview
The Beneficiary Travel module provides the ability to perform the functions involved in issuing beneficiary travel pay. Travel reimbursement is provided to specified categories of eligible veterans. It is also provided to non-employee attendants who are eligible for such reimbursement. These attendants will be issued travel pay under the veteran's name.
Payment for travel by special mode (ambulance, handicapped van, etc.) may be authorized if medically necessary and approved beforetravel begins, except in cases of medical emergency where delay would be hazardous to life or health.
For certain claims, the system will compute the amount payable from factors such as account type, parameter set-up of deductible amount per visit and per month, one-way or round-trip mileage, and applied costs.
Features
- Automatically computes the amount payable for claims with an account type of Compensation and Pension.
- Allows each site to define and edit site-specific beneficiary travel parameters.
- Produces a variety of statistical reports for a specified date range.
- Provides the ability to reprint the standard pre-formatted beneficiary travel form for cash reimbursement.
Compensation and Pension Records Interchange (CAPRI)
Overview
The Compensation and Pension Records Interchange (CAPRI) software was designed to promote efficient communications between the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and the Veterans Benefits Administration (VBA). It offers VBA Rating Veteran Service Representatives and Decision Review Officers help in building the rating decision documentation through on-line access to medical data. It creates a more efficient means of requesting compensation and pension examinations and navigating existing patient records.
CAPRI provides a Graphical User Interface (GUI) for the VistA Automated Medical Information Exchange (AMIE) II application. AMIE II is a List Manager application that automates the administrative procedures involved in sending medical information used in determining veteran benefit payments from the VA Medical Centers to the VA Regional Offices.
CAPRI handles most administrative aspects of the examination process.
Features
- Ability to add, edit, cancel exam requests.
- Allows patient record navigation to view such items as health summaries, progress notes, lab reports, consult requests/results, etc.
- Provides individual and cumulative pending exam tracking.
- Generates managerial and statistical reports.
- Integrates compensation and pension examination results into the veteran's medical record.
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT)
Overview
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes are used for reporting medical services and procedures performed by physicians. The purpose of the code is to provide a uniform language that will accurately describe medical, surgical, and diagnostic services, thereby providing an effective means for reliable nationwide communication among physicians, patients, and third parties. This system of terminology is the most widely accepted nomenclature for the reporting of physician procedures and services under government and private health insurance programs.
The CPT software includes all CPT codes to code outpatient services for reimbursement and workload purposes (as determined by the American Medical Association) and Health Care Financing Administration's Current Procedural Coding System (HCPCS) from the Health Care Financing Administration (HCFA). These codes may also be used to report inpatient services in certain instances.
Features
- Provides annual updates for CPT and HCFA codes.
- Provides several reports to display new, revised, or inactivated codes.
- Supplies detailed descriptions of CPT and HCFA codes.
Decision Support System (DSS) Extracts
Overview
The VistA Decision Support System (DSS) Extracts software provides a means of exporting data from selected VistA software modules and transmitting it to a Decision Support System (DSS) resident at the Austin Automation Center (AAC). This transfer is accomplished through a set of extract routines, intermediate files, audit reports, transmission, and purge routines. Data from VistA packages is stored by the extract routines in the intermediate files, where it is temporarily available for local use and auditing. The data is then transmitted to the AAC where it is formatted and uploaded into commercial software. After the data has been successfully uploaded into the commercial software, it is purged from the intermediate files.
Extracts consist of the following functions: implementation of extract processes; scheduling extracts, verifying extracts against other VistA reports, transmission of extracts to the commercial software, verification of transmission, and purging extracts.
Features
- Extracts data from the following VistA software packages:
- Audiology and Speech Pathology (QUASAR)
- Dental
- Event Capture
- Inpatient Medications
- Laboratory
- Mental Health
- Nursing
- Pharmacy Prescriptions
- PIMS (ADT and Scheduling Modules)
- Prosthetics
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Uses a roll-and-scroll format that allows users to perform the various functions by selecting the appropriate menu options.
- Uses VA Mailman to transmit data to commercial software resident at the AAC.
Diagnostic Related Group (DRG) Grouper
Overview
The Diagnostic Related Group (DRG) Grouper is based on the Medicare Grouper requirements as defined by the Health Care Financing Administration and as reported in the Federal Register. Each DRG represents a class of patients who are deemed medically comparable and who require approximately equal amounts of health care resources.
The module groups diagnostic and operation/procedure codes into the DRGs based on the combination of codes, age, sex, discharge status, and occurrence of death.
Features
- Provides annual updates that conform to the latest release of the commercial grouper.
- Functions within or apart from other modules.
- Supplies detailed descriptions of DRGs, diagnostic codes, and operation/procedure codes.
- Accepts one primary diagnosis and multiple secondary diagnostic codes and operation/procedure codes.
- Displays weighted work unit values as well as national and local high and low trim point values for each DRG.
Engineering
Overview
Engineering, also known as Automated Engineering Management System/Medical Equipment Reporting System (AEMS/MERS), facilitates the management of information needed to effectively discharge key operational responsibilities normally assigned to VA engineering organizations, such as:
- Equipment Management
- Work Control
- Space/Facility Management
The Engineering package was designed as a resource that can be shared by medical center administrative staff. Safeguards against unauthorized editing of key data elements of non-expendable (NX) equipment records have been designed into the system. Engineering maintains integration agreements with Integrated Funds Distribution, Control Point Activity, Accounting and Procurement (IFCAP) such that the status of work orders is automatically updated on the basis of orders for parts or service. The Engineering package is the VA's official record of inventory for capitalized personal property.
Features
- Uses bar codes for equipment inventory and preventive maintenance. Completed work orders are automatically posted to equipment histories.
- Tracks and controls work orders, maintaining annotated repair histories for medical and non-medical equipment. There is a separate menu option for display of incomplete work orders.
- Manages electronic work orders. Staff throughout a facility can enter work requests via a terminal or workstation. These requests are promptly reviewed by Engineering personnel and assigned to the appropriate maintenance shop.
- Identifies building features (square footage, floor coverings, window types, etc.) and keeps track of locks and keys.
- Provides capitalized personal property data to the Fixed Assets subsystem of the Financial Management System (FMS).
Equipment/Turn-In Request
Overview
The Equipment/Turn-In Request software provides additional functionality within the Integrated Funds Distribution, Control Point Activity, Accounting and Procurement (IFCAP) package, including the ability to enter an electronic request for new, non-expendable equipment and replacement equipment. It adds the functionality for tracking the request through the many stages of review, prior to its approval and becoming a permanent transaction. Users are allowed to turn in old equipment currently tracked in the Equipment Inventory file, generate an Engineering work order, and track its movement to its final disposition and removal from the inventory list. The Equipment/Turn-In Request serves as a records maintenance system, allowing the user to record important events throughout the ordering process. Such records can be printed in report format as supporting documentation about the equipment life cycle.
Features
- The software introduces a new position to the IFCAP package, the Consolidated Memorandum of Receipt (CMR) official. The CMR official is ultimately responsible for new and existing equipment located at the medical facilities.
- A requester can enter an electronic request for new or replacement equipment via a terminal.
- A requester can enter an electronic request to dispose of obsolete equipment.
- The CMR official can approve, edit, or cancel an equipment request.
- Engineering work orders can be generated for initial, additional, and replacement equipment.
Event Capture
Overview
The Event Capture software provides a mechanism to track and account for procedures and delivered services that are not handled in any other VistA package. The procedures and services tracked through Event Capture are associated with:
- The patient to whom they were delivered.
- The provider requesting the service or procedure.
- The Decision Support System (DSS) Unit responsible for delivering the service.
DSS Units typically represent the smallest identifiable work unit in a clinical service at the medical center and are defined by the VAMCs. A DSS Unit can represent any of the following:
- An entire service.
- A section of a service.
- A small section within a section.
- A medical equipment item used in patient procedures.
When creating or editing DSS Units, users choose what (if any) data is sent to PCE. The advantage of using Event Capture to send data to Patient Care Encounter (PCE) is that it eliminates the duplicate effort of entering the same workload data in the Scheduling software, then transmitting to PCE.
Features
- Allows each VAMC to utilize the software for its own resource/costing needs.
- Implements DSS Units.
- Assigns user access to all or specific DSS Units.
- Sets up Event Code Screens to define relevant procedures for a DSS Unit.
- Allows single and batch data entry for patient procedures.
- Generates reports for workload and other statistical tracking.
- Provides a Graphical User Interface to the ECS application.
- Allows user to upload patient encounter data to Event Capture from a spreadsheet.
- Files encounter records in PCE for DSS Units defined to send data to PCE.
- Generates DSS extracts.
Fee Basis
Overview
The Fee Basis package supports VHA's Fee for Service program, which is care authorized for veterans who are legally eligible and are in need of care that cannot feasibly be provided by a VA facility. A VA facility unable to meet the patient care requirements of a veteran may authorize fee basis services for short-term care, ongoing outpatient care, or home heath care from non-VA health care facilities. Bills for service are then submitted to the authorizing VA facility. The bill is reviewed by the facility and certified for payment through VA's payment center in Austin, Texas.
The Fee Basis package provides for more efficient and accurate operation of the fee for service program with reduction of paperwork, savings in staff hours, minimization of errors, and by allowing medical facilities to have greater control over disbursement of fee medical, pharmacy, and travel monies.
Features
- Performs entire fee for service process, both authorized and unauthorized, for Outpatient Medical Fee, Civilian Hospital, Community Nursing Home, and Pharmacy Fee.
- Automatically sends vendor updates from the central system to keep all files accurate and up-to-date.
- Provides money management for all payments through the interface with the Financial Management System.
- Automatically receives payment confirmations from the U.S. Department of the Treasury, populating payment histories with check numbers and payment dates.
- Outpatient Medical Fee:
- Authorizes fee basis treatment.
- Enters fee providers and payments.
- Creates, closes out, and releases batches of invoices.
- Records travel payment.
- Civilian Hospital:
- Provides ability to perform complete payment process, from entering patient authorizations to transmitting completed batch data (including the calculation of Medicare reimbursement).
- Community Nursing Home:
- Provides ability to perform complete payment process.
- Pharmacy Fee:
- Provides the means to administer the Hometown Pharmacy.
- Provides payment for medications furnished veterans on an emergency basis.
- Facilitates the quick completion of previously repetitive actions and gives quick, accurate access to patient payment history.
- State Home:
- Provides ability to track veterans receiving care provided by a state home facility.
Generic Code Sheet
Overview
The Generic Code Sheet module allows code sheet data to be entered and transmitted electronically from the medical facility service level to the national database. The module has eliminated the resources previously required for keypunching code sheets. Security is provided to prohibit unauthorized access to code sheets and data can easily be entered and edited via VA FileMan. Reports are available which help manage the code sheets from creation through batching and transmission and tool are included within the module to aid in the development of new code sheets at the local or national level.
Features
- Contains approximately 250 automated code sheets.
- Allows new code sheets to be automated and included within the module.
- Allows easy on-line input of code sheet data from a VA FileMan or word processing format.
- Eliminates keypunch and typing errors.
- Provides code sheet security at the medical facility service or module level.
- Allows code sheets to be grouped (batched) and transmitted to any domain connected to the VA network.
- Allows easy on-line editing and modifications to code sheets and batches.
- Generates reports that detail the status of a code sheet or batch and prints the data contained within a code sheet or batch.
Incomplete Records Tracking (IRT)
Overview
The Incomplete Records Tracking (IRT) package provides the medical center the ability to monitor incomplete records. Interim summaries, discharge summaries, and both inpatient and outpatient operation reports are tracked.
Records may be incomplete or deficient for one or more of the following reasons - not dictated, not transcribed, not signed, or not reviewed.
A list of the deficiencies each site will track is distributed with the software. These deficiency names and categories are highlighted on the screen display and are not editable. Sites may add new deficiencies. Deficiencies that are entered by the site are not highlighted on the screen display and can be edited.
Features
- Provides the ability to enter a new or edit an existing incomplete record in the IRT tracking system, edit a completed IRT record, and delete an IRT entry.
- Allows each site to establish and edit site-specific IRT parameters.
- Produces a variety of statistical reports for a specified date range.
Integrated Funds Distribution, Control Point Activity, Accounting and Procurement (IFCAP)
Overview
The Integrated Funds Distribution, Control Point Activity, Accounting and Procurement (IFCAP) module automates a spectrum of VA financial activities. VA employees use IFCAP to manage budgets, order goods and services, maintain records of available funds, determine the status of a request, compare vendors and items to determine the best purchase, record the receipt of items into the warehouse, and pay vendors. IFCAP automates the written regulations and policy for VA funding and procurement, which define the actions taken on requests for goods and services as formal transactions, orders, and payments are created for these requests.
Features
Allows users in different services to view the same document on-screen.
- Automates funds distribution, request for goods and services, purchase order, funds obligation, and the receipt process.
- Standardizes funds management. Automatically generates yearly budget elements for IFCAP control points.
- Maintains year-to-date balance for control points. Integrates service-level requisitions and facility administrative activities, and updates service-level records.
- Shares vendor and item master data to eliminate duplicate input and promote user accuracy.
- Affixes processing status to each request at each step in the ordering cycle. Enhances security with the use of a unique electronic signature code for each user required to authorize an action.
- Each record that is signed is set with an encoded value based on key fields from the record.
- Transmits financial and inventory data to VA central accounting and inventory systems.
- Automatically updates IFCAP records with central accounting system data. Provides various reports that give the current status of any request, a service fund balance, data required for budget analysis, and a listing of requests sorted according to control point specifications.
- Enables electronic transmission of purchase orders to vendors through Electronic Data Interchange (EDI).
- Updates purchase order status automatically.
- Enables authorized users to purchase goods using Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) process for total electronic processing between vendor and buyer.
- Supports the ordering of goods under contract from specific vendors via delivery orders.
- Supports the payment for goods/services via the government purchase card and the subsequent on-line reconciliation.
- Inventory management functionality includes defining desired stock levels of items, autogeneration of replenishment orders, dispensing of goods to supported services or end user, identification of items via bar code technology, supporting communication of inventory information between a secondary inventory point and its associated automated supply cabinet(s), and reports displaying inventory level, distributions, and dollar values.
Integrated Patient Funds
Overview
The Integrated Patient Funds software automates the mini-banking system that VA provides for patients to manage their personal funds while hospitalized in a VA medical facility.
Patient funds clerks create an individual patient account with information on a patient's psychological classification, financial status, and cash balance. Additional transactions consist of the deposit and withdrawal of funds.
Features
- Shares patient account data to eliminate duplicate input and promote accuracy.
- Records deposits and withdrawals.
- Promotes security with the use of unique electronic signature codes.
- Allows withdrawal restrictions for designated patients.
- Allows users (e.g., patient funds clerk and agent cashier) to view the same information on-line.
- Allows reconciliation of patient funds records with Fiscal Service.
- Provides varied reports with the current status of patient accounts, summary transaction information, restriction lists, and suspense files.
Integrated Billing (IB)
Overview
The Integrated Billing (IB) software contains all the features necessary to create bills for patients and third party carriers. It allows for the capture and storage of insurance data including policy information and related benefits. A Claims Tracking feature is available to assist utilization review staff in tracking episodes of care, completing pre-certifications, completing continued stay reviews, and processing appeals and denials. Patient charges (pharmacy, inpatient and outpatient co-payments as well, as per diems) are automatically processed. An Automated Biller is provided to assist billing clerks with billing third party carriers.
This software is highly integrated with other VistA packages. It is dependent on data from Registration, Scheduling, Outpatient Pharmacy, (Patient Care Encounter (PCE), and Prosthetics to determine billable events. Bills and charges created in IB are passed to Accounts Receivable for processing.
Features
- Tracks events requiring insurance company reviews from the time of the actual event until final payment is resolved.
- Provides the ability to establish group plans and record the annual benefits covered by the plans.
- Automates billing of patient charges for prescriptions, inpatient and outpatient co-payments, and long term care co-payments. For medication co-payments, it tracks charges billed to a veteran at all sites to ensure that the annual maximum billing cap is not exceeded.
- Automates the creation of third party billing claims forms (UB�€"92, HCFA�€"1500).
- Automates pricing of Third Party claims using Reasonable Charges based on care provided, payer, and provider.
- Provides the ability to include inpatient stays, outpatient visits, prescriptions, and prosthetic supplies on third party claims.
- Provides an Automated Biller, which automatically generates reimbursable bills identified in claims tracking that meets specific requirements as provided for in the site parameters.
- Provides insurance company-specific billing parameters so bills can better reflect local insurance company requirements.
- Includes a Charge Master, which allows facilities to load lists of billable rates into VistA.
- Includes an Output Formatter to allow sites to locally configure claims forms.
- Provides an extensive set of diagnostic reports that allow sites to monitor various aspects of the billing program.
- Provides a module for sites to track and price the services provided to out-of-network patients.
- Provides tools to maintain and/or modify the Insurance Company file.
- Provides EDI capabilities using standard transactions that are transmitted through a translator at the Austin AAC prior to being forwarded to a clearinghouse for dissemination to the appropriate payers. Supported EDI transactions include the transmission of healthcare claims and the verification of patient health insurance coverage.
Patient Care Encounter (PCE)
Overview
Patient Care Encounter (PCE) captures clinical data resulting from ambulatory care patient encounters. The captured clinical data documents �€œencounters�€ and related encounter information, such as problems treated at encounter, procedures done, immunizations, patient education, and skin tests.
PCE provides a data repository for long-term clinical data. A goal of PCE is to support many data capture methods for integrating clinical data from many environments. Pilot efforts have included population of the PCE clinical repository via scanner technologies and workstations.
The key users of this clinical data are clinicians, management, and Quality Management personnel.
Features
- Acts as VA's long-term clinical repository, documenting encounters from local and non-VA facilities.
- Provides a primary and secondary clinical visit management utility based on appointments and related services.
- Interfaces with the Health Summary package to provide components based on data captured and stored in the PCE clinical repository.
- Supports capture of outpatient encounter data. Data collection methods include:
- Interface between scanner/workstation and clinical repository.
- On-line data capture using List Manager user interface.
- Historical load utilities for lab and outpatient pharmacy.
- Future methods will include automatic protocol event driver.
Personnel and Accounting Integrated Data (PAID)
Overview
Enhanced Time and Attendance
The Enhanced Time and Attendance System (ETA) automates time and attendance for employees, timekeepers, payroll, and supervisors. It provides employees the ability to request leave and display both the status of pending requests and leave balances and allows payroll to manage time and leave (T&L) units and tours of duty. It provides timekeeping, supervisory certification, and overtime management.
Education Tracking
Education Tracking documents employee and student participation at mandatory and ward in-services, continuing education programs, and all other employee training. Training information is protected with varying levels of access.
Features
Enhanced Time and Attendance
- Timekeepers can enter and edit employee's time, view data for current and prior pay periods, and view time card status for each employee.
- Payroll can view processing status of T&Ls, locate uncertified or incomplete timecards.
- Payroll may also manage T&L units by enter/edit of supervisors, timekeepers and employees.
- Payroll may view pay period data, master records, and accounting data for employees.
- Payroll can create searches of master record and accounting data for custom local reports.
- The payroll supervisor transmits all payroll data to the Austin Automation Center (AAC) and monitors transmission status.
- The system automatically builds and updates employee records with AAC data.
- Authorized personnel may display and search master record and accounting data for all employees.
- Employees may submit electronic leave requests and view leave balances, status of requests, and service records.
- Supervisors can approve electronic requests and timecards and view employee leave reports.
Education Tracking
- Creates a class database with pertinent class information: class name, presenter, location, purpose, category, type, mandatory review group, sponsoring agency, cost, accrediting organizations, employer/student expenses, contact hours, etc.
- Contains a class registration component that limits class registrants by number or service.
- Credits class participation to individual attendee records and allows attendance corrections.
- Provides site-configurable mandatory training groups, accrediting organizations, presentation media, supplier demographics, and class purpose.
- Contains reports, such as a calendar of events, a registration roster, service-based class, and a variety of employee training reports.
Voluntary Service System (VSS)
Overview
The Voluntary Service System (VSS) software is the first application to be developed in the current VistA Migration effort. VSS is a national-level application replacing the site-based Voluntary Timekeeping System (VTK). VTK has been used for many years at VA medical centers to track and manage the hours of service contributed by volunteers and volunteer organizations.
To improve data collection and reporting, users interact directly with a national, centralized database. Consolidated national reporting no longer requires data transmissions back and forth between sites and the Austin Automation Center. Direct access to data provides instantaneous updates and up-to-minute reporting for all users. Central Office administrators and Voluntary staff thus have broader and more reliable data for managing Volunteer services.
The VSS application helps Voluntary staff accomplish their tasks more easily through a Web-based graphical user interface. Users at the local and national level are able to generate a wider array of reports about volunteers and sponsoring organizations. In addition, volunteers are able to log their own hours and print meal tickets themselves at secure log-in �€œkiosks.�€
Features
- Provides multi-lingual interaction with volunteers during log-in.
- Supports and enhances security for multiple division facilities.
- Displays/prints entire master record for a single volunteer.
- Provides local printing of address labels and telephone lists.
- Reduces workload required to input mass award code changes.
- Prints individual meal ticket for volunteer after Auto Log-in.
- Provides real-time national reporting of data for all stations.
Information and Education Systems
Information and Education Systems with an emphasis on �€œeHealth�€ include prescription refills, appointments, fillable forms online, and My HealtheVet (Web-based access to health record, online health assessment tools, and high quality health information).
- Improve service to veterans and stakeholders
- Information that is accurate, up-to-date, readily available at any time, any place
- VA Internet primary gateway to trusted VA information and services for veterans and their families
Automated Safety Incident Surveillance Tracking System (ASISTS)
Overview
Automated Safety Incident Surveillance Tracking System (ASISTS) was designed to manage the data from all employee accidents, create a Report of Accident (VA Form 2162) from the data, and produce both the Office of Worker's Compensation Programs Form CA-1 (Instructions for Completing Employee's Notice of Traumatic Injury and Claim for Continuation of Pay/Compensation) and Form CA-2 (Federal Employee's Notice of Occupational Disease and Claim for Compensation).
Improving tracking and management of employee accidents, in general, and exposures to bloodborne pathogens from needle sticks and sharps, in particular, is a high priority of VHA. Consequently, the package contains fields specific to needle stick, sharps, and bodily fluid exposures. The data collected from ASISTS is electronically transferred to a national database and used to identify system-wide problems and opportunities for focused education and to conduct research.
The electronic submission of workers' compensation claims to the Department of Labor is improving submission rates and reducing duplicate data collection and data entry.
Features
�'� Electronic signature is used extensively throughout this program. All three forms (VA Form 2162, CA-1, and CA-2) require appropriate signatures including that of the employee for the CA-1 and CA-2, which is used when electronically transferring the data to the Department of Labor.
�'� Bulletins alert employee health and infection control of any exposures to bloodborne pathogens. The employee's supervisor, the safety officer, Human Resources Management, and union representatives are notified of every incident. Electronic signatures trigger bulletins from the employee to the supervisor and union representatives, and from the supervisor to the safety officer, alerting the recipient of action that should be taken.
- Every medical center employee has access to a menu structured specifically to the level of his/her involvement in the process: employee health, supervisor, safety officer, union representative, workers' compensation personnel, and employee.
- The graphical user interface (GUI) for ASISTS facilitates the input and processing of accident reports and claims and improves the reporting functionality, including a revised OSHA and Needlestick log and graphical representation of the incident reports.
- Future versions will include a comprehensive employee health module for tracking and following numerous health issues.
Library
Overview
The Library module is designed to automate the entire serials management process in VA Library Services. VA library staff spend the largest share of local materials budgets on serials. The process of ordering, tracking, claiming, and listing these titles is tedious and error-prone when done manually. Automation of serials management allows a faster and more accurate process for work simplification. Library management is assisted through improved statistics and information.
Staff is able to use Library Patron options to see whether the local Library Service owns a journal title and, if so, the holdings and location for that title.
The Serials Control module has three components. The Serials Management component creates the local library's serials database, along with retrospective holdings and purchasing information and copy information, such as location and category. The module is designed so that access to this component may be restricted, if desired, to the serials expert on the library staff, usually a medical librarian or the Chief. Access to the Serials Control component where daily actions are managed (e.g., check-ins, routing, and generation of reports) may be given to other Library Service staff members. A minor component of the module, Library Site Parameters, allows for the initialization of the module.
Library makes it possible for local sites to carry only locally active entries in their local database. When new entries are needed, they can be downloaded automatically from the national database into a site's local database.
Features
The Serials Control module:
- Creates a local serials database.
- Provides acquisition and retention information.
- Provides purchasing and vendor information.
- Provides holdings information and shelving location information.
- Categorizes by type and subject.
- Provides check-in with next issue prediction.
- Generates routing slips.
- Tracks materials returned from routing.
- Displays check-in history.
Generates 20 management reports (e.g., listings, monthly check-in statistics, monthly routing statistics, tracking of unreturned routed issues, missing issue reports for claiming replacements or reports, etc.).
A centrally produced Title Authority file, a database of over 9,477 serials titles owned by VALNET (VA Library Network) libraries, was preloaded with standard bibliographic data and provided as a part of this module.
Police and Security
Overview
The Police and Security module supports the VA Police in their responsibilities of crime prevention, preliminary investigation of crimes, apprehension, legally correct handling of suspected offenders, and the transfer of suspected offenders to appropriate authorities.
Features
- Serves as the repository file for the names, addresses, and other demographic data of persons who come in contact with the VA Police and Security staff.
- Allows for the retrieval and display of stored information for a selected person.
- Stores electronic data normally entered on the VA Police Uniform Offense Report, Investigative Notes, Case Log, and other documentation assembled during an investigation.
- Contains all violation information on US District Court Violations Notices and Courtesy Warnings issued by VA Police Officers at the medical facility.
- Assembles selective data into a standardized report format documenting the numbers and types of criminal incidents that are occurring at the site.
- Records information necessary for the Vehicle Registration program.
- Records any data pertinent to individuals currently under any type of criminal proceedings or other legal restraining document.
- Provides a system to record all information contained on the Evidence Property Custody Record (VA Form 10-3524).
- Allows each police officer to record the specific activities performed during a shift and the time required to complete the activities.
- Stores all information relative to training completed by staff members assigned to the Police and Security Service.
- Stores all information entered on the VA Police Daily Operations Journal (VA Form 10�€"1433) and Continuation Sheet (VA Form 10-1433a).
- Transmits Monthly Crime Reports and selected Offense Reports through MailMan to VA Headquarters.
- Produces supervisory management, quality management, and crime trend studies; a standardized Uniform Offense Report, Uniform Crime Report, and Evidence Register Report; and Case Progress Notes and Case Assignment Register.
Cross-Cutting Monographs
Cross-cutting Issues include the VA and VHA architectures, information security, data quality, and leadership and management. These issues cut across all systems and ensure effective implementation and operations of the major systems.
Duplicate Record Merge
Overview
Since the inception of automated medical information management within the Department of Veterans Affairs medical facilities, and as entries have been made in the PATIENT file (#2), a number of duplicate records have been introduced. Estimates of the number of duplicate entries currently present range as high as one to two percent of the VHA total record base. Past attempts to consolidate duplicate records have resulted in the loss of valid data. Invalid records were simply deleted and real data was lost through incomplete conversion of pointers.
The Duplicate Record Merge application enhances the ability to associate appropriate data with a single patient identifier. It provides the tools necessary to automatically identify patient records identified as being duplicates.
Features
The overall process consists of three modules: the search for potential duplicate record pairs, review and verification of those pairs, and the merge process. The search and identification of potential duplicate records is based on the Duplicate Record Merge features of Kernel Toolkit. Once the search has been completed, the process of verifying record pairs begins. Reviewers view data associated with the potential duplicate pairs and determine a status. Once verified, the merge process may be initiated.
- Search for Potential Duplicate Record Pairs
- Comparisons made on key fields; i.e., Name, SSN, Date of Birth, Date of Death, Last Separation Date (Last Discharge Date), Mother's Maiden Name, and Claim Number.
- Comparison results in computed value.
- Resulting value measured against the Potential Duplicate Threshold Percentage. (When record pair scores evaluate above this percentage, they are considered to be potential duplicates.)
- Review and verification may begin while search is running.
- Review and Verification
- Site-designated reviewers: Primary reviewer(s) for the Patient File, Ancillary reviewer(s) for other files (e.g., Laboratory).
- Reviewers view screens of patient data for comparisons.
- Reviewers resolve potential duplicate pairs: Verified Duplicate, Verified Not Duplicate, Unable to Determine.
- Notification of review actions via alerts and/or e-mail messages.
- Merge Process
- User-initiated process.
- Runs as a single process merging multiple pairs. One or more jobs may be designated to run in parallel to reduce processing time (i.e., threads).
- Halt/Restart merge process maximizes site control.
- Three phases within merge: 1) merge records in main file, 2) DINUMed pointers and cross-references, and 3) all other pointers.
Health Level Seven (HL7)
Overview
In today's health care environment, computer systems from multiple vendors and at geographically dispersed sites are used in conjunction with core facility computer systems to create integrated delivery of information to the end-user. Linking such systems to exchange data and work together is a non-trivial task, particularly given the complexity of health care data.
Health Level Seven (HL7) is an American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard messaging protocol that specifies the set of transactions and encoding rules for electronic data exchange between health care computer systems. HL7 provides an open, standards-based framework that computer systems can use to exchange health care data with each other. The HL7 standards development group is directly focused on health care informatics standards and cooperates closely with developers of other standards.
The Veterans Health Information Systems and Technology Architecture(VistA)HL7 package enables M-based (VistA)applications running on core facility computer systems to exchange health care information with other computer systems. It provides messaging services and a single toolset for M-based VistA applications to create, send, receive, and process HL7 messages.
Many VistA applications use VistA HL7 to exchange data in HL7 format with other facilities and/or applications, including Anesthesiology, Mater Patient Index/Patient Demographics (MPI/PD), Laboratory, Outpatient Pharmacy, Patient Management System (PMS), Radiology, and Veteran ID Card (VIC).
The VistA HL7 package is also used to integrate commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) health care applications with M-based core facility computer systems.
Features
- Communication�€"Facilitates Point-to-Point and Publish-and-Subscribe messaging between two or more applications; and provides the transport mechanism using HL7-supported lower level transmission protocols (e.g., Hybrid Lower Level Protocol [HLLP], X3.28, or Minimum Lower Level Protocol [MLLP] over Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol [TCP/IP]), which provide error detection and session control; provides dynamic routing of messages.
- Processing�€"Queues incoming and outgoing messages for reliable messaging; validates HL7 Message Header (MSH) information for all incoming messages; and sends HL7 acknowledgment (ACK) messages back to sending applications upon message receipt.
- Message Administration�€"Provides functionality to assist the application developer in setting up HL7 interfaces by hiding the complex lower level communication; monitors message transmissions statuses; and provides reports on pending transmissions and those with errors.
- Programming Utilities�€"Provides the developer with a rich collection of Application Programmer Interfaces (API) to facilitate the creation, exchange, and transmission of messages; provides a set of predefined variables to use for building HL7 messages/segments; automatically creates all HL7 Message Header (MSH) segments; and invokes the appropriate application routine to process message data when a message is received.
Kernel
Overview
Kernel provides a portability layerbetween the underlying operating system and application code. This results in the entire Veterans Health Information Systems and Technology Architecture(VistA)system being portable among different computers, operating systems, and M implementations. This, together with the database portability provided by VA FileMan, eliminates the cost of application conversions each time VHA changes its computing platforms.
Kernel also offers shared servicesfor VistA applications, resulting in reduced development costs and a common user interface, and provides system management toolsfor managing VistA computer systems.
Integrated Single Sign-on�€"The RPC Broker supports a singlesign-on point from a client workstation to the server. Users need only sign on once when accessing multiple VistA applications on the same workstation.
Features
- ZOSF/ZOSV Operating System Interface�€"The core of Kernel's portability layer. Insulates applications from being tied to any particular hardware platform, operating system, or M implementation.
- Sign-On and Security Management�€"Controls user access by device, time, and day of week; controls user access to programs, menus, files, fields, and devices; audits by user, device, program, file, and field; and provides electronic signature capability.
- Menu Manager�€"Manages all application menus to provide a standard user environment; customizes menus for individual users; shares or restricts menus to a user or a set of users; provides secure delegation of menu management authority; and delivers priority system alerts.
- Error Processing�€"Provides a consistent method for recording and processing application errors.
- Device Handler�€"Defines generic terminal types to reuse for similar peripherals; supports host files in layered operating system environments; insulates programmers from device- and operating system-specific coding; and provides standard user device selection across different environments.
- Task Manager�€"Provides flexible background job scheduling; allows users to control their own tasks; and permits specification of device, priority, and time of execution.
- Kernel Installation and Distribution System (KIDS)�€"Provides a mechanism to create a distribution of packages and patches; allows distribution via a MailMan message or a host file; and allows queuing the installation of a distribution for off-hours.
- Library Functions�€"Provides Date, String, Mathematical, Hyperbolic Trigonometric, Measurement, and Utility Functions.
- Domain Name Resolution�€"Provides an Application Programmer Interface (API) to resolve domain names into an Internet Protocol (IP) address.
Kernel ToolKit
Overview
Kernel Toolkit (also referred to as �€œToolkit�€) supplements the Kernel software package. It provides Development and Quality Assessment Tools, Capacity Planning Tools, and System Management Utilities.
Features
Development and Quality Assessment Tools
- Promote standard programmer interfaces.
- Provide programmer and systems management.
- Provide a portable routine and global editor.
- Check adherence to programming standards and correct syntax with %INDEX tool.
- Provide standard error trapping, storing, and reporting.
- Support quality assessment tools for the comparison of routines and data dictionaries.
- Provide software project management utilities.
- Provide tools to work with data in Extensible Markup Language (XML).
Capacity Planning Tools
- Collect accurate site data for review and monitoring of database, software, option workload, and file size information, which is useful in determining future growth rates and trends.
- Produce system status reports and usage statistics.
- Provide system response time logging for performance management.
- Provide automated system monitoring and reporting tools.
- Perform automated performance analysis tools.
- Alert system managers to dangerous or unusual conditions.
- Deliver reports automatically via MailMan.
- Provide tools for software optimization and application sizing.
System Management Utilities
- Customize and tune site parameters for local requirements.
- Provide a Kermit file transfer utility.
- Provide a Multi-Term Lookup Utility for enhanced VA FileMan lookups.
- Provide Duplicate Resolution utilities for the creation of file maintenance applications.
- Provide PARAMETERS file (#8989.5) for user-specific to system-level tracking of parameter values.
Kernel Toolkit �€" continued
Sample Capacity Planning Report
List Manager
Overview
The List Manager was developed to provide an efficient way for applications to present a list of items to the user for action. It is a developmental tool that enables programmers to:
- Display a list of items to the user.
- Allow the user to browse back and forth through the items one at a time or by screen.
- Allow the user to select items from the list.
- Specify the actions that can be applied to selected items from the list.
- Call List Manager again as part of an action.
Protocols are the "actions" that users can take against items on the list. A number of standard protocols come as part of the List Manager utility. Most of these are actions that allow the user to browse the list of items.
The List Manager contains the Workbench programmer utility, which allows the development of a List Manager application without having to move from one development tool to another.
Features
List Manager provides a generic method of presenting lists of items to terminal users. Its core features are:
- Displays a list of items in a screen format and allows users to browse through the list, select items that need action, and take action against those items.
- In addition to the various actions that are specific to the option being worked in, provides generic actions applicable to any List Manager screen (i.e., Up a Line, Next Screen, First Screen, Search List).
- Provides a list of available menu functions that can be performed from the screen without having to exit and enter a new menu option for each one.
- Allows action pre-selection and list entry pre-selection by user.
- Provides programmer Workbench for application development.
MailMan
Overview
MailMan is an electronic messaging system that transmits messages, computer programs, data dictionaries, and data between users and applications located at the same or at different facilities. Network MailMan disseminates information across any communications medium.
When MailMan is integrated into an application, it notifies individuals and groups about important events. From VA FileMan, a change in the value of a field can trigger a message called a bulletin. MailMan is easy for the user to learn and to use and provides extensive online help. There is also an extensive set of MailMan Application Programmer Interfaces (API) for the developer.
Features
- Delivery Options�€"Users can send messages to individuals, mail groups, and devices. Users can also stagger delivery of messages and specify to what basket a message should be delivered.
- Chained Responses�€"Message response chains are managed automatically. Responses are threaded in sequence following the original message and are instantly available to anyone currently reading the message, providing a "real-time" conversation among message recipients. All responses are available for review at any time by all recipients.
- Configurable Interface�€"Users can customize and configure the MailMan reader interface and set other personal properties best suited to their needs.
- Mail Basket Organization�€"Users can organize mail into any number of user-specified mail baskets.
- Mail Filtering�€"Users can filter their mail based on one or several filter criteria.
- Search Capabilities�€"Users can search for messages based on one or several search criteria.
- Reminders/Notifications�€"Messages can be used as a tickler file to remind/notify you of specific events (e.g., bulletins and alerts).
- Secure Messages�€"Messages can be secured (scrambled), requiring a key to unlock them. MailMan provides multiple layers of local and network security.
- Surrogate Capability�€"Users can designate a surrogate to read and/or answer their own messages.
- Software Message Processing�€"Messages can be sent and processed by software. All application outputs can be directed into MailMan messages.
- Software Code Transport�€"Veterans Health Information Systems and Technology Architecture (VistA) software can be conveniently transported via messages. Whole modules and patches for installation at a remote site are sent in Kernel Installation and Distribution System (KIDS)/PackMan messages.
- Network Transmissions Over TCP/IP�€"Network transmissions can be made across Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) channels to any Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)-compatible mail system.
- Statistics Collection�€"Extensive mail system statistics can be collected.
- Dom'ain Name Service (DNS)-aware'�€"It creates automatic replication of IP address changes to every VistA MailMan system as a result of only one central database edit (i.e., performs DNS lookups).
Master Patient Index (MPI) and Master Patient Index/Patient Demographics (MPI/PD)
Overview
There are approximately 140 Veterans Health Administration (VHA) databases in use across the country in VA facilities that are accessible via VistA systems. Because of this wide distribution of information, there is great potential for individual patient data to be kept under more than one identification number. The Master Patient Index (MPI) has been created to support maintenance of a unique patient identifier and a single master index of all VA patients, and to allow messaging of patient information among the institutional partners [i.e., VHA, Veterans Benefits Administration (VBA), Board of Veterans Appeals (BVA), and National Cemetery Administration (NCA)].
The ability to uniquely identify a patient and the facilities where that patient receives care is a key asset in the delivery of quality care. It is upon this foundation that the CPRS Remote Data Views project is able to allow the clinician to retrieve clinical information from wherever the patient has received care. As the Integration Control Number (ICN) is populated at the Health Eligibility Center (HEC) and other national databases, this ability to uniquely identify patients assists in the elimination of duplicate records throughout the systems. The need also exists between the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) and other agencies such as Indian Health Service (IHS) and Department of Defense (DoD), to uniquely identify and share information regarding any patient that has received care from more than one facility/agency.
There is a suite of applications that make up the VHA MPI. The suite contains the following three modules:
- Master Patient Index Austin Automation Center (AAC)
- Master Patient Index (MPI) VistA
- Patient Demographics (MPI/PD)
Features
Master Patient Index Austin Automation Center (AAC)
- Create Unique Patient Index�€"The MPI, located at the AAC in Austin, Texas, maintains a unique patient index by establishing a correlation between each unique system record and the MPI's unique identifier (ICN). The correlated list is maintained to enable the sharing of patient data between operationally diverse systems and to maintain the integrity of the correlations to the ICN.
- Assign ICN and CMOR�€"VA medical centers send local patient entries to the MPI for Integration Control Number (ICN) assignment via an initialization process or during daily operations at the VAMC.
- Maintain/Update Index�€"The Index is maintained and updated as patients are added or their data is updated at VA medical facilities.
- Manage/Mitigate Data Quality Issues�€"Houses the resolution journal and related applications, used to manage and mitigate data quality issues that are identified by the system or users.
MPI and MPI/PD �€" continued
Master Patient Index (MPI) VistA
- Request Patient ICN'�€"'This software resides in VistA at a site and sends local patient entries to the MPI in Austin for ICN assignment.
- Maintain/Update Patient Data'�€"'The MPI-VistA, Master Patient Index/Patient Demographics (MPI/PD), and Patient Information Management System (PIMS) keeps the data in the MPI (AAC) up-to-date. [NOTE: The initialization of the MPI (AAC) consisted of each VAMC sending batch Health Level Seven (HL7) messages to the MPI in Austin requesting ICNs for all of the patients whose records reflected activity in the past three fiscal years (i.e., patient records that contain CMOR Activity Scores).]
- Provide Site Query Capability�€"MPI-VistA enables sites to query MPI (AAC) for known data, to request the assignment of an ICN. When a new patient is created or an existing patient record becomes active at the local VAMC, a query is sent to the MPI in Austin to see if this patient has an ICN already on the MPI. If the MPI already has an ICN assigned for this patient, the ICN, CMOR, and the Treating Facility List (a list of all locations that know of this ICN) are returned to the local VAMC. If the MPI doesn't know of this patient, a new ICN is created and the local VAMC is made the CMOR. The ICN and CMOR are then returned to the local VAMC.
- Inactivate Patient from MPI'�€"'The site has the ability to inactivate an ICN on the MPI if the patient was inappropriately added to the MPI (i.e., a Test patient) or to allow the patient to be matched with another existing ICN.
- Request/Manage CMOR Updates�€"The CMOR is initially the first site to notify the MPI of a patient. The VAMCs have an array of options that allow them to request to be the CMOR as well as "push" their current CMOR assignment for a patient to another site in the treating facility list. The Change of CMOR options also allow for the management of these requests.
Patient Demographics (MPI/PD)
- Act as Authoritative Source of Patient Demographics�€"The function of the Coordinating Master of Record (CMOR) site (one VAMC) is to be the authoritative source of the patient's demographic data.
- Utilize CMOR�€"Uses the patient's CMOR as the single source of current key demographic information on the MPI and at the patient's other treating facilities.
- Support Demographic Changes�€"Supports the review of demographic changes that occur at other facilities for patients at which your site is the CMOR.
- Synchronize Key Data�€"Synchronizes key patient demographic data at all sites where the patient is treated.
- Support Duplicate Record Merge�€"Provides support to the duplicate record merge software for the merging of MPI/PD related data.
- Manage Exceptions�€"Allows the management of Exceptions that prevent a patient from getting an ICN assignment.
My HealtheVet
Overview
My HealtheVet (MHV) is a Web-based application that creates a new, on-line environment where veterans, family, and clinicians may come together to optimize veterans' health care. Web technology combines essential health record information enhanced by online health resources to enable and encourage patient/clinician collaboration. It is the first web-based application created by the Office of Information for the exclusive use by veterans.
MHV provides one-stop shopping for information on VA benefits, special programs, and health information and services. MHV also provides services and tools to enable veterans to increase their knowledge about health conditions, better record their health status and communicate with their care providers, and become better-informed participants in improving their health. Veterans can now partner with their clinicians to gain a better understanding of their health status and take a more active role in self-management and in shared health care decision-making.
Features
Fall 2003 Release
- Enables all veterans to participate voluntarily and have access to and control of his/her customizable online environment.
- Provides a commercial Health Education Library that contains information on medical conditions, medications, health news, and preventive health.
- Makes the library available to clinicians; addressable from the CPRS toolbar and included in order sets.
- Showcases education and program information developed by VHA program offices.
- Contains the latest VA/VHA news.
- Contains a prescription checker, health calculators, and self-assessment tools.
- Maps to benefits and resources available in VA and other federal sources.
Summer 2004 Release
- Provides online prescription refills for veterans enrolled in VA health care.
- Provides ability to view next appointment date and time at a VA health care facility.
- Provides ability to see total co-payment balance.
- Enables ability to enter and store personal information in a secure eVAult.
- Provides ability to format and print reports, such as information cards and medication profiles.
- Enables veterans to journal readings and chart progress in five self-entered metrics (elogs)�€"blood pressure, blood sugar, cholesterol, weight, and heart rate.
- Enables veterans to define additional elogs, journal readings, and chart progress.
My HealtheVet �€" continued
Winter 2005 Release
- Allows veterans to request and store key portions of their VA health record in a secure, unique, and personal repository.
- Enables veterans to let a delegate access and manage all or some of their health information to others, such as family or veteran advocates, and VA and non-VA providers.
- Allows veterans to receive wellness reminders ,written specifically for the patient, to provide effective delivery of preventive medicine serves through standardized reminders.
Network Health Exchange (NHE)
Overview
Network Health Exchange (NHE) is a Veterans Health Information Systems and Technology Architecture (VistA)module that provides clinicians quick and easy access to patients' information from any VA medical facility where a patients has received care. NHE provides the computer mechanism for clinicians to retrieve this patient data.
The NHE package accesses information concerning clinic visits, diagnoses, prescriptions, laboratory tests, radiology exams, and hospital admissions. It enables clinicians to request medical or pharmacy records for a patient from a single site or several sites. NHE obtains Health Summary information through an interface with the Health Summary VistA module.
NHE uses predefined formats, thus requiring less input by the user and resulting in simpler, faster access to patient data. Patient data is displayed in a format similar to that of Health Summary and can be viewed on-screen or printed.
NHE is an interim bridge to a more fully integrated clinical patient data exchange system in the future.
Features
- Simple User Interface: Users simply select the data type (Clinical or only Pharmacy data) and the amount of patient data they would like returned (all data or 12 months only), then enter the patient's name or Social Security Number in order to initiate the request for data from another VA facility.
- Retrieval and Printing of Patient Data�€"Retrieved patient data (Clinical Record or Pharmacy information, either a comprehensive history or activity only within the last 12 months) can be printed or viewed on-screen.
- Quick Response�€"NHE is fully automated and user requests are generally fulfilled in a matter of minutes.
- Data Returned in Health Summary Format�€"Patient data is returned in an NHE mail message, formatted similarly to the Health Summary, beginning with patient demographics, followed by categorized medical information, and indicating the name of the VA facility where the data resides.
- User Notification with Alerts�€"The user requesting patient data via NHE is notified of data receipt through an alert that appears within the menu system.
- Purging Retrieved Patient Data�€"In order to allow sites to control disk space usage, NHE provides an option to purge the retrieved patient data messages nightly.
- Special Security Features�€"This system is intended for use by health professionals who have direct patient care responsibilities and have need for clinical information. NHE generates a bulletin if data is requested from a sensitive patient record. The bulletin is directed to the same user group that currently reviews notices about access to sensitive patient records.
- Package Management�€"The availability of NHE options is based on the level of menu access granted to each user.
Patient Data Exchange (PDX)
Overview
Patient Data Exchange (PDX) is a VistA module designed to electronically request and receive patient demographics, episodes of care, medications, and diagnostic evaluations from other VA facilities. Data is retrieved from files at a remote site and is assembled into a coherent, composite record, greatly enhancing the quality of care provided for the patient.
PDX allows for the setup of a work group of selected facilities that agree to an automatic data exchange. For facilities in the work group, data is returned automatically, within minutes after a request is entered. There are exceptions, however, such as records that have been flagged as sensitive. Any record that does not meet the criteria for automatic processing is reviewed and processed manually.
Once the request is processed, the patient's record is forwarded to the requesting facility. The requests and data are moved from one facility to another using MailMan, VA's electronic mail utility. The requesting facility receives administrative, pharmaceutical, and clinical information that is stored in its files and is available for terminal display or printing.
Features
- Requests data electronically for a selected patient from another facility.
- Allows automatic processing of requests from selected facilities.
- Allows for manual processing of requests from facilities outside the work group or of certain records, such as those flagged as sensitive.
- Allows sending information to a remote site without first receiving a request.
- Allows data received from the remote site to be displayed/printed.
- Allows select demographic data from a remote site file to be loaded/edited into the local site file.
- Allows checking on status of requests.
- Allows displaying/printing of statistics each time a regular or unsolicited PDX request is made or processed.
- Allows for the encryption of site-specific patient information.
- Allows sending/requesting data for a patient from multiple sites for multiple segments.
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Broker
Overview
A major goal for Veterans Health Information Systems and Technology Architecture(VistA)is providing Windows-based graphical user interface (GUI) software applications. This type of software application typically runs as a client in a client/server environment. One of the challenges in creating such applications is establishing communication between the client workstation and VistA's M-based servers. In a secure manner over a Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) network, users need to be able to log onto a server, initiate activities on the server, and retrieve and update data on the server.
VistA's Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Broker software provides functionality so that GUI developers can:
- Establish a connection from a client workstation to a VistA M Server.
- Run RPCs on the VistA M Server.
- Return data to the client workstation.
The RPC Broker supports 32-bit Windows client applications (e.g., applications running under Microsoft Windows 2000 and Windows XP).
The VistA M Server continuously runs an RPC Broker listener process whose purpose is to establish connections with clients. When the listener process receives a connection request from a client, it spawns a separate handler process, which then handles all communications with the client.
Once connected, the client can execute Remote Procedure Calls on the VistA M Server. RPCs are written in M and accessed through the VistA M Server's REMOTE PROCEDURE file (#8994).
RPCs can:
- Receive data from the client workstation.
- Return data to the client workstation.
- Execute other actions on the VistA M Server.
Features
- Broker Developer Kit (BDK)�€"The RPC Broker Delphi components provide Delphi developers with an easy, object-based access to the Broker. When placed on a Delphi form, these components provide a connection to the VistA M Server and the ability to reference M data.
- Dynamic Link Library (DLL) Interface�€"The RPC Broker provides a set of DLL functions that allow applications written in any MS Windows-based development environment [e.g., Borland's Delphi, Microsoft Visual Basic, and other commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS)/Hybrid Open System Technology (HOST) products] to take advantage of all the features offered by the RPC Broker Delphi components.
Remote Call Procedure �€" continued
- Client/Server Security�€"For security purposes, to execute an RPC on the VistA M Server all of the following conditions must be met:
1. The user must be an authorized user on the VistA M Server.
2. The client workstation application must invoke a supported application context authorized to the user.
3. The RPC must itself be authorized to the specified application context.
- Integrated Single Sign-on�€"The RPC Broker supports a single sign-on point from a client workstation to the server. Users need only sign on once when accessing multiple VistA applications on the same client workstation.
- Silent Sign-on�€"The RPC Broker provides silent login functionality. Any GUI application that uses the Broker can log in to a VistA M Server silently (i.e., without any user dialogue).
- Shared Broker�€"Broker applications running on the same server and port can share the same connection, resulting in a single job running on the server. This functionality is available for Broker applications compiled with the TSharedRPCBroker component. Only connections associated with the first application must log in.
- Non-callback Connection�€"The RPC Broker provides a non-callback connection, which results in less problems for applications using the Broker for connections across firewalls.
- CCOW-enabled�€"The RPC Broker supports CCOW, which allows Delphi-based applications to incorporate Single Sign-On/User Context (SSO/UC) functionality into their applications. This functionality is available for Broker applications compiled with the TCCOWRPCBroker component.
VA FileMan
Overview
VA FileMan is Veterans Health Information Systems and Technology Architecture's (VistA) database management system (DBMS). It runs in any American National Standards Institute (ANSI) M environment. The majority of Veterans Health Administration (VHA) clinical data is stored in VA FileMan files and is retrieved and accessed through VA FileMan Application Programmer Interfaces (API) and user interfaces.
Features
|
For Users |
For Developers |
|
|
= Performance =
Over the years, demand on VHA systems has grown. The compactness and efficiency of M and VA FileMan provide fast database performance and high utilization of our computer systems.
= Portability =
Portable, platform-independent database services provided to applications by VA FileMan, combined with the operating system portability layer of Kernel, allow VHA to upgrade its hospital computing platforms without significant changes to application code. Thus, VHA has not encountered the kinds of problems normally associated with computer platform changes and is free to competitively bid out for new systems.
= Openness =
VA FileMan is open; it facilitates data access from outside applications. The Database Server (DBS) API enables client/server access to VA FileMan data. The FileMan Delphi Components take advantage of the DBS API to encapsulate the details of retrieving, validating, and updating VA FileMan data within a Delphi application. VA FileMan's Import and Export tools support data interchange with outside applications such as PC spreadsheets and database programs. SQLI helps make VA FileMan data available to outside applications. It also includes native support for Keys and compound cross references (Indexes), and thus, helps pave the way for the opening of VistA even further to outside software.
VistALink
Overview
VistALink provides a synchronous communication mechanism between MUMPS or M applications and rehosted applications, supporting Veterans Health Administration's (VHA's) ongoing transition to HealtheVet-VistA.
Technically, VistALink is a transport layer between M and Java. It consists of an M-side listener and Java-side adapter libraries compliant with the J2EE Connectors specification for Enterprise Information System (EIS) adapters. "The Connector architecture is an integral part of the J2EE platform, and, as a key component in J2EE's support for application integration, it ensures that J2EE applications can connect to and use a multitude of EIS and legacy systems."[#sdfootnote1sym 1]
= Reasons for VistALink =
While alternatives for communication between Java and M applications have been produced, the needs of applications for robust, synchronous communication have not been met by these alternatives. The limitations of each of these alternatives are described below:
- Remote Prodcedure Call Broker�€"The RPC Broker is COM-based, rather than Java-based. Wrapping the COM-based Broker was proven by the Care Management team to have unacceptable performance limitations. Also, the RPC Broker was not designed for n-tier applications.
- Vitria�€"Vitria is used as an HL7 interface engine by the VHA. HL7 messaging is an effective tool for asynchronous communication. But in many instances, applications need synchronous access to RPCs, as they are run while a user is waiting for results.
- Cache�€"Cache provides a number of connectivity mechanisms between itself and Java that initially showed potential for use. However, the Cache-specific features have proved not to have all the functionality needed by rehosted applications.
- Third-Party J2EE Connector-Compliant Adapters�€"At least one company markets an adapter for J2EE-M connectivity that is J2EE Connector compliant (as is VistALink). This adapter, however, is for Development Standard MUMPS (DSM) systems only and has other limitations when measured against VHA application requirements.
Features
- v1.0: Client/Server connectivity from Java client to M�€"Officially released. This version of VistALink was designed to meet the needs of Care Management (CM). It is for Java rich client applications connecting to M servers and executing RPCs on those servers. VistALink v1.0 provides the equivalent of RPC Broker functionality for Java.
- v1.5. J2EE Application Server connectivity to M�€"This version will allow applications and services running on a J2EE application server to initiate a call to an M server and execute RPCs. This version fully implements the Java 2 Enterprise Edition (J2EE) Connectors specification. Applications requesting this version include Patient Advocate Tracking System (PATS), Veterans Personal Finance System (VPFS), Computerized Patient Record System �€" Reengineering (CPRS-R), Scheduling, Standard Data Service (SDS), Blind Rehabilitation and Spinal Cord. Scheduled for release in mid-2004.
VistALink �€" continued
- v2.0: Connectivity from M to J2EE�€"This version will add bi-directional connectivity, that is, allow applications and services running on M to initiate a call to resources on a J2EE application server. Release is tentatively planned for late 2004. Applications requesting this version include Scheduling and CPRS-R.
VistA DEVELOPMENT HISTORY
In 1982, VHA committed to building an electronic health care architecture called DHCP (Decentralized Hospital Computer Program). The focus was the implementation of software applications easily integrated into a complete hospital information system. VA selected MUMPS (Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System) as the primary programming language for DHCP, and began developing applications using VHA programmers who worked directly with user groups in software prototyping environments. MUMPS, now known simply as �€œM", is an American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) standard language. By 1990, VHA had upgraded computer capacity at all medical facilities, and now implements software on a national scale supporting integrated health care delivery.
In 1996, VHA introduced VistA...Veterans Health Information Systems and Technology Architecture, a rich automated environment that supports day-to-day operations at local VA health care facilities. VistA is built on a client-server architecture, which ties together workstations and personal computers with graphical user interfaces at VHA facilities, as well as software developed by local medical facility staff. VistA also includes the links that allow commercial off-the-shelf software and products to be used with existing and future technologies. The Decision Support System (DSS) and other national databases that might be derived from locally generated data lie outside the scope of VistA.
When development began on the Decentralized Hospital Computer Program (DHCP) in the early 1980s, information systems were in their infancy in VA medical facilities and emphasized primarily hospital-based activities. DHCP grew rapidly and is used by many private and public health care facilities throughout the United States and the world. Although DHCP represented the total automation activity at most VA medical centers in 1985, DHCP is now only one part of the overall information resources at the local facility level. VistA incorporates all of the benefits of DHCP as well as including the rich array of other information resources that are becoming vital to the day-to-day operations at VA medical facilities.
ON THE HORIZON
- Pharmacy Re-Engineering�€�
The Pharmacy Re-Engineering (PRE) project is a key component in the implementation of the overall HealtheVet VistA effort. Two important results in the long term will be access to up-to-date drug information and VA-developed custom screens for all medication orders.
By 2005, the PRE team expects to release Application Program Interfaces (APIs) for all current references to the various VistA Drug files and for all non-order specific Pharmacy files, such as Medication Routes, Schedules, and Dosage Forms. All other applications accessing these files will be required to use the released APIs.
- Upcoming Outpatient and PDM Enhancements�€�
The Outpatient Pharmacy portion of the Laser Labels Phase II project allows Prescription Medication Information (PMI) sheets and warning labels to be printed in another language if the system has the other language fields populated in Pharmacy Data Management and the individual patient is identified with the other language preference flag. The Pharmacy Data Management portion of this project allows for warning label combinations from the old warning label file and/or the new commercial data source. These warnings can also be gender specific when certain flags are set accordingly.
- Upcoming BCMA Enhancements�€�
The BCMA Read-Only option will allow clinical staff not authorized to administer medications to view information from the BCMA GUI. The Read-Only GUI will have the same look and feel of the current GUI, except will not allow users to take an action on a medication.
The BCMA Coversheet will display and allow access to all medication orders over a 24 hour period. In addition, visual queues will aid in the quick and accurate review of all medication administration data presented.
The BCMA Reports Re-design will allow a user to customize reports via selectable fields and filters. The report re-design will provide both User and Manager reports, with definable reports at each site. All data will be pulled from the BCMA Medication Log File.
OTHER RESOURCES
- VistA Documentation Library: http://www.va.gov/vdl
This library contains a collection of available end-user documentation for all current applications (software packages), and also includes some tools not listed in the monograph. All documents can be viewed, downloaded, and printed. Some documents have links to a Web version, and may optionally have an archive file (.ZIP or .EXE) containing the Web pages for download.
- Request for New Information Technology Services: http://vista.med.va.gov/pas/NewITRequestForm.asp
Requests for new software or software enhancements must be endorsed by and submitted to the VHA NLB Information Data Management Committee (IDMC). The initial review and recommendation must go through the IDMC Screening Committee prior to submitting to IDMC for final approval. This site provides an on-line request form along with guidance on submissions.
- VHA Enterprise Architecture: http://www.va.gov/vha-ita/ita-p.html
VHA has developed and Enterprise Architecture that provides a technical framework to promote a one technology vision across the VHA so that corporate systems and systems across Veterans Integrated Service Networks are interoperable.
- Capital Investment Planning: http://www.va.gov/budget/capital/
Planned IT capital asset expenditures that exceed $10 million acquisition or $30 million life cycle costs, or have high levels of risk or visibility, must apply to the Capital Investment Board for approval.
The VA Capital Investment Board (VACIB) oversees the approval of all capital investment proposals that exceed certain threshold requirements, represent a high risk or high visibility or are cross-cutting. Approved proposals constitute the VA Capital Plan and support annual budget requests.
- Corporate Database Monograph: http://vaww.va.gov/../nds/CorporateDatabasesMonograph.asp
The Corporate Database Monograph provides an overview of the active VHA national databases. Information contained in this monograph allows stakeholders to identify opportunities for database consolidations, determine authoritative data sources, and work with VHA Data Quality committees to implement data standardization and quality control processes for corporate databases.
- VA Information Technology Strategic Plans: http://vista.med.va.gov/vistaarch/itstrategy.htm
- VistA Monograph on the Internet: http://www.va.gov/vista_monograph/
For additional information related to VistA software, you may contact the VHA Office of Information National Help Desk by E-mail at VHACIONHD@med.va.govor by phone at 1-888-596-4357.
ACRONYMS
ADT Admission, Discharge, Transfer
AICS Automated Information Collection System
AMIE Automated Medical Information Exchange
AR Accounts Receivable
ART Adverse Reaction Tracking
AR/WS Automatic Replenishment/Ward Stock
ASISTS Automated Safety Incident Surveillance Tracking System
ASU Authorization/Subscription Utility
BCMA Bar Code Medication Administration
CMOP Consolidated Mail Outpatient Pharmacy
COTS Commercial Off The Shelf
CPRS Computerized Patient Record System
CPT Current Procedural Terminology
CS Controlled Substances
DA Drug Accountability/Inventory Interface
DRG Diagnostic Related Group
DSS Decision Support System
EPI Emerging Pathogens Initiative
FOIA Freedom of Information Act
GIP Generic Inventory Package
HBPC Hospital Based Patient Care
HEC Health Eligibility Center
HINQ Hospital Inquiry
HL7 Health Level Seven
IB Integrated Billing
ICR Immunology Case Registry
IFCAP Integrated Funds Distribution, Control Point Activity, Accounting and Procurement
IV Intravenous
IVM Income Verification Match
KIDS Kernel Installation and Distribution System
LEDI Laboratory Electronic Data Interchange
MCCR Medical Care Cost Recovery
MPD Minimal Patient Dataset
MPI Master Patient Index
NDF National Drug File
NHE Network Health Exchange
NOIS National On-Line Information Sharing
OE/RR Order Entry/Results Reporting
PAID Personnel and Accounting Integrated Data
PBM Pharmacy Benefits Management
PCE Patient Care Encounter
PCMM Primary Care Management Module
PDM Pharmacy Data Management
PDX Patient Data Exchange
PPP Pharmacy Prescription Practices
QUASAR Quality Audiology and Speech Pathology Audit and Review
RAI/MDS Resident Assessment Instrument/Minimum Data Set
ROES Remote Order Entry System
RPC Remote Procedure Call
SCD Spinal Cord Dysfunction
TIU Text Integration Utilities
UD Unit Dose
UI Universal Interface
URL Universal Record Location
VIC Veteran Identification Card
VIST Visual Impairment Service Team
VistA Veterans Health Information Systems and Technology Architecture
[#sdfootnote1anc 1] Sharma, Rahul; Stearns, Beth; Ng, Tony, J2EE Connector Architecture and Enterprise Application Integration �€" Addison-Wesley, 2001.